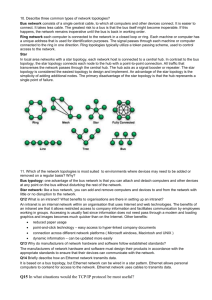
13.8.1 Point To Point Topology - Home
advertisement

Summary of LAN hardware for the network design: LAN network To connect two computers To connect two computers over long distances To connect more than two computers To connect more than two computers in small network which can filter traffic. For large network . LAN hardware NIC Repeater Description Problem Network interface card for connecting two computers on LAN Extends the distance limitations of Ethernet cable by boosting the signal Cannot connect over long distances Hub hub is a multiport device for building starconfigured topologies with twisted-pair cable Bridge Provides repeater functions along with selective filtering of traffic to reduce congestion and contention Switches Basically a multiport bridge that segments a network into many smaller collision domains while maintaining the broadcast characteristics. Greatly improves the performance of LANs Only two computers can be connected if you want to connect more computers then it is a problem It cannot filter traffic It is confined to small network maximum nodes can be 30 Bridges have limited ports It introduce latency for large networks. Here network traffic travels to all LAN segments without knowing the exact IP address of the destination segment. It controls collision domains but not broadcast domains. For Router internetworks ( connecting more than one LAN network with high speed and flexibility) Routers make forwarding decisions based on network layer addresses. …………………………. In addition to controlling collision domains, routers control broadcast domains Switching: Circuit-switching networks In this technique, first the complete physical connection between two computers is established and then data are transmitted from the source computer to the destination computer Dedicated paths are used between source and destination. no queuing Example: telephone systems. Message Switching In this technique, the source computer sends data or the message to the switching office first, which stores the data in its buffer. It then looks for a free link to another switching office and then sends the data to this office. This process is continued until the data are delivered to the destination computers. Owing to its working principle, it is also known as store and forward. That is, store first (in switching office), forward later, one jump at a time. The network receives the entire messages, stores them in a Secondary storage and transmit them. It provides long term storage even after the message has been delivered. Example: Hop-by-hop Telex forwarding and UUCP are examples of message switching systems. E-mail is another example of a message switching system Packet Switching . In packet switching no fixed path is created between devices that communicate; it is broken into packets, each of which may take a separate path from sender to recipient. The message is divided into a number of slices called Packets of certain fixed size. Each packet has its destination address. Queuing involved Routing is needed errors involved Example: when you connect to the Internet using a dial-up modem. Network topologies: In Computer Networking “topology” refers to the layout or design of the connected devices. Topology can be classified into two : 1-D (bus) 2-D (tree, stars, rings, mesh, etc.) 13.8.1 Point to Point Topology Point to Point topologies are simplest and most straightforward. Point-to-point (PTP) topology connects two nodes directly together You can think of as a chain of devices and another name for this type of connectivity is called daisy chaining. Most computers can 'daisy chain' a series of serial devices from one of its serial ports. Networks of routers are often configured as point-to-point topologies. The following examples are pure point to point links: Two computers communicating via modems. A mainframe terminal communicating with a front end processor. A workstation communicating along a parallel cable to a printer. Advantage: It is easy to set up Installation Cost is low Fault identification is easy Allows flexibility in communication hardware, packet formats, etc. Provides security and privacy because communication channel is not shared Disadvantages Number of wires grows as square of number of computers Connections between buildings can be prohibitive Adding a new computer requires N - 1 new connections 13.8.2 Linear Bus A linear bus topology consists of a main run of cable with a terminator at each end . All nodes (file server, workstations, and peripherals) are connected to the linear cable. Access and control of bus networks are typically maintained by a method called contention, whereby if a line is unused, a terminal or device can transmit its message at will, but if two or more terminals initiate messages simultaneously, they must stop and transmit again at different intervals Fig. 1. Linear Bus topology Advantages of a Linear Bus Topology The advantage of the Bus network is that if one computer fails in the network the others are still not affected and they continue to work. Bus network is very simple and easy to set up. If there is an urgent need to set up a network and perhaps be used on a short term basis then the Bus network is the best possibility. Bus networks use the least amount of cable to set up making it cost effective. Disadvantages of a Linear Bus Topology Entire network shuts down if there is a break in the main cable. Terminators are required at both ends of the backbone cable. Difficult to identify the problem if the entire network shuts down. Not meant to be used as a stand-alone solution in a large building. 13.8.3 Star Topology A star topology consists of a central connection hub to which devices are connected with UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair) Ethernet. Contrary to the bus topology, a star topology utilizes a point-to-point connection to connect each node to the central hub. The hub acts as a signal booster as well, and all the data traffic that transverses the network passes through this hub. The entire network is dependent upon the central hub in a star topology, so if the entire network is not working, it means that there is problem in the hub. This makes it easy to troubleshoot the network because of the only one point for error correction. As all the computers in star topology are independent to each other and dependent only on the central hub, network failure or other network problems are less likely to happen. The privacy of each of the computers is also maintained in this topology. In star topology, new devices and nodes can be easily added and by just extending a cable from the hub. Advantages of star topology: A star topology is simple in functionality and easy to manage. If a problem occurs in the network, it can be easily isolated and cleared. It is very easy to expand the star topology because of its simple format. Disadvantages of star topology: The entire network of the star topology is completely dependent on the hub. If the hub fails, the whole network fails. Network connection may slow down when the number of nodes increases or the cable lengthens. Star topology needs more cable length than other topologies. It is more expensive compared to bus topology. Star Topology 13.8.4 Ring Topology A ring topology consists of network of computers in which each node connects to exactly two other nodes. This forms a single continuous path for the flow of signals through each nodes of the network. Data travels from node to node, with each node along the way handling every packet. Each of the nodes in the ring topology are connected to each other through only one pathway, so the failure of only one link disrupts the whole network. To overcome this fallacy, the data in a ring topology is transmitted both clockwise and counter clockwise, so that if there is single break of the cable, all the nodes on both sides can be reached. Ring Topology Advantages of Ring Topology It is an orderly network in which all the nodes in the network have equal access to all the resources. Its performance is far better compared to star topology under heavy network. It does not need network servers to manage the connections. Disadvantages of Ring Topology If one of the workstations fails to operate, it may lead to the unusability of the whole network. Addition and removal of devices in the network can affect the entire network. Ring network is slower than the Ethernet network. 13.8.5 Tree topology A tree topology consists of bus and star topologies framed in a common network. The tree like structure of this network allows the colleges, schools, universities and other institutions to maintain their own network as a branch of a bigger network through which they can maximize their area of access to the network. This type of network topology is most suitable for such networks which are widely spread and divided into many branches. On tree topology the hubs of each smaller topologies are connected to the central hub that controls the entire network. However, some nodes can be directly connected to the central hub. Tree topology Advantages of tree topology It is possible to form a point to point connection with tree topology. All the computers can access other computers which are in other larger and immediate networks. Tree topology is best suited for branched out networks. Disadvantages of tree topology In this topology, the length of the network depends on the type of cable utilized to form the network. The entire tree topology would fail if the central trunk fails as it forms the backbone of the network. The tree topology is comparatively more complex than the bus and star topologies. If it gets bigger, it would be difficult to configure and manage it. It is expensive as more hubs and cables are required to install the network. 13.8.6 Mesh Topology The mesh topology incorporates a unique network design in which each computer on the network connects to every other, creating a point-to-point connection between every device on the network. The purpose of the mesh design is to provide a high level of redundancy. If one network cable fails, the data always has an alternative path to get to its destination An example of a Mesh Network is the Mobile Adhoc Network or MANet. Mesh topology can also be called as fully connected network as each node is connected to other node via cables in the network. Mesh Topology Advantages of Mesh topology As it has multiple routes between the source and the destination, if one route fails, there would be a number of other routes through which data transfer can take place. Traffic problem is minimized in this topology. Troubleshooting is easier compared to other networks like star and ring. Heavy load of data transfer has little impact on the performance of this topology. This network can be easily expanded without affecting the existing users. Disadvantages of Mesh topology It is expensive as it requires more cable than other topologies. Installation is difficult and complicated. 13.8.7 Hybrid Topology A hybrid topology, as the name suggests, is an interconnection of two or more networks. The component networks may be ring, star, tree, mesh or any other, depending upon the requirement of a firm or institution. For example, in an institution, if there is a ring topology in one department, bus topology in the next department, star topology in another department and so on, all the departments can connect to each other through a bus topology that connects the ring, bus and star topologies of each department to each other. Such a topology that consists of more than one type of individual topologies is known as hybrid topology. Hybrid topology Advantages of hybrid topology Hybrid topologies are reliable and have increased fault tolerance than other topologies. A hybrid topology can efficiently diagnose and isolate faults. Hybrid topologies are flexible and are designed to suit a variety of network environments and needs. A hybrid topology is able to tap into the strengths of other topologies and ignore their weaknesses. This results in a complex network that is more efficient and effective than individual topologies Disadvantages of hybrid topology Comparatively expensive than other topologies. Freeware Software which is distributed free by the author. freeware is proprietary software made available free of charge. It is the programming that is offered at no cost and is a common class of small applications available for downloading and use in most operating systems. Although it is available for free, the author retains the copyright, which means that it cannot be altered or sold. Free software is distinct from freeware; Free software may be packaged and distributed for a fee; the "free" refers to the ability to reuse it, modified or unmodified, as part of another software package. As part of the ability to modify, users of free software may also have access to and study the source code. The term 'free' does not mean free of charge. It refers to a user's freedom to run, copy, distribute, study, change and improve the software without the payment of a royalty or obtaining express permission. Everyone is free to sell copies of free software, to use it commercially, and to charge for distribution and modifications. Because anyone who has a copy may distribute the software at no cost, the software generally is available at no cost. Free software business models are usually based on adding value such as support, training, customization, integration, or certification like open source softwares are free softwares. 13.13.4 Shareware Software distributed freely, but with certain conditions applying to it. It is distributed free on a trial basis with the understanding that the user may need or want to pay for it later. Either the software is released on a trial basis only, and must be registered after a certain period of time, or in other cases no support can be offered with the software without registering it. In some cases direct payment to the author is required. Some software developers offer a shareware version of their program with a built-in expiration date (after 30 days, the user can no longer get access to the program). Other shareware (sometimes called liteware) is offered with certain capabilities disabled as an enticement to buy the complete version of the program. 13.13.5 FLOSS/FOSS FLOSS is common and combined term of Free/Libre/Open Source Software. Actually this term for free software and open source where free means it was cost free software Libre means liberty : to make changes Open source means code or patch files are available openly to fix bugs, and for further development. 13.13.6 GNU GNU is a computer operating system composed entirely of free software. Its name is a recursive acronym for GNU's Not Unix, which was chosen because its design is Unix like, but differs from Unix by being free software and by not containing any Unix code.GNU was founded by Richard Stallman and was the original focus of the Free Software Foundation GNU Public License (GPL) Most new open source software around these days uses this license, as does Moodle. In a nutshell, the GPL says: Anyone can download, use, modify and distribute this software All modified versions must ALSO be under the GPL license All copyright notices must be maintained, and all modifications must be clearly marked All distributions must include the full source code There is no warranty on the software 13.13.7 FSF The Free Software Foundation (FSF)was established in 1985 to promote the development of free software with full rights to use, study, copy, modify, and redistribute computer programs. particularly the GNU operating system, used widely in its GNU/Linux variant. Its a non profit, non political and international organization provides standards for developing free softwares. 13.13.8 OSI Open Source Initiative (OSI) is a non-profit corporation dedicated to managing and promoting the Open Source Definition for the good of the community, specifically through the OSI Certified Open Source Software certification mark and program. The basic idea behind open source is to read, redistribute, and modify the source code for a piece of software, the software evolves. People improve it, people adapt it, people fix bugs. We in the open source community have learned that this rapid evolutionary process produces better software than the traditional closed model, in which only a very few programmers can see the source and everybody else must blindly use an opaque block of bits. 13.13.9 Linux : Examples of Open source software Like Windows and Unix ,Linux is also an operating system developed Linus Torvalds but this operating system was freely distributed as Open Source i.e code is freely available to read ,edit and fix bugs. Apart from the fact that it's freely distributed, Linux's functionality, adaptability and robustness, has made it the main alternative for proprietary Unix and Microsoft operating systems. IBM, HewlettPackard atre the top companies which has embraced Linux and support its ongoing development. It was primarily adapted as a server platform. Mozilla An open-source XML/HTML browser have with dynamic image and table resizing, quick insert and delete of table cells, improved CSS support. It is a free web browser descended from the Mozilla Application Suite, managed by the Mozilla Corporation. It is the second-most popular browser currently worldwide, after Internet Explorer. Firefox includes tabbed browsing, a spell checker, incremental find, live bookmarking, a download manager, and an integrated search system that uses the user's desired search engine. Functions can be added through around 2,000 add-ons created by third-party developers, the most popular of which include NoScript (script blocker), Stumble Upon (website discovery), Tab Mix Plus (adds many customizable options to tabs), FoxyTunes (controls music players), Adblock Plus (ad blocker), DownThemAll! (download functions) and Web Developer (web tools). Apache HTTP Server The Apache HTTP Server is to develop and maintain an open-source web server for modern operating systems including UNIX and Windows NT. The goal of this project is to provide a secure, efficient and extensible server that provides HTTP services in sync with the current HTTP standards.Apache has been the most popular web server on the Internet since April 1996. Uses of apache are: Serves both static content and dynamic Web pages on the World Wide Web. Apache provides environment to run web applications like java based and XML MYSQL MySQL is the world's most popular open source database software. It is a structured query language like SQL used for managing database systems.Many of the world's largest and fastest-growing organizations use MySQL to save time and money powering their high-volume Web sites, business-critical systems and packaged software -- including industry leaders such as Yahoo!, Alcatel-Lucent, Google, Nokia. POSTGRES PostgreSQL is an object-relational database management system (ORDBMS). It is released under as a free software. And like other open-source programs, PostgreSQL is not controlled by any single company, but relies on a global community of developers and companies to develop it. PANGO Pango is a free and open source computing library for rendering internationalized texts in high quality. Pango has been integrated into most Linux distributions. It most notably provides the rendering for text in the Mozilla Firefox web browser Different font backends can be used, allowing cross-platform support. PHP: Hypertext Pre Processor (PHP) is a server side technology introduced to design dynamic and interactive web pages. PHP is the widely-used, free, and efficient alternative to competitors such as Microsoft's ASP. PHP is perfectly suited for Web development and can be embedded directly into the HTML code. The PHP syntax is very similar to Perl and C. PHP is often used together with Apache (web server) on various operating systems. It is based on open source technology under PHP license to develop graphic and web applications. It was written as a set of Common Gateway Interface (CGI) binaries in the C programming language by the Danish/Greenlandic programmer Rasmus Lerdorf in 1994, to replace a small set of Perl scripts he had been using to maintain his personal homepage. PYTHON Python is a multi-paradigm programming language (functional, object oriented and imperative) which has a fully dynamic type system and uses automatic memory management; it is thus similar to Perl, Ruby, Scheme, and Tcl. The language has an open, community-based development model managed by the nonprofit Python Software Foundation. TOMCAT Tomcat is an application server developed at the Apache Software Foundation (ASF). To run java applications on web server It has its own internal HTTP server and implements the Java Servlet and the JavaServer Pages (JSP) specifications from Sun Microsystems, providing an environment for Java code to run in cooperation with a web server. OPENOFFICE The OpenOffice.org project aims "To create, as a community, the leading international office suite that will run on all major platforms and provide access to all functionality and data through open-component based APIs and an XML-based file format like Microsoft Office”. It is free and open source office suit, including Writer : A word Processor Calc : Spread sheet software similar to Micrpsofyt Excel Quick Review: Definitions: Network: Internet A network is an interconnected collection of autonomous computers It is the network of networks that transmit data by packet switching using a standardised Internet Protocol (IP) and many other protocols. Interspace Interspace is the networked virtual reality system on the Internet. Bandwidth: The range of transmission frequencies that can be carried on a communication line is referred to as the bandwidth of the line device, which converts digital signal into analog, and the reverse, is known as modem. Modem: Modulation: The technique by which a digital signal is converted to analogform is known as modulation. Topology refers to the layout or design of the connected devices Protocol A protocol is a set of rules that governs the communications between computers on a network. is a protocol for remote computing on the Internet. It allows a computer to act as a remote terminal on another machine, anywhere on the Internet Wireless local loop (WLL) technology simply means that the subscriber is connected to the nearest exchange through a radio link instead of through these copper wires. is the text communication service component of phone, web or mobile communication systems, using standardized communications protocols that allow the exchange of short text messages between fixed line or mobile phone devices Telnet Wireless local loop Short Message Service (SMS) Voice Mail : The electronic transmission of voice messages over the Internet. The messages are stored on a computer until the recipient accesses and listens to them Email, also sometimes written as e-mail, is simply the shortened form of electronic mail, a protocol for receiving, sending, and storing electronic messages chatting: On line talk in the form of text is known is chatting. video conferencing: A videoconferencing or video conference (also known as a videoteleconference) is a set of interactive telecommunication technologies which allow two or more locations to interact via two-way video and audio transmissions simultaneously Viruses : Cookies Firewall Cyber Law Computer programs written by devious programmers and designed to replicate themselves and infect computers when triggered by a specific event. are small bits of information that get stored on your hard drive (persistent cookies) or in memory (non-persistent cookies) of your computer. They are placed on your computer by the websites you are visiting. stands between the company’s network and a public network, effectively shielding your computers from malicious hacker activity, and controlling the flow of data is the law governing cyber space.It is a very wide term and includes computers, networks, software, data storage devices (such as hard disks, USB disks etc), the Internet, websites, emails and even electronic devices such as cell phones, ATM machines etc. World Wide Web It is a repository of information containing a set of programs , standards and protocols that allows the multimedia and hypertext files to be created , displayed and linked on the internet. W3C The organization responsible for managing standards for the WWW. Browser A browser is an application which provides a window to the Web. For example : Internet explorer ,Mozilla Firefox. Web Page A document formatted for distribution over the web. Most often a web document is formatted in a markup language like HTML or XML. Web Document A document formatted for distribution over the web. Most often a web document is formatted in a markup language like HTML or XML. Website A collection of related web pages belonging to a company or an individual. URL (Uniform A URL refers to an address in the special format on the internet. Resource Locator) It is a standard way to address web documents (pages) on the Internet (like: http://www.microsoft.com/). URL are of two types: absolute URL ,relative URL Web Host A web server that "hosts" web services like providing web site space to companies or individuals. Web Hosting The action of providing web host services. Domain name A domain name is a unique name for a web site, like ntchosting.com .Domain names must be registered An Internet Protocol address (IP address) is a numerical label that is assigned to any device participating in a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication between its nodes In 1969 by the development of first network called ARPANET , led to the development of internet . ARPANET ( Advanced Research Projects Agency NETwork) was the project for connecting computers at different Universities and U.S. defense. network architecture: peer to peer network ,client server networking. peer to peer networks : All computers are of equal importance. Software and data are stored on each computer. client/server network: Software and data are held on a file server and may be used by other computers on the network. Security is controlled centrally. Local-Area Networks (LANs) The computers are geographically close together (that is, in the same building). Wide-Area Networks (WANs) The computers are farther apart and are connected by telephone lines or radio waves. MAN - Metropolitan Area Network : It covers large span of physical area than LAN but smaller than WAN, such as a city. Personal area network (PAN) is a computer network designed for communication between computer devices(including telephones and personal digital assistants close to one person) The Internet, or simply the Net, is the information superhighway. The end devices that wish to communicate with each other are called stations. The switching devices are called nodes there are three types of switching: Circuit Switching ,Packet Switching and Message Switching In circuit switching, a circuit is first established and then used to carry all data between devices. example: telephone system In packet switching no fixed path is created between devices that communicate; it is broken into packets, each of which may take a separate path from sender to recipient. example : connecting internet using dial up modem. message switching: In this technique, the source computer sends data or the message to the switching office first, which stores the data in its buffer.example : email Frequency is measured in hertz(Hz). 1 MHz = 1million Hz Baud: It describes the rate of change of the signal on the line i.e.how many times (per second) the signal changes its pattern. Data Transfer rate : A data transfer rate is the amount of digital data that is moved from one place to another in a given time usually in seconds. In general, the greater the bandwidth of a given path ,higher the transfer rate. Bit rate : A data transfer rate expressed in bits per second . Kbps= 1000 bits per second Mbps=1000 kbps=1,000,000bps Gbps=1000 mbps Tbps=1000gbps Twisted pair cable : two type shielded and unshielded Twisted Pair(UTP) o Advantages: Reasonable cost ,High Speed ,Easy to add additional network devices ,Supports large number of network devices, Easy to install, because of physical flexibility, low weight & easy connectivity. o Disadvantages of twisted pair: Signals loose energy due to attenuation, so repeaters are required, Bandwidth is low, High attenuation (signal loss) limits individual runs to 100 meters Cat-5Short for Category 5, network cabling that consists of four twisted pairs of copper wire terminated by RJ45 connectors. Cat-5 cabling supports frequencies up to 100 MHz and speeds up to 1000 Mbps. It can be used for ATM, token ring, 1000Base-T, 100BaseT, and 10Base-T networking. Computers hooked up to LAN s are connected using Cat-5 cables, so if you're on a LAN, most likely the cable running out of the back of your PC is Category 5. Coaxial cable : Coaxial cable, in its simplest form, is a single wire wrapped in a foam insulation,surrounded by a braided metal shield, then covered in a plastic jacket o advantages: greater bandwidth ,greater channel capacity and low error rates. o disadvantage: Problems with the deployment architecture, Bidirectional upgrade required, Great noise, High installation costs, Susceptible to damage from lightning strikes. Infrared ,radiowave ,microwave and satellite are wireless technology for communication. NIC known as network interface card : network device required to access the network . Hub: a network device to connect more than two computer on network .it is preferred for small network where number of nodes are less than 30. Switch: Basically a multiport bridge that segments a network into many smaller collision domains while maintaining the broadcast characteristics. Greatly improves the performance of LANs A Router is responsible for connecting two physical and logically different networks. A repeater connects two segments of your network cable. A bridge is a product that connects a local area network (LAN) to another local area network that uses the same protocol (for example, Ethernet or Token Ring). Topology can be classified into two : o 1-D (bus) o 2-D (tree, stars, rings, mesh, etc.) Protocol can be classified into two groups : network and communication protocol. Network protocol : Ethernet ,FDDI,ATM, Local talk ,token ring. Communication protocols : HTTP,FTP,TCP/IP,SMTP,SLIP,PPP,POP3 SMTP and POP3 are email protocols. Wireless and mobile communication technology: o FDMA o GSM o TDMA o CDMA o 3G o 4G EDGE and Wimax are 3G technologies . CDMA(Code Division Multiple Access) : It is a digital cellular technology which uses spread spectrum techniques means the data is sent in small pieces over a number of discrete frequencies available for use in the specified range .All the users will transmit in the same wide spectrum. Each user‘s signal is spread over the entire bandwidth by a unique spreading code . At the receiver’s end same unique code is used to recover the signal. CDMA has been used in many military applications, such as: Anti-jamming (because of the spread signal, it is difficult to jam or interfere with a CDMA signal). Ranging (measuring the distance of the transmission to know when it will be received). Secure communications (the spread spectrum signal is very hard to detect). Time Division Multiplexing:TDMA works by dividing a radio frequency into time slots and then allocating slots to multiple calls . In this way ,a single frequency an support multiple, simultaneous data channels Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA): allocates users with different carrier frequencies of the radio spectrum.The radio spectrum is available to the users where communications signals are pass through that spectrum. Multiple access enables allows more than one communications signal to pass within a particular band Enhanced Data rates for GSM Evolution (EDGE) or Enhanced GPRS(EGPRS), It is an Advanced technology over GSM which is widely used in digital mobile phone technology which allows increased data transmission rate .This technology was developed in North America and used extensively in packet switched applications such as Internet Connection, VDO services ,multimedia services . Protocols for chat and video conferencing : VoIP. Network security : protection from threats to network. In 1981 - First virus Elk Cloner was transmitted by floppy disk. Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP), is a technology that allows you to make voice calls using a broadband Internet connection instead of a regular (or analog) phone line. Threats to network security are viruses ,worms ,Trojan horse In a computer, a worm is a self-replicating virus that does not alter files but resides in active memory and duplicates itself. Worms use parts of an operating system that are automatic and usually invisible to the user. Spam is flooding the Internet with many copies of the same message, in an attempt to force the message on people who would not otherwise choose to receive it. There are various ways to protect from network threats some are : o Authentication Definition o Authorization Definition o Identity Management o Firewall o Identification methods o Antiviruses The Information Technology Act 2000 (ITA-2000)(IT ACT) is an Act of the Indian Parliament for cyber related issues. hackers are intelligent people who breaks into a system for gaining knowledge ,freely share what they have discovered, and never, ever intentionally damage data. crackers are “ evil hackers “who breaks into or otherwise violates the system integrity of remote machines, with malicious intent. HTML :Hypertext markup language for designing web sites. XML( EXtensible Markup Language) is a standard, simple, self-describing way of encoding both text and data so that content can be processed with relatively little human intervention and exchanged across diverse hardware, operating systems, and applications server side scripting languages:The code which is executed at server end is called server side script and computer languages used to write this script are called server side scripting languages Examples of server side scripting languages are CGI, ASP and PHP,JSP Client side scripting:The response or output of web server is send to requesting client. This response consists of HTML and some other script. The HTML is rendered by browser. Browser also executes the script received from server. This script or small program embedded in HTML is called client side script and languages used to write this script are client side scripting languages .Forex: JavaScript and VB Script. The term ‘Web 2.0’ refers to the idea of the “New Internet”, or the second wave of the World Wide Web. Web 2.0 is not a specific application or technology, but explains two paradigm shifts within Information Technology, ‘user-generated content’ and ‘thin client computing’. Major difference between bridge ,router and gateway is bridges are used to connect same network and having same network protocols while router is used to connect same LAN network with different set of protocols while gateway is used to connect different networks. To connect very high range of network use satellite communication where range of signals is very high. Thick Coaxial cables support up to 500ms for greater than that range use optical fibers for better .data transmission. Switch manages the data required for larger network approximately 50 and above . High level connectivity could be provided by radio transmission using satellite channels . Wireless networking known as WLL speed comes in 54mbps,108mbps. HTML is used for designing web pages has predefined tags to be used while in XML you can define your own tags. A newsgroup is online community bulletin board where users can post messages , respond to posted messages or just read them. ARCHIE is a software tool that help you search for the files stored on FTP server. Cyber law means a wide variety of political and legal issues related to the Internet and other communications technology, including intellectual property, privacy, freedom of expression, and jurisdiction. Important Definitions : 1. DHTML -- (Dynamic Hypertext Markup Language) : DHTML refers to web pages that use a combination of HTML, JavaScript, and CSS to create features such as letting the user drag items around on the web page, some simple kinds of animation, and many more. 2. Extranet : An intranet that is accessible to computers that are not physically part of a company’s' own private network, but that is not accessible to the general public, for example to allow vendors and business partners to access a company web site. Often an intranet will make use of a Virtual Private Network. (VPN.) 3. Fire Wall : A combination of hardware and software that separates a Network into two or more parts for security purposes. 4. FTP -- (File Transfer Protocol) : A very common method of moving files between two Internet sites. FTP is a way to login to another Internet site for the purposes of retrieving and/or sending files. There are many Internet sites that have established publicly accessible repositories of material that can be obtained using FTP, by logging in using the account name "anonymous", thus these sites are called "anonymous ftp servers". 5. Gateway : The technical meaning is a hardware or software set-up that translates between two dissimilar protocols, for example America Online has a gateway that translates between its internal, proprietary e-mail format and Internet e-mail format. Another, sloppier meaning of gateway is to describe any mechanism for providing access to another system, e.g. AOL might be called a gateway to the Internet. 6. Email -- (Electronic Mail) : Messages, usually text, sent from one person to another via computer. E-mail can also be sent automatically to a large number of addresses. 7. GIF -- (Graphic Interchange Format) : A common format for image files, especially suitable for images containing large areas of the same color. GIF format files of simple images are often smaller than the same file would be if stored in JPEG format, but GIF format does not store photographic images as well as JPEG. 8. Gopher : Invented at the University of Minnesota in 1993 just before the Web, gopher was a widely successful method of making menus of material available over the Internet. Gopher was designed to be much easier to use than FTP, while still using a text-only interface. 9. Hypertext : Generally, any text that contains links to other documents – words or phrases in the document that can be chosen by a reader and which cause another document to be retrieved and displayed. 10. Internet (Upper case I) : The vast collection of inter-connected networks that are connected using the TCP/IP protocols and that evolved from the ARPANET of the late 60's and early 70's. The Internet connects tens of thousands of independent networks into a vast global internet and is probably the largest Wide Area Network in the world. 11. Intranet : A private network inside a company or organization that uses the same kinds of software that you would find on the public Internet, but that is only for internal use. Compare with extranet. 12. IP Number -- (Internet Protocol Number) :Sometimes called a dotted quad. A unique number consisting of 4 parts separated by dots, e.g. 165.113.245.2. Every machine that is on the Internet has a unique IP number - if a machine does not have an IP number, it is not really on the Internet. Many machines (especially servers) also have one or more Domain Names that are easier for people to remember. 13. ISDN -- (Integrated Services Digital Network) : Basically a way to move more data over existing regular phone lines. ISDN is available to much of the USA and in most markets it is priced very comparably to standard analog phone circuits. It can provide speeds of roughly 128,000 bits-per-second over regular phone lines. In practice, most people will be limited to 56,000or 64,000 bits-per second. Unlike DSL, ISDN can be used to connect to many different locations, one at a time, just like a regular telephone call, as long the other location also has ISDN. 14. ISP -- (Internet Service Provider) : An institution that provides access to the Internet in some form, usually for money. 15. JPEG -- (Joint Photographic Experts Group) : JPEG is most commonly mentioned as a format for image files. JPEG format is preferred to the GIF format for photographic images as opposed to line art or simple logo art. 16. Leased Line : Refers to line such as a telephone line or fiber-optic cable that is rented for exclusive 24-hour, 7-days-a-week use from your location to another location. The highest speed data connections require a leased line. 17. Modem -- (Modulator, Demodulator) : A device that connects a computer to a phone line. A telephone for a computer. A modem allows a computer to talk to other computers through the phone system by converting digital signals to analog and vice versa. Basically, modems do for computers , what a telephone does for humans. Modem are of two types: Internal modem : are the modem that are fixed within the system. External modem : are the modems that are connected externally to a computer as other peripheral devices are connected. 18. Mosaic : The first WWW browser that was available for the Macintosh, Windows, and UNIX all with the same interface. Mosaic really started the popularity of the Web. The source-code to Mosaic was licensed by several companies and used to create many other web browsers. 19. PDF -- (Portable Document Format) : A file format designed to enable printing and viewing of documents with all their formatting (typefaces, images, layout, etc.) appearing the same regardless of what operating system is used, so a PDF document should look the same on Windows, Macintosh, Linux, OS/ 2, etc. The PDF format is based on the widely used Postscript document description language. Both PDF and Postscript were developed by the Adobe Corporation. 20. OSS : Open source software. 21. OSI: Open Source Initiative (OSI) is a non-profit corporation dedicated to managing and promoting the Open Source Definition. 22. Berkeley Source Distribution (BSD):one of the license for open source software 23. Apache – open source web server software . 24. Mozilla is open source web browser. 25. Linux is an open source operating system. 26. PHP is an open source web scripting language 27. Tomcat is the web server supports java applications to run. 28. Python is an open source programming language like Perl etc. 29. MySQL is an open source database language. FAMILY OF PROTOCOLS 30. SMTP - Simple Mail Transfer Protocol : The SMTP protocol is used for the transmission of e-mails. 31. MIME - Multi-purpose Internet Mail Extensions : The MIME protocol lets SMTP transmit multimedia files including voice, audio, and binary data across TCP/IP networks. 32. IMAP - Internet Message Access Protocol : The IMAP protocol is used for storing and retrieving e-mails. 33. POP - Post Office Protocol : The POP protocol is used for downloading emails from an e-mail server to a personal computer. 34. FTP - File Transfer Protocol : The FTP protocol takes care of the transmission of files between computers. 35. NTP - Network Time Protocol : The NTP protocol is used for synchronizing the time (the clock) between computers. 36. SNMP - Simple Network Management Protocol : The SNMP protocol is used for the administration of computer networks. 37. ICMP - Internet Control Message Protocol : The ICMP protocol takes care of error handling in the network. 38. ARP - Address Resolution Protocol : The ARP protocol is used by IP to find the hardware address of a computer network card based on the IP address. 39. RARP - Reverse Address Resolution Protocol : The RARP protocol is used by IP to find the IP address based on the hardware address of a computer network card. 40. PPTP - Point to Point Tunneling Protocol : The PPTP protocol is used for setting up a connection (tunnel) between private networks. 41. SMTP - Simple Mail Transfer Protocol : The SMTP protocol is used for the transmission of e-mails. SMTP takes care of sending your email to another computer. Normally your email is sent to an email server (SMTP server), and then to another server or servers, and finally to its destination. SMTP can only transmit pure text. 42. POP - Post Office Protocol : The POP protocol is used by email programs (like Microsoft Outlook) to retrieve emails from an email server. If your email program uses POP, all your emails are downloaded to your email program (also called email client), each time it connects to your email server. 43. IMAP - Internet Message Access Protocol “ The IMAP protocol is used by email programs (like Microsoft Outlook) just like the POP protocol. The main difference between the IMAP protocol and the POP protocol is that the IMAP protocol will not automatically download all your emails each time your email program connects to your email server. Short Questions 1. What is networking? Ans Networking is the term used to describe connectivity between the systems with or without Cables or satellites. 2. What is website? Ans It is the collection of web pages used to link text or images with each other. Ex www.yahoo.com 3. Define the term topology. Ans It is the framework or arrangement of systems on network ex: ring ,star, bus etc 4. What are the two types of topology. Ans Star Topology Bus Topology 5. What is LAN? Ans LAN stands for Local Area Network. It is the connectivity of systems within the local organization covers around 100 ms area 6. What do you understand by protocol. Ans A set of rules or instructions govern communication on computer network are called protocols. 7. EDGE stands for… ………… Ans Enhanced Data rates for GSM Evolution 8. Which protocol is used for sending and receiving emails respectively? Ans SMTP used for sending emails and POP for receiving emails. 9. How TCP/IP works. Ans TCP/IP(Transmission Control Protocol /Internet Protocol) A collection of Internet communication protocols between two computers. The TCP protocol is responsible for an error free connection between two computers, while the IP protocol is responsible for the data packets sent over the network. TCP splits message into fixed size datagram which are then tagged with destination address and sent to receiver where the datagram are merged to form proper message. IP is the protocol controlling addressing on the network . As and when any computer gets connected to the network, it must owe a unique address with which it will be identified by other systems. IP protocol assigns address to the different system on the network. 10. FDDI is an example of ________ Ans token ring network 11. Token ring is based on ___________ Ans ethernet 12. MODEM is used for _____________ and _________________ Ans modulation demodulation 13. What is the significance of HTTP and FTP . Ans HTTP (Hyper Text Markup Protocol ) : This protocol is responsible for accessing hypertext documents on world wide web. Set of rules governing exchange of hypertext between two computers is commonly known as HTTP. It consists of 2 distinct items a set of requests from browsers to servers a set of responses from server to browsers FTP (File transfer protocol ) :It defines a method for transferring large files from one computer to another over a network. Set of rules, which enables files to be uploaded or downloaded on a network is known as FTP. It is very effective way to get a geographically dispersed group to co-ordinate on a project and share information on the internet. It serves as client server process. Downloading : refers to transfer of files from FTP server to your computer. Uploading : refers to transfer of files from your computer to FTP servers. Only authorized users can upload a file .Most common use of FTP is to download and upload a file 14. What is XML?. Ans XML (eXtensible Markup Language) : It is a meta language for describing the markup languages A simplified version of SGML especially designed for web documents, developed by the W3C.. There is no predefined tag set. It will be defined by either the application that process them or by style sheets. 15. What do you understand by the term e-commerce. Ans Ecommerce stands for electronic commerce i.e buying and selling of products or services over electronic systems such as the Internet and other computer networks. 16. Explain the types of networks. Ans Types of networks: LAN-Local area network Privately owned networks Used to connect PC’s and workstation within a building or computers in an area upto 100mts of range. Speed of data transmission is not very high MAN-Metropolitan Area Network Bigger version of LAN May be private or public Covers a group of nearby offices or city WAN-Wide area network Spans a large geographical area like countries Public Network Speed very high 17. What is search engine .Name any four search engines. Ans A search engine is program or an information retrieval system designed to help find information stored on a computer system. Search engines help to minimize the time required to find information and the amount of information on any topic . Ex: www. google.com, www.yahoo.com, www.khoj.com, www.altavista.com 18. What is web browser .Name any two commonly used web browsers.. Ans A web browser is a program which is used to visit web pages . The two most well known are Netscape Navigator and Microsoft Internet Explorer which are used by vast majority .Some other browsers are MOSAIC , LYNX , OPERA etc. 19. What is the syntax of URL?. Ans A Uniform Resource Locator refers to an address in the special format on the internet .It is a standard way to address web documents (pages) on the Internet (like: http://www.microsoft.com/) 20. What is bandwidth and baud rate. Ans The range of transmission frequencies that can be carried on a communication line is referred to as the bandwidth of the line .In digital systems bandwidth is data speed in bits per second (bps). Baud rate: It describes the rate of change of the signal on the line i.e.how many times (per second) the signal changes its pattern. The baud rate is the measure of the modulation rate ,the number of discrete signaling events per second. In low speed modem the baud is same as bit rate. 21. Explain the following terms: a. Email b. Chatting c. Videoconferencing d. Domain Name System e. GSM f. Telnet g. Veronica h. Usenet i. WAIS j. Mosaic Ans a. Email : Electronic mail is the way of sending and receiving messages electronically. Major advantage is easy record maintenance, Low cost and fast delivery. b. Chatting: On line talk in the form of text is known is chatting. In chatting as you type a message on the screen which is immediately received by the recipient then the recipient can type a message in response to your message which is received by you instantly. Sites which provide this facility are http:/ chat .yahoo.com , chat.123india.com , chat.sify.com c. Videoconferencing: is a set of interactive telecommunication technology which allow two or more locations to interact via two-way video and audio transmissions simultaneously. d. Domain Name System : A domain name is a unique name for a web site, like yahoo.com .Domain names must be registered. When domain names are registered they are added to a large domain name register, and information about your site - including your internet IP address - is stored on a DNS server. e. DNS stands for Domain Name System. A DNS server is responsible for informing all other computers on the Internet about your domain name and your site address f. GSM(Global system for Mobile): It is one of the leading digital cellular system for mobile communication .The digital nature of GSM allows data, both synchronous and synchronous data, to be transported as a bearer service to or from an ISDN terminal. The data rates supported by GSM are 300 bps, 600 bps, 1200 bps, 2400 bps, and 9600 bps. The most basic teleservice supported by GSM is telephony. A unique feature of GSM compared to older analog systems is the Short Message Service (SMS). Supplementary services are provided on top of teleservices or bearer services, and include features such as international roaming, caller identification, call forwarding, call waiting, multiparty conversations, and barring of outgoing (international) calls, among others. g. Telnet : It is an internet facility that supports remote login. This facility allows users to access files and execute programs on a remote computer without being physically present at the actual site of working. h. Veronica: ‘Veronica’ actually stands for “Very Easy Rodent-Oriented Netwide Index to Computerized Archives.” It’s a program that allows you to search the files of the internet’s Gopher servers using keywords. It is a search engine system for the Gopher protocol. After entering a particular keyword for searching, Veronica displays a list of gopher menus and articles containing the keyword you searched for. The more recent versions of Veronica can also search certain Web pages, newsgroups, and FTP sites. i. Usenet : It is the public bulletin board of the internet and used as a means to share news and other information among users . It is many to many conversation. j. WAIS : Wide area information Network ) : is the facility on the internet that can search for a given item in the database which may be on the different sites on the internet . Searching can be possible by specifying the search string or a topic. k. MOSAIC : It is a graphical WWW browser created by (NCSA) National center for super Computing applications. It can display hyper text documents that include digital video , audio , graphic images and text in a variety of formats. 22. Expand the following terms: a. TCP/IP b. HTTP c. FTP e. DNS f. IP address g. SMTP i. IMAP j. SLIP k.WLL m. TDMA n. FDMA o. XML q. NFS r. CSMA/CD s. NNTP u. PSTN v. ISDN w. W3C y. MODEM Ans a) TCP/IP b) HTTP c) FTP d) URL e) DNS f) IP address g) SMTP h) POP i) IMAP j) SLIP d. URL h. POP l.CDMA p.WDM t. GSM x. WLL : Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol : Hyper Text Transfer Protocol : File Transfer Protocol : Uniform Resource Locator : Domain Name System : Internet Protocol address. : Simple Mail Transfer Protocol. : Post Office Protocol. : Internet Message Access Protocol. : Serial Line Internet Protocol (SLIP) k) WLL l) CDMA m) TDMA n) FDMA o) XML p) WDM q) NFS r) CSMA/CD s) t) u) v) w) x) y) NNTP GSM PSTN ISDN W3C WLL MODEM : Wireless Local Loop : Code division multiple access (CDMA) : Time division multiple access (TDMA) : FDMA (frequency division multiple access) : Extensible Markup Language (XML) : wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM) : Network File System (NFS) : Carrier Sense Multiple Access / Collision Detection : Network News Transfer Protocol : Global system for Mobile. : Public Switched Telephone Network : Integrated Services Digital Network : World wide web Consortium : Wireless in Local Loop : Modulation Demodulation 23. What is web hosting? Ans Web hosting means storing your web site on a public server. It normally includes email services and often includes domain name registration. 24. What is WAN? Ans WAN-Wide area network Spans a large geographical area covering countries Public Network Speed very high 25. What is the significant of ARPANET in the network? Ans ARPANET ( Advance Research Projects Agency NETwork) was the project for connecting computers at different Universities and U.S. defense . Soon the engineers ,scientists ,students and researchers who were part of this system began exchanging information and messages on it .ARPANET started with a handful of computers but it expanded rapidly. 26. What do you understand by peer to peer network Ans It is also known as non dedicated server . where in small networks work station that can be doubled up as a server is known as non-dedicated server , since it is not completely dedicated to the cause of serving. It is a slower and requires more memory. The small networks using such servers are known as peer to peer network. 27. What is client server model. Ans It is a network in which a workstation (client ) can request information from a computer that can share resources (server) and fulfills request. The client/server model provides a convenient way to interconnect programs that are distributed efficiently across different locations. Computer transactions using the client/server model are very common. Advantage : Distribution of work between the client and the server . Server is available to many clients. 28. Give the usage of the following network devices. a. Hub b. Repeater c. Switch d. Bridge e. Router f. Gateway Ans a. Hub : It is a hardware device used to connect several computers together. Hubs act as junction boxes ,permitting new computers to be connected to the network as easily as plugging a power cord into an electrical socket, and provide an easy way to connect network cables .It also act as a repeater or amplifier .Hubs are sometimes also called concentrators, multistation access units or transceivers. b. Repeater: It is a simple device that amplifies all incoming signals on a communication channel and transmits them back the regenerated signal. It connects two segments of your network cable. It retimes and regenerates the signals to proper amplitudes and sends them to the other segments. c. Switches : A switch is a device that is used to divide network into different subnetworks called LAN segments.It typically provides 10/100Mbps network access speed for each device connected to it. This is different to a hub which typically operates at 10/100 Mbps but this is the maximum throughput for all devices attached to it. Hubs cannot cope with the increased demands of today’s high bandwidth applications, e.g. video conferencing and therefore should be phased out in favour of switches. d. Bridge : It is a device that links two networks together which are physically separate but logically same i.e.the networks that follow the same protocols but different type of cables. e. Router :It is a device that works likes a bridge but can handle different types of protocols . It is also used to balance the traffic on various parts of the network. It uses logical address whereas the bridge uses physical address . f. Gateway : It is a system that joins two dissimilar networks together. A network gateway can be implemented completely in software, completely in hardware, or as a combination of the two. It expands the functionality by performing data translation and protocol conversion before transmission. It provides flexibility in communication. 29. Explain the following topologies diagrammatically for five workgropus connected with the server: a. Star topology b. Ring topology c. Bus topology d. Tree topology. Give two advantages and disadvantages for all of the above topologies. Ans a: Star Topology- Most common type of topology used in homes and offices and well suited for smaller networks. In a star topology, various nodes are connected to a central connection point called hub which can be computer hub or sometimes switch alone. The drop cables are extended in all directions and each device is connected to the hub via these cables. . It is inherently fault tolerant . Advantages If a node goes down, network keeps on working without interruption, only one computer might get affected and not the entire network. Network management is easy because of its simplicity in functionality Fault detection is easy , the problems can be easily located logically in a Star Topology Disadvantages The Star Topology is fully dependant on the hub and the entire working of the network depends on the hub or the switch. More cabling is required If there are many nodes and the cable is long then the network may slow down The Star Network Topology typically needs more cable to be networked than the usual Bus topology Example : Archnet , Ordinary telephone conversation b. Ring Topology- Also known as daisy chain topology, is large circular cable and each node is connected to two of its adjacent nodes, thus forming a ring Advantages One node can transmit at a time and collisions do not occur Need for repeaters is reduced Disadvantages Each node must handle data transmitted by other nodes. If one node fails whole network goes down. Example : Mitrenet c. Bus Topology( Multi-drop topology) - It is a method of transmission on networks that uses a common vehicle (backbone cable) for transmissions and thus it is categorized as shared communication. Bus topology only one device is allowed to transmit at a given point of time. A bus structure uses a main trunk called backbone. The two ends of the backbone are terminated by absorbers, which absorb the signals passed by all the devices. On the backbone that is a twisted pair co-axial cable, peripherals and PCs connected with the help of short cables called drop cables. Advantages Wide range of equipments are attached to such networks. A new node can be attached to network without disrupting the network Low cabling cost, very easy to set up , Use least amount o cable Disadvantages One message can travel at a time When a message from two nodes comes, a collision can occur. If the data transfer rate is high then the Bus network does not perform very well because the data travels in a stream and cannot be overloaded Reliability is low because a single break in backbone can bring the whole network down Fault detection & isolation is difficult Example : Ethernet d. Tree Topology: The shape of network is an inverted tree with central root branching and then sub-branching till extremes of network. . It is a modification of pure topologies ( combination of star and bus topology ) so is also called hybrid topology. It is best suited where when the network is widely spread and vastly divided into many branches & hierarchical flow of data is required. Advantages Data communication is very fast as there is a direct link between nodes. A point to point connection is possible with Tree Networks Best topology for branched out networks Disadvantages Cabling and setup is quite complex.For big networks it is difficult to configure and get complicated . The Tree Topology network is entirely dependant on the trunk which is the main backbone of the network. If that has to fail then the entire network would fail. 30. What is multiplexing. Ans A term used to refer to a process where multiple analog message signals or digital data streams are combined into one signal. Ex. Time division mutiplexing, Frequency Division Multiplexing . 31. Explain FDM and TDM. Ans FDM(Frequency Division Multiplexing): where multiple baseband signals are modulated on different frequency carrier waves and added together to create a composite signal. In analog transmission, signals are commonly multiplexed using frequencydivision multiplexing (FDM), in which the carrier bandwidth is divided into subchannels of different frequency widths, each carrying a signal at the same time in parallel. TDM (Time division Multiplexing): a type of multiplexing that combines data streams by assigning each stream a different time slot in a set .It works by dividing a radio frequency into time slots and then allocating slots to multiple calls . In this way ,a single frequency an support multiple, simultaneous data channels. TDM repeatedly transmits a fixed sequence of time slots over a single transmission channel. Within T-Carrier systems, such as T-1 and T-3, TDM combines Pulse Code Modulated (PCM) streams created for each conversation or data stream. 32. How CDMA is different from all other channel allocation techniques. A It is a digital cellular technology which uses spread spectrum techniques means the data is sent in small pieces over a number of discrete frequencies available for use in the specified range. 33. What do understand by 3G system. Ans 3G is short for third-generation mobile telephone technology. The services associated with 3G provide the ability to transfer both voice data (a telephone call) and non-voice data (such as downloading information, exchanging email, and instant messaging. 34. What provisions will you take to make your network secure. A Providing Firewall and antivirus solutions. 35. What is the importance of cookies. Ans A cookie is a small file that web server can store on your machine . It is the temporary file that stores information at the client side by the server and thus reduce the overhead of the server. 36. How firewall acts as security solution. Ans It is a combination of specialized hardware and software set up to monitor traffic between an internal network and an external network (ie the Internet). Its primary purpose if for security and is designed to keep unauthorized outsiders from tampering with or accessing information on a networked computer system. 37. Write any two components of openoffice. Ans OpenOffice has these components: writer ,calc and draw. 38. How will you explain the concept of WLL. Ans WLL is a system that connects subscribers to the public switched telephone network (PSTN) using radio signals as a substitute for copper for all or part of the connection between the subscriber and the switch. This includes cordless access systems, proprietary fixed radio access, and fixed cellular systems. 39. What are the following software use for ? a. PHP b. Linux Ans PHP : Short of Hypertext Preprocessor. It a server side side technology introduced to design dynamic web pages like ASP,It is based on open source technology under PHP license to develop graphic and web applications Linux is an open source operating system. 40. What is token ring? What type of cables are used for token ring? Ans Token ring is the IEEE 802.5 standard that connects computers together in a closed ring. Devices on the ring cannot transmit data until permission is received from the network in the form of an electronic 'token'. There are three major physical token ring cabling systems; Shielded Twisted Pair (STP), Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP), and optic fiber. 41. What is Ethernet ? To which OSI layer does Ethernet belongs? Ans Ethernet is a Local Area Network (LAN) cabling and signaling specification for baseband networks. Ethernet uses a bus or star topology for connecting different nodes in a network. Ethernet belongs to both the Physical Layer (Layer 1) and the Data Link layer (Layer 2) in the OSI architecture. 42. What is a collision ? How is "collision" handled in Ethernet networks? Ans At any one instance, in an Ethernet network, only one device can transmit. If two devices transmit at the same instance, then the signals from both devices will collide and a "collision" will occur. When a "collision" occurs, the signals will get distorted and the frame will be lost. Collisions are very common in a Ethernet network. Ethernet uses the Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection (CSMA/CD) media access control mechanism to detect and recover from a collision. 43. What is CSMA/CD? Ans CSMA/CD is a media access control mechanism used in Ethernet to recover from frame collision. The following steps are followed to recover from a collision. Step 1: Before an Ethernet device sends a frame on the Ethernet cable, it listens to find if another device is already transmitting a frame (Carrier Sense). Step 2: Once the device finds that other devices are not transmitting any frame, it starts transmitting the frame. If two devices detect that the Ethernet cable is free at the same time, then both will start transmitting the frames (Multiple Access). This will result in collision. Step 3: The Ethernet devices while transmitting the frames, also listen for the collision. (Collision Detect). Step 4: If they detect a collision, both the devices stop sending the frame (back off). Step 5: They retry the transmission after a logarithmic time-out period. This process is repeated till the frame is transmitted successfully, for a maximum of 16 times. The frame is discarded after the 16th retry. 44. What is protocol? How many types of protocols are there? Ans. When computers communicate each other, there needs to be a common set of rules and instructions that each computer follows. A specific set of communication rules is called a protocol. Some protocol: PPP, HTTP, SLIP, FTP, TCP/IP 45. What is the difference between Networking and Remote Networking? Ans. The main difference between Networking and Remote Networking, is the network which we use in offices or other places locally such LAN or INTERNET and remote networking is one which we use TERMINAL Services to communicate with the remote users such WAN. 46. What is point-to-point protocol? Ans. A communication protocol used to connect computer to remote networking services include Internet Service Providers. In networking, the Point-to-Point protocol is commonly used to establish a direct connection between two nodes. Its primary use has been to connect computers using a phone line. 47. How gateway is different from router? Ans. A gateway operates at the upper levels of the OSI model and translates information between two completely different network architectures. Routers allow different networks to communicate with each other. They forward packets from one network to another based on network layer information. A gateway can interpret and translate the different protocols that are used on two distinct networks. Unlike routers that successfully connect networks with protocols that are similar, a gateway perform an application layer conversion of information from one protocol stack to another. 48. What is the role of network administrator? Ans. Basic tasks for which a network administrator may be responsible: Setting up and configuring network hardware and software. Installing and configuring network media and connections. Connecting user nodes and peripherals of all kinds to the network. Adding users to and removing users from the network. Managing user account. Ensuring the security of the network. Provide training to the users to utilize the network’s resources. 49. What is the differences between POP3 and IMAP Mail Server? Ans. IMAP is a standard protocol for accessing e-mail from a local server. A simpler email protocol is Post Office Protocol 3 (POP3), which download mail to the computer and does not maintain the mail on the server. IMAP, e-mails are stored on the server, while in POP3, the messages are transferred to the client’s computer when they are read. 50. Name different layer of the ISO-OSI Model. Ans. ISO-OSI (International Standard Organization – Open Systems Interconnection) has seven layers; Physical Layer Data Link Layer Network Layer Transport Layer Session Layer Presentation Layer Application Layer 51. What is client server architecture? Ans. To designated a particular node which is well known and fixed address, to provide a service to the network as a whole. The node providing the service is known as the server and the nodes that use that services are called clients of that server. This type of network is called Client-Server Architecture. 52. What is FDM? Give example. Ans. FDM-Frequency Division Multiplexing is used in analog transmission. It is often used in short distance. It is code transparent and any terminal of the same speed can use the same sub-channel after the sub-channel is established. The best example if FDM is the way we receive various stations in a radio. 53. What is interspace? Ans The Interspace is a vision of what the Internet will become, where users crosscorrelate information in multiple ways from multiple sources. 54. Compare twisted pair cable and co-axial cable. Ans A twisted pair consists of two insulated copper wires, each with its own plastic insulation, twisted together in a helical form. Coaxial cable is an electrical cable consisting of a single round conducting wire, surrounded by an insulating spacer, surrounded by a cylindrical conducting sheath, and usually surrounded by a final insulating layer. 55. Define the following terms : Share ware , GSM , TCP/IP Ans Shareware: A method of marketing software where a program is distributed freely, and users may try it before paying for it. GSM: Global System for Mobiles, it is the international standard for wireless technology. GSM allows users to utilize one phone and one number in many countries throughout the world. TCP/IP: Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol. A group of protocols that specify how computers communicate over the Internet. 56. Describe the following in brief: i) MOSAIC ii) USENET iii) WAIS Ans. i) MOSAIC: is the program for cruising the internet. The National centre wrote this program for Super Computer application at the university of Illinois. It has a simple window interface, which creates useful hypertext links that automatically perform some of the menu bar and button functions. ii) USENET: is the way to meet people and share information. Usenet newsgroup is a special group set up by people who want to share common interests ranging from current topic to cultural heritages. iii) WAIS: is a WIDE AREA INFORMATION SERVER. 57. What is FLOSS. Ans FLOSS is common and combined term of Free/Libre/Open Source Software. Actually this term for free software and open source where free means it was cost free software. Libre means liberty : to make changes Open source means code or patch files are available openly to fix bugs, and for further development. 58. Explain the term GPL. Ans GNU Public License (GPL) Most new open source software around these days uses this license, as does Moodle. In a nutshell, the GPL says: Anyone can download, use, modify and distribute this software All modified versions must ALSO be under the GPL license All copyright notices must be maintained, and all modifications must be clearly marked All distributions must include the full source code There is no warranty on the software 59. What is FSF. Ans The Free Software Foundation (FSF)was established in 1985 to promote the development of free software with full rights to use, study, copy, modify, and redistribute computer programs. particularly the GNU operating system, used widely in its GNU/Linux variant.Its a non profit, non political and international organization provides standards for developing free softwares. 60. What is GNU. Ans GNU is a computer operating system composed entirely of free software. Its name is a recursive acronym for GNU's Not Unix, which was chosen because its design is Unix-like, but differs from Unix by being free software and by not containing any Unix code.GNU was founded by Richard Stallman and was the original focus of the Free Software Foundation. 61. What is OSI. Ans Open Source Initiative (OSI) is a non-profit corporation dedicated to managing and promoting the Open Source Definition for the good of the community, specifically through the OSI Certified Open Source Software certification mark and program.. The basic idea behind open source is to read, redistribute, and modify the source code for a piece of software, the software evolves. People improve it, people adapt it, people fix bugs. We in the open source community have learned that this rapid evolutionary process produces better software than the traditional closed model, in which only a very few programmers can see the source and everybody else must blindly use an opaque block of bits. 62. What is W3C. Ans W3C (World Wide Web Consortium) The organization responsible for managing standards for the WWW. 63. Define the following: a. Open source software: Open Source software which simply means any software certified by the OSI and openly available with the source code.Open source software generally allows anybody to make a new version of the software, port it to new operating systems and processor architectures, share it with others or market. b. Freeware Software which is distributed free by the author. Although it is available for free, the author retains the copyright, which means that it cannot be altered or sold. c. Shareware. Software distributed freely, but with certain conditions applying to it. Either the software is released on a trial basis only, and must be registered after a certain period of time, or in other cases no support can be offered with the software without registering it. In some cases direct payment to the author is required. d. Proprietary software. Software which is privately owned or controlled is known as proprietary software. Proprietary software is not free software or open source software as end-users generally do not have the ability to: Run the software for any purpose Study and modify the software Copy the software and provide it to third parties Make and release improvements to the software e. Localization. localization is the adaptation of an object to a locality. An example is in software localization, where the messages that a program presents to a user need to be translated into various languages. Language localization refers to the process of adapting a language for a specific country or region. f. UNICODE. It’s a Character coding system which is replacing older ASCII code thesesdays due to its compatibility,size and scope .it is extensively used these days in Java,XML and other languages. 64. Why Linux is popular now a days. Ans Like Windows and Unix ,Linux is also an operating system developed Linus Torvalds but this operating system was freely distributed as Open Source i.e code is freely available to read ,edit and fix bugs. Apart from the fact that it's freely distributed, Linux's functionality, adaptability and robustness, has made it the main alternative for proprietary Unix and Microsoft operating systems. IBM, Hewlett-Packard atre the top companies which has embraced Linux and support its ongoing development. It was primarily adapted as a server platform. 65. What is Mozilla Firefox? Ans Mozilla Firefox is a free web browser , from the Mozilla Application Suite, managed by the Mozilla Corporation. It is the second-most popular browser currently worldwide, after Internet Explorer. Firefox includes tabbed browsing, a spell checker, incremental find, live bookmarking, a download manager, and an integrated search system that uses the user's desired search engine. 66. Why Mozilla is different from other web browsers. Ans An open-source XML/HTML browser have with dynamic image and table resizing, quick insert and delete of table cells, improved CSS support. 67. Explain the webserver Apache.Where it is used. Ans The Apache HTTP Server is to develop and maintain an open-source web server for modern operating systems including UNIX and Windows NT. The goal of this project is to provide a secure, efficient and extensible server that provides HTTP services in sync with the current HTTP standards.Apache has been the most popular web server on the Internet since April 1996. Uses of apache are: Serves both static content and dynamic Web pages on the World Wide Web. Apache provides environment to run web applications like java based and XML 68. Write short note on MySQL. Ans MySQL is the world's most popular open source database software. It is a structured query language like SQL used for managing database systems.Many of the world's largest and fastest-growing organizations use MySQL to save time and money powering their high-volume Web sites, business-critical systems and packaged software -- including industry leaders such as Yahoo!, Alcatel-Lucent, Google, Nokia. . 69. Write brief note on Postgres. Ans PostgreSQL is an object-relational database management system (ORDBMS). It is released under as a free software. And like other open-source programs, PostgreSQL is not controlled by any single company, but relies on a global community of developers and companies to develop it. 70. What is Pango. Ans Pango is a free and open source computing library for rendering internationalized texts in high quality. Pango has been integrated into most Linux distributions. It most notably provides the rendering for text in the Mozilla Firefox web browser Different font backends can be used, allowing crossplatform support. 71. What is Open office. Ans The OpenOffice.org project aims "To create, as a community, the leading international office suite that will run on all major platforms and provide access to all functionality and data through open-component based APIs and an XMLbased file format like Microsoft Office. 72. Explain Tomcat,PHP,Python. Ans Tomcat: Apache Tomcat is an application server developed at the Apache Software Foundation (ASF). To run java applications on web server It has its own internal HTTP server and implements the Java Servlet and the JavaServer Pages (JSP) specifications from Sun Microsystems, providing an environment for Java code to run in cooperation with a web server. PHP: short of Hypertext PreProcessor.It a server side side technolgy introduced to design dynamic web pages like ASP,It is based on open source technolgy under PHP licence to develop grahic and web applications. It was written as a set of Common Gateway Interface (CGI) binaries in the C programming language by the Danish/Greenlandic programmer Rasmus Lerdorf in 1994, to replace a small set of Perl scripts he had been using to maintain his personal homepage. Python: Python is a multi-paradigm programming language (functional, object oriented and imperative) which has a fully dynamic type system and uses automatic memory management; it is thus similar to Perl, Ruby, Scheme, and Tcl. The language has an open, community-based development model managed by the non-profit Python Software Foundation. 73. What are the merits and demerits of open source. Ans Merits : Source code is openly available. Freely distributed User is free to make changes and fix bugs without any licencing. Compatible and secured as per the application . One Common license requires to publish software i.e. GNU and gets poularity easily in the market. DeMerits: No sole authority for any sort of complaints as it is constantly developed and bugs are fixed by any third person. It can not be centrally managed and co-ordinated, and there are fewer "odd gaps" in its development as such. In case of closed source model new versions of the software are continually being introduced, with lots of new features being added. Revenue generation is very high due to target based applications. 74. Is freeware is same as free software ,If not, Why? Ans No, Free software is distinct from freeware; freeware is proprietary software made available free of charge. Everyone is free to sell copies of free software, to use it commercially, and to charge for distribution and modifications. Because anyone who has a copy may distribute the software at no cost, the software generally is available at no cost. Free software business models are usually based on adding value such as support, training, customisation, integration, or certification like open source softwares are free softwares. 75. What are the two popular open source licenses ? How they are different. Ans GNU Public License (GPL) Most new open source software around these days uses this license, as does Moodle. In a nutshell, the GPL says: Anyone can download, use, modify and distribute this software All modified versions must ALSO be under the GPL license All copyright notices must be maintained, and all modifications must be clearly marked All distributions must include the full source code There is no warranty on the software Berkely Source Distribution (BSD) The BSD license is even simpler - all it basically says is: Anyone can download, use, modify and distribute this software in any form All existing copyright and usage notices must be kept in the software There is no warranty on the software The names of the original authors can't be used in promotion without written permission from the original authors. 76. Write the difference between Adware and baitware. Ans Adware is any software program in which advertising banners are displayed while the program is running. Baitware: term is composed by bait and -ware and refers to a buggy freeware software, released to deceptively attract users and drive them to commercial products. 77. Differentiate between the following: a. LAN and MAN b. Microwave and Radiowave c. Gopher and WWW d. Star and Ring topology e. Router and Gateway f. Hub and Switch g. Client and Server h. CSMA/CD and token passing i. Circuit switching and Message Switching. j. Coaxial cables and optical fibers k. Mobile Technology and Wireless Technology l. SMS and 3G m. XML and HTML n. Hacker and Cracker. o. Baseband and Broadband transmission p. Domain and workgroup Ans a. LAN a) Local Area Network. are privately owned networks b) Used to connect PC’s and workstation within a building or computers in an area upto 10 kms of range. c) Speed of data transmission is not very high MAN MAN-Metropolitan Area Network Bigger version of LAN Extends within metropolitan area. Covers a group of nearby offices or city Speed of transmission is very high. b. Microwave Parabolic antennas are mounted on Radiowave Waves are omni directional i.e.-travel in towers to send a beam to other antenna. all directions from source to source Higher the tower, greater is the range destination need not be physically aligned Used for outdoor communication Used for both indoor and outdoor communication Are subjected to weather easily . Subject to interference. c. Gopher A menu based browser that lets you search for and retrieve desired information on the internet WWW World wide web is a repository of information containing a set of programs , standards and protocols that allows the multimedia and hypertext files to be created , displayed and linked on the internet. Star In a star topology, various nodes are connected to a central dedicated computer called hub of the star If a node goes down, network keeps on working without interruption Ring Ring topology has a large circular cable and each node is connected to two of its adjacent nodes, thus forming a ring If one node fails whole network goes down d. e. Router is a device joins similar networks but can handle different types of protocols . A router works by looking at the IP address in the packet and decides if it is for internal use or if the packet should move outside the network (to the WAN). f. Gateway is a system that joins two dissimilar networks together gateway acts as a conversion from one protocol to another or in the case of VoIP from the VoIP network to the POTS network Hub Hub receives data and sends to all PC connected through cables resulting in collision. Switch In case of switch most of the network traffic only goes where it needs to rather than to every port. Every computer connected to the hub "sees" everything that every other machine on the hub sees Hub are less efficient and slower . .It sends data according to the address assigned and managing the network traffic. On busy networks this can make the network significantly faster g. Client Node refer to the computers attached to the network and are seeking to share the resources of the network. Server A computer that facilitates the sharing of data , software and hardware resources on the network is termed as server Every workstation is known as It is of high capacity to share clients at a client.It is of lower configuration as common resource point. compared to server. h. CSMA / CD Traffic cannot be regulated Waiting time cannot be determined TOKEN PASSING Traffic can be regulated Waiting time can be determined before a node transmits. Nodes are given access on first come Nodes can be prioritized for getting first serve basis . access privilege. Collision rate is high in high traffic. Performance is good in low traffic. No collision. Even in low traffic the nodes have to wait unnecessarily . Circuit Switching Message Switching i. Switching techniques of sending data through establishing physical connection between sender and receiver. Ex: Telephone communication It’s a techniques based on store and forward principle where data is first sent to the switching office and then further transferred accordingly. Ex: Email j. Coaxial cables Consists of a solid wire core surrounded by one or more foil or wire shield each separated by some kind of plastic insulator. Optical fibres These are then strands of glass or glass like material constructed to carry light from one source at one end fiber to a detector at other end Bandwidth and data transmission is in the form of electric signals which is less as compared to optical fire is less an Offers electrical interference . Bandwidth potentially very high. Data transmission rate is also high due to form of laser spectra. optical fibres do not experience any electrical interference. Regenerators are required at every 2- Regenerators are required at least after 3 kms 50km Used for cable T.V, telephone ,audio It can be used for high rate TV cable channels etc. channels,purposes of illumination ,in sensors k. Mobile technology It is the data communication without the use of landlines. This may involve cellular phones ,two way radio, fixed wireless , ,Laser or satellite communication. Here the computing device is continuously connected to the base network. Not all wireless technologies are Wireless Technology Mobile computing means that the computing device is not continuously connected to the base or the central network .Mobile devices includes PDA’s ,laptop computer an many cell phones . mobile. a base location with or wireless These products may communicate with connection. m. XML It is the subset of SGML where we are free to define our own tags. XML was designed to describe data and to focus on what data is. HTML It is a language where we have predefined tags . HTML was designed to display data and to focus on how data looks. It is extensively used with other It is used as basic design platform for languages like C# ,java to store and any web document and implements send information. scripting and server side technologies in it. n. Hackers Are the experts keeps on mastering the computer and related technologies Hackers constantly seek further Crackers A cracker is a person who breaks into or otherwise violates the system integrity of remote machines, with malicious intent Crackers, having gained unauthorized access, destroy vital data create viruses knowledge, freely share what they or do script attacks. have discovered, and never, ever intentionally damage data. o. Baseband Baseband is a bi-directional transmission Entire bandwidth of the cable is consumed by a single signal Broadband broadband is a unidirectional transmission. Broadband transmission, signals are sent on multiple frequencies, allowing multiple signals to be sent simultaneously. Digital signals Analog signals No Frequency division multiplexing Frequency division multiplexing possible possible Uses for short distance Uses for long distance p. Domain One or more computers are servers If you have a user account on the domain, you can logon to any computer on the domain. There can be 100+ computers The computers can be on different local network Workgroup All Computers are peers. Each computer has a set of accounts. Typically not more then 20-30 computers All computers must be on the same local netork. HOTS ( HIGH ORDER THINKING SKILLS) 78. The Netsavvy has set up a new office in the hill station Mussorie .It has 4 wings as shown in the diagram below: Wing A Wing C Wing B Wing D Center to center distance between various blocks Wing A to Wing B 75m Wing A to Wing C 150 Wing B to Wing C 25 Wing A to Wing D 50 Wing C to wing D 100 Number of computers in each wing Wing A 25 Wing B Wing C Wing D i) 50 125 10 Suggest the most suitable topology to network all the wings. Ans Most suitable topology to network all wings is star topology. A B C D Total distance ==150+100+25 = 275 ii) Suggest the most suitable place to house the server .Justify your choice. Ans C is the most suitable to house the server as it has max number of computers and located centrally iii) Where and why should repeaters be used. Ans Repeaters is required between A-------B ,A----------C and C---------D where distance is more than 50 ms (iv) The Mussorie office has to be linked with its headquarters in Mumbai .suggest the most economical way to connect it. The organization is ready to compromise on the speed of connectivity. Ans 79. LML Organization has set up its new center at Mumbai for its office and web based activities. It has 4 Blocks of buildings as shown in the diagram below: Block A Block C Block D Block B Center to center distance between various blocks Block A to Block B 50 m Block B to Block C 150 m Block C to Block D 25 m Block A to Block D 170 m Block B to Block D 125 m Block A to Block C 90 m Block A 25 Block B 50 Block C 125 Block D 10 Number of Computers a. Suggest a most suitable cable layout of connections between the Blocks. b. Suggest the most suitable places (i.e. Block) to place the server of this organization with a suitable reason. c. Suggest the placement of the following devices with justification: 1. Repeater 2. Hub/Switch d. The organization is planning to link its head office situated in City in a desert region where cable connection is not feasible, suggest an economic way to connect it with reasonably high speed? Ans: a. Block A Block C Block B Block D Cable Lyout is suggested to connect all computers on the network with minimum cable length and cost. Therefore if we connect A-B =50 m A-C=90m C-D=25m i.e total cable length comes 165m this is the best way to have cable connectivity in the above scenario. Other way is through connecting block C i.e A-C and B-C and C-D Which comes 90+ 150+25=265m So considering the first case coaxial cables CAT 6 /5 can be placed . b. Server is placed as to get connected with maximum connectors in the center location .Also Server rule 80-20 design rule also says that server should be placed to balance the network traffic and data communication in the most easy manner. In the above scenario server should be placed in Block C c. Repeater is used to amplify the signals .It can be placed in between Block A –Block C Hub/Switches :Each building should have hub/switch to connect its local machines. Block AHub Block B Hub Repeater Block C Hub Block D Hub d. In that case organization can go for radio wave communication as radiowave communication is cheaper and will serve the purpose of data communication in the best manner as it has following features : Easy to generate Travel over long distances Used for communication both indoors & outdoors Waves are Omni directional i.e.-travel in all directions from source to source destination need not be physically aligned 80. Zercon Pvt Ltd. has decided to network all its offices spread in five buildings of C.P. (Shown below). Building 2 Building 3 Building 1 Building 5 Center to center distance between various blocks Between 1 and 2 50m Between 2 and 3 50m Between 3 and 4 120 Between 4 and 5 30 Between 3 and 5 75 Between 1 and 5 60 Between 2 and 5 50 Building 4 Between 3 and 4 50 Number of Computers 1 40 2 45 3 110 4 70 5 60 a) Suggest cable layout(s) for connecting the buildings. b) Where do you think , additional repeaters would be required by networking buildings? c) Company wants to minimize traffic . Which network device is/should be used for this? d) The company also has another office in the same city but at a distant location about 25-30 kms away. How can link be established with this building (i.e. suggest the transmission medium). Ans: a). Possible cable layouts are: Building 1 Building 2 Building 5 Building 3 Building 4 Connecting Building 1-2-3-4-5 Total length =50+50+50+30=180ms Best possible layout. OR Building 5---1—2—3---4 but length comes 280 which is high as compared to that. b. Repeaters could be placed between building 2 and 3 to amplify signals . c. Bridge as it does not broadcast data but sends data direct to its destination as per machine address. d. In that case organization can go for radio wave communication as radiowave communication is cheaper and will serve the purpose of data communication in the best manner as it has following features : Easy to generate Travel over long distances Used for communication both indoors & outdoors Waves are omni directional i.e.-travel in all directions from source to source destination need not be physically aligned 81. Rai Industries has set if its new center at Tri Nagar for its office and web based activities. The company compound has 4 buildings as shown in the diagram below: R Building F Building H Building J Building Center to center distances between various buildings is as follows: H Building to R Building 50 m R Building to F Building F Building to J Building J Building to H Building H Building to F Building R Building to J Building 60 m 25 m 170 m 125 m 90 m Number of Computers in each of the building is follows: H Building R Building F Building J Building (a) (b) 15 150 15 25 Suggest a cable layout of connections between the buildings. Suggest the most suitable place (i.e., building) to house the server of this organization with a suitable reason. (c) Suggest the placement of the following devices with justification: (i) Internet Connecting Device /Modem (ii) Switch (d) The organization is planning to link its sale counter suitable in various parts of the same city. Which type of network out of LAN, MAN or WAN will be formed? Justify your answer. Ans: a) Possible cable layout is : Layout : 1 H-R-F-J 50+60+25 = 135m Layout 2 50 + 60 + 90 = 200 m Hence layout 1 is suggested. b) The most suitable place / block to house the server of this organization would be Building R, as this building contains the maximum number of computers, thus decreasing the cabling cost for most of the computers as well as increasing the efficiency of the maximum computers in the network. c) i.) Modem should be placed at building R where server is housed. ii.) Switch : Each building should have its switch to connect computers locally. d) MAN : Metro area network connectivity of computers of different types (LAN) in a city.