Study Guide Master
advertisement

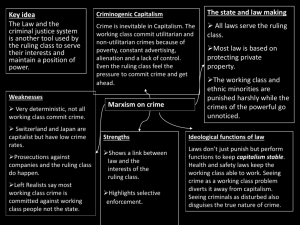
Name :______________________________ Crime and Punishment Unit 1 Study Guide White Collar: White-collar crimes are crimes that committed by people of high social status who commit their crimes in the context of their occupation. Blue Collar: used to describe crimes that are committed primarily by people who are from a lower social class. Assault: An unlawful physical attack or threat of attack Aggravated assault: An attack or attempted attack with a weapon Burglary: Unlawful or forcible entry or attempted entry of a residence. Embezzlement: The unlawful misappropriation of money or other things of value, by the person to whom the property was entrusted Identity theft: the stealing of someone’s identity Larceny: The unlawful taking of property other than a motor vehicle Organized Crime: Organized crime is crime committed by structured groups typically involving the distribution of illegal goods and services to others. Forgery: faking someone’s signature Vehicular manslaughter: when you kill someone with a car or motor vehicle First degree murder: premeditated murder, pre-planned Second degree murder: heat of the moment, didn’t plan to kill them but you did Manslaughter: accidental murder Crime: a wrong against society Society: is not static, it evolves Consensus Model: assumes that as people gather together to form a society, its members will naturally come to a basic agreement with regard to shared norms and values. Conflict model: different segments – separated by social class, income, age, and race – are engaged in a constant struggle with each other for control of society. Deviance is a behavior that does not conform to the norms of a given community or society. The purpose of Criminal Justice: To control crime; to prevent crime; to provide and maintain justice Local Law Enforcement – split between counties and municipalities State Law Enforcement – state police and highway patrol Hawaii is the only state that does not have state law enforcement. Federal Law Enforcement – FBI (Federal Bureau of Investigations), Drug Enforcement Agency (DEA), U.S. Secret Service, Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, and Firearms (ATF), Department of Homeland Security The U.S. has a dual court system, state court and federal court Federal system includes district court, circuit courts of appeals, and the U.S. Supreme Court. The prosecution – charged with trying the case on behalf of the state, trying to prove guilt. The defense – hired or appointed, their job is to prove innocence. Probation – most common, you remain under supervision of an agent of the court, or a probation officer Beyond a Reasonable Doubt: The standard that must be met by the prosecution's evidence in a criminal prosecution