Scarcity

Fundamental
Economic
Concepts
What is Economics?
- The study of mankind’s unlimited desires in a world of limited resources.
-Economics is a social science , dealing with how people react to changing variables.
-Economists form theories , based on economic models in which they manipulate variables .
-These theories, models and variables are used to describe what is (Positive Economics) and what ought to be (Normative Economics).
What is the Economy?
Why Do We Study It?
1. Description
2. Analysis
3. Explanation
4. Prediction
What? or How Much?
How? or Why?
OR…
When?
Why do we study Economics?
So we don’t get screwed.
Scarcity
Situation that occurs when wants are greater than available resources.
In this classroom, is/are _________ scarce?
Desks?
Water?
Books?
Wants are satisfied by available resources
But not in the hallway…
…
Gasoline?
Jolly Ranchers?
No want for it in classroom, but outside… yes
Wants exceed available resources
Good looking economics instructors?
Good looking economics instructors?
We must consider…
Examples: Shelter is a need, a mansion is a want.
Food is a need, a large pizza is a want.
Scarcity forces us to ask the following questions…
WHAT to produce?
HOW to produce?
FOR WHOM to produce?
Imagine a scenario where…
…we take an all-expensespaid class trip to…
Australia!
Our plane is forced to make a “water landing,” and we are able to swim to an uncharted island.
What will we need to do? What questions will we have to answer?
FACTORS OF PRODUCTION
Land – all gifts of nature
Labor – human efforts and abilities
Capital – tools, equipment, space
Entrepreneurship – risk taking, ideas
◦ **The “spark” or driving force of the economy**
EXAMPLES:
Adam Smith
“Wealth of Nations”
◦ 1776
Invisible hand
◦ Meat
◦ Bread
◦ Candles
◦ How do we decide to provide these?
Utility
The satisfaction that consumption of a good or service provides
DIMINISHING MARGINAL UTILITY
Paradox of Value
Water vs. Diamonds
Monetary Value
◦ Must be scarce
◦ Must give utility
Are diamonds scarce?
Do they give utility?
Conspicuous consumption
Cost – Benefit Analysis
Question? :
What do you want
RIGHT NOW?
Cost – Benefit Analysis
Follow up question? :
Why don’t you go get it?
Cost – Benefit Analysis
• We all make decisions in our own self-interest
• All decisions come with certain trade-offs and alternatives
• Opportunity Cost: the next-best alternative given up when making a choice
Opportunity Cost
VS.
VS.
VS.
Marginal Cost
Marginal = Additional, next
Additional cost vs. additional benefit
We constantly engage in marginal analysis
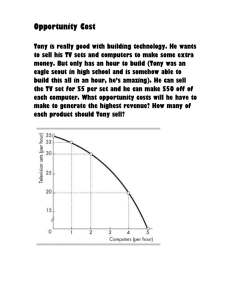
Production Possibilities Frontier
All possible combinations of two products that can be produced when employing 100% of available resources.
Guns (thousands) Butter (tons)
80
75
60
0
150
300
30
0
400
450
Production Possibilities Frontier
CIRCULAR FLOW