ppt culture 2 - Fort Bend ISD
advertisement

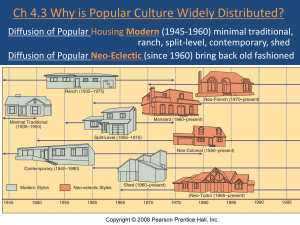
Food Customs • People in a MDC are likely to have the income, time, and inclination to facilitate greater adoption of popular culture. • Consumption of large quantities of alcoholic beverages and snack foods are characteristic of the food customs of popular societies. American Food Customs • Choice, in part, on the basis of preference for what is produced, grown, or imported locally. • Cultural backgrounds also affect the amount and types of alcohol and snack foods consumed. • Low Alcohol consumed because Baptists are concentrated in the Southeast and Mormons in Utah, these regions have relatively low consumption rates. Housing • The house is a product of both cultural tradition and natural conditions. • A reflection of cultural heritage, current fashion, functional needs, and the impact of the environment • Materials Used • Wood when forest are available. • Bricks of dried wet mud, when trees are in limited supply. • Also used are resources such as stone, grass, sod, and skins. • Drywall for interior wall is used to save money. Housing and Environment • Pitched roofs in wet and snowy climates to facilitate runoff. • Windows face south in temperate climates to take advantage of the Sun’s heat and light. • In hot climates, window opening may be small to protect the interior from the heat of the sun. Major hearths of folk house forms in U.S US Housing Types Today Ranch Style • Single story with low pitched gable roof and deep-set eaves • Horizontal, rambling layout • Large windows • Sliding glass doors leading out to patios • Attached garage Split Level House • Popular variant between the 50s-70s. • The lower level contained the garage and the newly invented family room. • The kitchen, formal living, and dining room were on the intermediate level. • Bedrooms were on the top level Contemporary Style • Especially popular choice between the 1950s and 1970s for architect-designed houses. • Frequently had flat or low pitched roofs. Shed House • Popular in the late 1960s, • Characterized by high-pitched shed roofs, giving the house the appearance of a series of geometric forms Neo-eclectic House Styles • Became popular in the late 1960s, and by the 1970s had surpassed modern styles in vogue. • “Great Room” replaced separate family room and formal living room. – Mansard – Neo-Tudor – Neo-French – Neo-colonial Mansard House • Popular in the late 1960s and early 1970s. • Shingle-covered second or third-story walls sloped slightly inward and merged into the roofline. Neo Tudor House • Popular in the 1970s. • Characterized by dominant, steeppitched front-facing gables and halftimbered detailing Neo French House • Appeared in the early 1970s. • Was the most fashionable style for new houses by the 1980s. • Featured dormer windows, usually with rounded tops, and high-hipped roofs. Neo Colonial House • An adaptation of English colonial houses. • Has been continuously popular since the 1950s but never dominant Rapid Diffusion of Clothing Styles • Individual clothing habits reveal how pop culture can be distributed across the landscape with little regard for distinctive physical features • Improved Communications (internet) permit rapid diffusion of clothing styles from one region of Earth to another. • Inexpensive reproductions of designer’s originals An important symbol of the diffusion of western popular culture throughout the world. •Are available throughout Europe and Asia for under $10 • “Genuine” jeans made by Levi Strauss, priced at $50 to $100, are preferred as a status symbol. Diffusion of the Television TV 1950s-90s • Early 1950s TVs being sold in only 20 countries, and more than 85% of the world’s 37 million sets were in the US. • Early 1990s more than 180 countries had 900 million sets, with less than one-fourth in the US. 1954 1970 1999 Levels of TV Service • Latin America and poorer European states ownership of TVs is common but not universal • About 30 countries, most of which are in Africa and Asia, TVs have not rapidly diffused therefore few people own them Afghanistan TV • The Taliban made it illegal to own or watch television. • Typical punishment was three months in jail and confiscation of equipment • In most countries, the government(s) control television stations to minimize the likelihood that programs hostile to current policies will be broadcast . . . in other words, they are censored. • In most countries, operating costs are typically paid by the national government from tax revenues, although some government-controlled stations do sell air time to private advertisers. USA Television • Most television stations are owned by private corporations. • Some stations, however, are owned by local governments or other nonprofit organizations and are devoted to educational or noncommercial programs Owned by GE & Viacom Rupert Murdoch Comcast Newscorp Walt Disney Corporation Non Profit The Internet • Internet service is following the pattern established by television a generation earlier, and is likely to diffuse rapidly to other countries in the years ahead • Among rapid diffusion is happening faster in Latin American and Asia than in some African countries The Internet International diffusion of Pop Culture has led to two problems. 1. The diffusion of popular culture may threaten the survival of traditional folk culture in many countries. 2. Pop culture may generate adverse environmental impacts. Loss of Traditional Values • The Western business suit has been accepted as the uniform for business executives and bureaucrats around the world. • Wearing clothes typical of MDCs is controversial in some Middle Eastern countries. • Muslim women in MDCs are encouraged to discard the black Chador in favor of skirts and blouses. Changing Women’s Roles • Diffusion of pop culture threatens the subservience of women to men that is embedded in many folk customs. Fear of Foreign Media • Many LDCs view TV as a new method of economic and cultural imperialism on the part of the MDCs, especially the United States. • LDCs fear the effects of the newsgathering capability of the media even more than their entertainment function • Most LDCs criticize the Western concept of freedom of the press • American news organizations reflect American values and do not provide a balanced, accurate view of other countries. • The only reliable and unbiased news accounts come from the BBC World Service shortwave radio newscasts. Cultural Imperialism • The invasion of a culture into another with the intent of dominating the invaded culture politically, economically, and or socially • Globalization is often seen as cultural imperialism – McDonalds Uniform Landscape • The distribution of popular culture around the world tends to produce more uniform landscapes. • In fact, promoters of popular culture want a uniform appearance to generate “Product Recognition” and greater consumption. What are these products? • Uniformity in the appearance of the landscape is promoted by a wide variety of other popular structures in North America, such as gas stations, supermarkets, and motels. • Franchise an agreement which allows the local outlet use of the company’s name, symbols, trademarks, methods, and architectural styles. Fast Food • An example of uniform landscape. • Usually organized as franchises. • Originally developed to attract people who travel by car. • Recently buildings are more subdued. Pollution • Folk culture, like popular culture, can cause environmental damage, especially when natural processes are ignored. • MDCs produce endless supplies of pop culture have created the technological capacity both to create largescale environmental damage and to control it. • However, a commitment of time and money must be made to control the damage. • Video of new use of water bottle