Chapter 3 Lecture Notes
advertisement

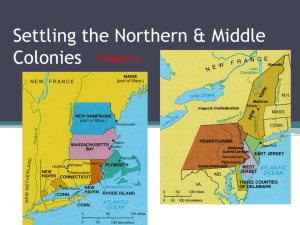
13th Declared slavery illegal in the USA 14th Gave citizenship to slaves and “DUE PROCESS” 15th Gave slaves/citizens the right to vote (men over 21 yrs.) 16th Creates the Federal Income Tax provisions 17th Provides for the direct election of Senators 18th Started PROHIBITION 19th Provides women the right to vote (suffrage) 20th Term of President & VP to end on January 20th 21st Ends PROHIBITION 24th Eliminated POLL TAX as a requirement to vote 26th Extends the right to vote to 18 yr. olds • • EARLY BRITISH COLONIES Settlements by the early European colonist was always by water;trade & transportion. Beginning in the early 1600s, the English established colonies along the eastern coast of North America • Joint-stock companies* formed by English merchants to find new markets for their goods. Pooling the money of many investors for large projects, such as establishing colonies. • • • 1607: Jamestown was first to be settled. Charter GUARANTEED them the same rights as Englishmen in Great Britain/England. John Smith led this group of settlers Colony struggled at first, then was saved by Tobacco crop John Rolfe, a Jamestown colonist, developed a strain of tobacco, that was marketable in England. The Jamestown colonist soon began growing large quantities of tobacco for profit – known as a CASH CROP. Gutenberg Printing Press 1450 PURITAN, OR “PILGRIM” • The 16th century Reformation caused a split in the Christian Church; Catholics and Protestants • One extreme group of Protestant reformers – the Puritans sought to cleanse or “purify” their religion of all traces of Catholicism Some Puritans called SEPARTISTS, broke away from the Anglican Church to start their own congregations. So, in 1608, one group of Separatist, who became known as PILGRIMS, fled to Holland, unhappy there, they decided to immigrate to AMERICA. The Pilgrims set sail for America on the MAYFLOWER in 1620 and settled in Plymouth. They Established the MAYFLOWER COMPACT. It was an agreement signed in 1620 by the Pilgrims to consult each other about the laws for the colony. It was the first form of self-government in the Americas. The Mayflower Compact November 11, 1620 The Mayflower Compact November 11, 1620 Written and signed before the Pilgrims disembarked from the ship. Not a constitution, but an agreement to form a crude govt. and submit to majority rule. (remember; first form of self government in the colonies) Signed by 41 adult males. NO WoMen Led to adult male settlers meeting in assemblies to make laws in town meetings. That First Year…. Winter of 1620-1621 Only 44 out of the original 102 survived. None chose to leave in 1621 when the Mayflower sailed back. Fall of 1621 First “Thanksgiving.” Colony survived with fur [especially beaver], fish, and lumber. Plymouth stayed small and economically unimportant. 1691 only 7,000 people Merged with Massachusetts Bay Colony. COLONISTS MEET RESISTANCE • New England Colonists (Puritans) soon conflicted with the Native Americans over land & religion • King Philip’s War was fought in 1675 between the Natives and Puritans ending a year later with many dead and the Natives retreating King Philip’s War (1675-1676} Only hope for Native Americans to resist white settlers was to UNITE. Metacom Leader of the Native Americans united Indians and staged coordinated attacks on white settlements throughout New England. Frontier settlements forced to retreat to Boston. King Philip’s War (1675-1676} The war ended in failure for the Indians Metacom beheaded and drawn and quartered. His son and wife sold into slavery. Never a serious threat in New England again!! NORTHERN COLONIES COMMERCE THRIVES • The development of cities, expansion of trade, and diverse economies gradually made the North radically different from the South • Philly was the 2nd largest British port, fishing & whaling and lumbering was big; shipbuilding • Farming differed from the South: smaller, more diverse crops in North, colder weather & rocky terrain limited farming LIBERTY BELL (subsistence farming) SETTLING THE MIDDLE COLONIES • Dominated by Dutch and Quaker settlers, the Middle Colonies were founded in the mid-1600s • William Penn led Quakers as they colonized Pennsylvania and Delaware Quakers believed that religion was a personal experience that did not need churches or ministers. They objected to all political and religious authority & advocated PACIFISM – Opposition to war or violence as a means of resolving conflict. The MIDDLE COLONIES contained some of North America’s most FERTILE FARMLAND. Most farmers produced surplus crops that they could sell for profit. WHEAT became the region’s most important CASH CROP. The rivers in the Middle Colonies allowed farmers to transport their products to ships on the Atlantic coast. During the early 1700s, Europe experienced a population explosion. The explosion created a huge demand for wheat to feed the booming population. The demand caused wheat prices to soar, making the Middle Colonies prosperous. The Middle Colonies were known as the BREAD BASKET of the colonies. Some colonist became wealthy as ENTREPRENEURS- who raised their money by buying land, equipment, & supplies to the new immigrants for profit. The WHEAT BOOM created a new group of CAPITALISTS who had money to invest in new business. Why didn’t the Southern Colonies have Big Cities, Manufacturing or a lot of roads? 1. Plantations 2. Cash crops – TOBACCO, Indigo & Rice 3. Waterways for travel & trade ___1. Founder of the most tolerant & democratic of the middle colonies ___2. Reformer whose religious ideas inspired English Puritans, Scotch Presbyterians, French Huguenots, & Dutch reformed ___3. Religious group persecuted in Massachusetts and New York but not in Pennsylvania ___4. Dominant religious group in Massachusetts Bay ___5. Promoter of Massachusetts Bay as a holy “city upon a hill” ___6. Small colony that eventually merged into Massachusetts Bay ___7. Conqueror of New Sweden who later lost New Netherland to the English ___1. Extends the right to vote to 18 year olds ___2. Declares slavery illegal in the USA. ___3. Provides women the right to vote (Suffrage). ___4. Creates the Federal Income Tax Provisions ___5. Provides for direct election of Senators ___6. Eliminated POLL TAX as requirement to vote ___7. Gave citizenship to slaves & due process ___8. Gave slaves/citizens the right to vote (over 21 yrs.) ___1. Extends the right to vote to 18 year olds ___2. Declares slavery illegal in the USA. ___3. Provides women the right to vote (Suffrage). ___4. Creates the Federal Income Tax Provisions ___5. Provides for direct election of Senators ___6. Eliminated POLL TAX as requirement to vote ___7. Gave citizenship to slaves & due process ___8. Gave slaves/citizens the right to vote (over 21 yrs.) ___1. Extends the right to vote to 18 year olds ___2. Declares slavery illegal in the USA. ___1. Founder of the most tolerant & democratic of the middle colonies ___2. Reformer whose religious ideas inspired English Puritans, Scotch Presbyterians, French Huguenots, & Dutch reformed ___3. Provides women the right to vote (Suffrage). ___3. Religious group persecuted in Massachusetts and New York but not in Pennsylvania ___4. Creates the Federal Income Tax Provisions ___4. Dominant religious group in Massachusetts Bay ___5. Promoter of Massachusetts Bay as a holy “city upon a hill” ___5. Provides for direct election of Senators ___6. Small colony that eventually merged into Massachusetts Bay ___6. Eliminated POLL TAX as requirement to vote ___7. Conqueror of New Sweden who later lost New Netherland to the English ___7. Gave citizenship to slaves & due process ___8. Gave slaves/citizens the right to vote (over 21 yrs.)