SCO 5 Natural Resources: Farming (pg. 250
advertisement

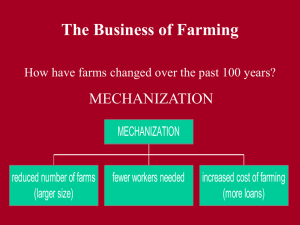
SCO 5 Name: KEY 1. Natural Resources: Farming (pg. 250-259) Each following statement is false. Make each statement true by replacing the incorrect word(s) with the correct word(s). Even though farming contributes only 1.7% 10.3% to Canada’s GDP, it is still important in supporting rural communities and providing Canadians with a safe, reliable food supply. (pg. 250) 2. Arable farmland in Canada makes up about 7% 20% of the country’s total land area. (pg. 250) 3. Ethics often never plays a role in the decision making on a farm. (pg. 252-253) Concern for animal welfare, no run off of waste into water supply, consider risks to water, soil, land & other animals when using pesticides 4. Pesticides have allowed for the production of food to double, and have often never caused problems with the environment or human health. (pg. 255) 5. The Agribusiness industry does not ensures that all stakeholders such as the farmers and grocery stores all share equally in the profit. (pg. 256) 6. Factory farms are corporation family owned farms where animals are raised in large barns or feedlots. (pg. 257) 7. Animals in feedlots are susceptible to diseases always healthy. (p257) 1 8. Animals in feedlots do don’t contaminate the soil or water supply. (p257) Bacteria from manure and chemicals that the animals consumed 9. What are five factors that affect agriculture? (pg. 252) Climate, landforms, soil Demands by consumers for certain products Transportation facilities that are available Proximity to market, where food products are bought and sold Competition from other lower-cost growers Changing prices for food on world markets 10. List five challenges that farmers face. (pg. 253) Natural hazards – early frost, drought, floods, animal diseases (mad cow disease in beef, avian flu in poultry) High costs for fuel and equipment Low crop prices Competition from farmers in other countries Competition from factory farms (owned by big corporations) 11. What is a subsidy? (pg. 254) Money given to farmers by the government (US and EU) to off-set some of their costs, such as expensive machinery or high fuel prices Helps keep prices of products low 2 12. A) What is the trend in the number and size of Canada’s farms? (fig 6.18 pg. 256) Average farm size is increasing Number of farms is decreasing B) In 1930, farmers made up about 32% of Canada’s total population; today, that figure stands at 3%. 3 13. What are two problems changing technologies in farming can cause for people? (pg. 255) High technology farm machinery, chemicals and high yield seeds Dangerous to human health (asthma, allergies, cancer, reproductive and development problems) Pose risks to the natural environment (air & water pollution, soil contamination) 14. What are two negative aspects of the agribusiness industry? (pg. 256) Transnational corporations take the bulk of the profit, leaving the farmer and grocery store with a very small percentage of the profit in the food system Compact too many animals into a small space (upto 5000 pigs in a barn) not giving them enough space to live 15. From what you have learned so far, why would it be better for the environment and the economy for Canadians to buy cereal produced in Canada? Explain. Local food security – better to support local economy Reduces shipping distance – lower ecological footprint 16. Explain why factory farming is a negative trend in farming. (pg. 257) Thousands of animals in small, contained space not animal friendly More susceptible to diseases Manure contaminates water supply with harmful bacteria and chemicals Processed foods are bad for our health (preservatives, additives) 4 17. Explain what “sustainable agriculture” means. (pg. 258) Method of farming that is profitable, protects the environment, conserves natural resources and supports the rural community Will last into the future Meets our need for food, don’t have to rely on imported food Efficient use of fossil fuels to run machinery Protects water supply, air & soil quality Reduces use chemicals (fertilizers/pesticides) Provides jobs and profitable industry Supports small farms Encourages positive contact between farmers and consumers 18. Explain why organic farming is a positive trend in farming. (pg. 259, see fig 6.22) Growing plants and animals without using chemicals (fertilizers/pesticides) or growth hormones or antibiotics Promotes sustainable agriculture Less toxins in peoples bodies (bio amp) – growth and reproductive issues Less toxins into water supply More nutritious 5 19. What are three things you and your family can do to contribute to sustainable agriculture? (pg. 259) Buy locally grown food Shop at farmers market Support smaller, independent stores Plant garden on rooftop, balcony or in backyard Participate in a community garden 6