ANP Course Review Sem 2
A&P 2
nd
Semester Course Review 1
Anatomy and Physiology Regular/Honors
Second Semester End of Course Review
Unit 10: Endocrine
1.
(Endocrine/Exocrine) gland produces non hormonal substances such as sweat and saliva.
2.
(Endocrine/Exocrine) gland releases hormones into the surrounding tissue fluid.
3.
(Endocrine/Exocrine) gland release secretions into a duct that leads out onto a surface.
4.
(Endocrine/Exocrine) gland contains a rich vascular system so that secretions can be received.
5.
An increase in concentration of glucose in the blood stimulates the pancreas to secrete insulin is an example of
(negative/positive) feedback.
6.
The onset of contractions during childbirth causes the release of oxytocin which stimulates further contractions of the uterus is an example of (negative/positive) feedback.
7.
Thyroxine levels are low causing the pituitary gland to release thyroid stimulating hormone, which stimulates the thyroid to release more thyroxine is an example of (negative/positive) feedback.
8.
Water concentration in the blood stream is low causing the release of antidiuretic hormone which causes the body to hold water and not release it as urine is an example of (negative/positive) feedback.
9.
Suckling stimulates the release of oxytocin which causes milk letdown from mammary glands, which stimulates more suckling, causing the release of more oxytocin resulting in increased milk letdown is an example of (negative/positive) feedback.
10.
The (endocrine/nervous) system regulates the activity of muscles and glands via electrochemical impulses delivered by neurons that provide (immediate/long term) response to changes. The (endocrine/nervous) system influences homeostasis by releasing hormones that provide (immediate/long term) response to changes.
11.
(Amino acid/Steroid) based hormones cannot diffuse through the plasma membrane and as a result require a secondary messenger in order to activate the target cell (HONORS).
12.
(Amino acid/Steroid) based hormones diffuse through the plasma membrane and directly affect the nucleus of the target cell (HONORS).
13.
List the possible changes that can occur when a hormone affects its target cell (HONORS).
a.
_________________________________________________________________________________________ b.
_________________________________________________________________________________________ c.
_________________________________________________________________________________________ d.
_________________________________________________________________________________________ e.
_________________________________________________________________________________________
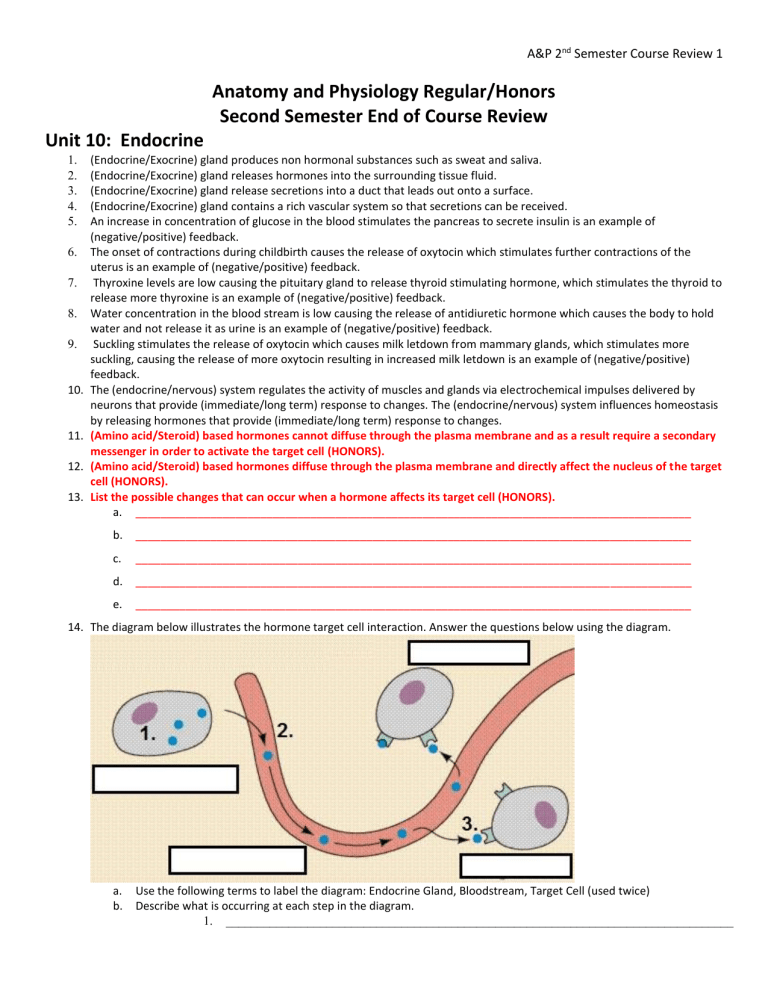
14.
The diagram below illustrates the hormone target cell interaction. Answer the questions below using the diagram. a.
Use the following terms to label the diagram: Endocrine Gland, Bloodstream, Target Cell (used twice) b.
Describe what is occurring at each step in the diagram.
1.
_________________________________________________________________________________
A&P 2
nd
Semester Course Review 2
2.
_________________________________________________________________________________
3.
_________________________________________________________________________________
MATCHING: Match the method of stimulus for hormone release with the definitions below.
15.
_____ Gland is stimulated by changing blood levels of ions/nutrients
16.
_____ Gland is stimulated by nerve fibers
17.
_____ Gland is stimulated by a hormone released from another gland
A. Hormonal Stimuli
B. Humoral Stimuli
C. Neural Stimuli
18.
Label the chart below with the following endocrine glands: Adrenals, Ovaries, Pancreas, Parathyroid, Pituitary, Testis, Thymus,
Thyroid.
19.
Fill in the chart below regarding the hormones released from the glands located on the diagram above.
Name of the
Endocrine Gland
Name of the
released hormone
Action of the hormone Target cell/organ of hormone
Pituitary Gland Growth Hormone
(GH)
Thyroid Stimulating
Hormone (TSH)
Follicle Stimulating
Hormone (FSH)
Luteinizing
A&P 2
nd
Semester Course Review 3
Thyroid Gland
Parathyroid Gland
Adrenal Gland
Pancreas
Gonad
Testes
Gonad
Ovaries
Hormone (LH)
Prolactin
Antidiuretic
Hormone (ADH)
Oxytocin
Thyroxine (TH)
Calcitonin
Parathormone
(PTH)
Epinephrine
Norepinephrine
Insulin
Glucagon
Testosterone
Estrogen
Progesterone
20.
Hypersecretion a.
Definition:_____________________________________________________________________________________ b.
Example (using one of the hormones from the chart above):_____________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
21.
Hyposecretion c.
Definition:_____________________________________________________________________________________ d.
Example (using one of the hormones from the chart above):_____________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
Unit 11: Blood
Cells
1.
What are the two major components of blood? o __________________________________________________________________ o __________________________________________________________________
2.
Connective tissue is characterized as having cells, fibers and ground substance. List the characteristics of blood in the chart below that explain why blood is classified as a connective tissue.
Fibers Ground Substance
A&P 2
nd
Semester Course Review 4
Match the component of blood to their descriptions below (answers can be used more than once.
3.
___Contains proteins that help with osmotic balance
4.
___The only formed element that is an actual cell
5.
___Essential for blood clotting
6.
___Biconcave disc
7.
___Fragments of megakaryocytes
8.
___55% of blood is composed of this
9.
___Causes blood to change to a scarlet red color when it bonds with oxygen
10.
___Contains hemoglobin
11.
___Uses chemotaxis and amoeboid motion in tissues
12.
___Solvent for carrying other substances
13.
___Performs diapedesis
14.
___Produced in red bone marrow (more than one answer)
15.
___An elevated number of these indicates infection
16.
___Specialized for oxygen transport
17.
Fill in the chart of hematopoiesis
Definition Where does it take place?
18.
Explain the events that occur in each of the steps of hemostasis below
Steps of hemostasis
Vascular spasms
Explanation of events
Platelet Plug Formation
A. Erythrocyte
B. Leukocyte
C. Plasma
D. Thrombocyte
What influences differentiation?
Coagulation
19.
Fill in the chart below on blood types
Blood group RBC antigens present Plasma antibodies present
AB
A
B
O
Blood that can be received Blood that can be donated to
20.
What does the positive or negative sign mean when we are discussing blood types? ________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________
21.
How does an improperly matched blood group contribute to transfusion reactions?_________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________
A&P 2
nd
Semester Course Review 5
Unit 12: Cardiovascular System
1.
(Arteries/Capillaries/Veins) carry blood away from the heart.
2.
(Arteries/Capillaries/Veins) carry blood towards the heart.
3.
(Arteries/Capillaries/Veins) site where nutrient/gas/waste exchange occurs between tissue cells and blood.
4.
Use the word bank to label the diagram bellows:
A. Right ventricle
E. Superior vena cava
B. Left Ventricle
F. Inferior vena cava
I. Right/left pulmonary arteries J. Chordae tendinae
M. aortic semilunar valve
P. Myocardium
C. Right atrium D. Left atrium
G. Right pulmonary veins H. Left pulmonary veins
K. AV tricuspid valve
N. pulmonary semilunar valve
L. AV bicuspid valve
O. aorta
5.
Using the word bank in Question 2 indicate the letters of the structures of the heart that would be part of the following circuits: a.
Systemic Circulation: _________________________________________________________________________ b.
Pulmonary Circulation:________________________________________________________________________
6.
Fill in the blanks below for the flow of one drop of blood through the heart
Superior/Inferior vena cava _______________ AV Tricuspid Valve _________________ ________________
______________ Lungs ______________ Left atrium ________________ __________________ Aortic
Semilunar Valve __________________
7.
The AV valves prevent backflow into the (atria/ventricles) when the (atria/ventricles) are contracting. The semilunar valves prevent backflow into the (atria/ventricles) when the (atria/ventricles) are contracting.
A&P 2
nd
Semester Course Review 6
Matching: The following are descriptions of terms related to blood pressure (answers may be used more than once)
8.
___ Pressure exerted by the blood against the blood vessel walls
9.
___ and ___ Factors that are directly related to blood pressure
10.
___Event primarily responsible for peripheral resistance
11.
___Amount of friction blood encounters as it flows through blood vessels
12.
___Blood pressure during heart contraction
13.
___Blood pressure during heart relaxation
14.
___Site where blood pressure determinations are normally made
15.
___The amount of blood pumped out of left ventricle
16.
Fill in the chart relating the pressure of arteries, veins and capillaries to their structure
Pressure
Arteries Veins
A. Blood pressure
B. Cardiac output
C. Constriction of blood vessels
D. Diastolic blood pressure
E. Over arteries
F. Peripheral resistance
G. Systolic blood pressure
Capillaries
Structural adaptations to pressure
Indicate what effect the following factors have on blood pressure. Indicate an increase in pressure by using and indicate a decrease in pressure by using
17.
___ Increased diameter of blood vessels
18.
___ Increased blood viscosity
19.
___ Increased cardiac output
20.
___ Anxiety, fear
21.
___ Physical exercise
27.
Fill in the chart below on the cardiac cycle.
Cardiac Cycle Event
Mid-to-late diastole (ventricular filling)
Explanation
22.
23.
___ Hemorrhage
___ Nicotine
24.
___ Arteriosclerosis
25.
___Increase urine output
26.
___Physical training
Ventricular systole (atria in diastole)
Early diastole
28.
When listening to the heart with a stethoscope, it is the (closing/opening) of the (AV/semilunar valves) that creates the lub sound. It is the (closing/opening) of the (AV/semilunar) valves that creates the dup sound.
29.
ECG Diagram: For each section of the wave indicate what is occurring in the heart (HONORS).
P-
QRS-
T-
30.
ECG Matching (HONORS): Match the picture with the descriptions below.
A&P 2
nd
Semester Course Review 7
A.
B.
C.
D.
____Bradycardia ____Myocardial infarction ____Normal ____Tachycardia
31.
Complete the following chart, comparing the structure of capillaries, arteries, and veins (HONORS).
Thickness of walls (thick, thin, or in-between)
Capillaries Arteries Veins
Layers in walls
(names)
Valves (yes or no)
Disease
32.
Compare and contrast hypertension and atherosclerosis
Hypertension
Cause Effect
Atherosclerosis
33.
What is the function of each of the following fetal vascular modifications? a.
Umbilical cord-_________________________________________________________________________________ b.
Ductus venosus-________________________________________________________________________________ c.
Foramen ovale-_________________________________________________________________________________
A&P 2
nd
Semester Course Review 8
d.
Ductus arteriosus-_______________________________________________________________________________
34.
Major Arteries and Veins: Use the word bank below to label the arteries and veins diagrams (HONORS).
A.
E.
Carotid arteries
Femoral arteries
I.
Jugular veins
B. Subclavian arteries
F. Renal arteries
J. Superior vena cava
C. Arch of aorta
G. Femoral veins
K. Inferior vena cava
D. Descending aorta
H. Renal veins
35.
The hepatic portal system is a series of (arteries/veins) that carry nutrient (poor/rich) blood from the intestines, spleen and pancreas to the (liver/rectum) (HONORS).
36.
How does the myocardium receive oxygenated blood (HONORS)? _______________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________
A&P 2
nd
Semester Course Review 9
Unit 13: Lymphatic System and Body Defenses
1.
Label the diagram to the right showing the relationship of lymphatic vessels to blood vessels using the following words: lymph capillary, lymph duct, lymph node, lymph vessel.
2.
Looking at the diagram to the right, list the steps that tissue
fluid takes once it is picked up by the lymphatic system until it enters back into the bloodstream.
a.
Fluid leaks out of capillaries into surrounding tissue
Lymphoid
Organ
Tonsils
Thymus
Spleen b.
______________________________________
c.
_________________________________________ d.
e.
Lymph node____________________________
______________________________________
f.
Lymph enters back into bloodstream
3.
Fill in the chart on lymphoid organs
Location Function
4.
What is the function of the immune system?_____________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
5.
The innate defense system also known as (nonspecific/specific) defense, responds immediately to protect the body form
(all/specific) foreign substances. The adaptive system, also known as (nonspecific/specific) defense mounts the attack against (all/specific) foreign substances.
For the following indicate whether the item is part of the innate or adaptive immune system.
6.
______________Skin 10.
______________Antibodies
7.
______________Lymphocyte
8.
______________Fever
11.
12.
______________Saliva
______________Mucous
13.
______________B cell 9.
______________Inflammation
Match the type of nonspecific response with the descriptions below.
14.
____Considered the first line of defense
15.
____ Can contain sticky mucus to trap microorganisms
16.
____ Engulfs foreign particles through phagocytosis
17.
____ Triggered whenever the body tissue is injured
18.
____ Abnormally high temperature
19.
____ Consists of keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
A. Fever
B. Inflammatory Response
C. Phagocytes
D. Skin and mucous membranes
A&P 2
nd
Semester Course Review 10
20.
____ Increases the metabolic rate of tissue cells so repair is sped up.
21.
____ Prevents the spread of damaging agents to nearby tissues
22.
____Creates four cardinal signs: redness, heat, swelling and pain
23.
What are the three important aspects of adaptive defense? a.
_______________________________________________________________________________ b.
_______________________________________________________________________________ c.
_______________________________________________________________________________
24.
Fill in the chart regarding the two branches of adaptive defense.
Cellular immunity
Lymphocyte How does it attack antigen?
Humoral immunity
Types of antigens it attacks
25.
When B cells encounter antigens and produce antibodies against them, you are exhibiting (active/passive) humoral immunity.
26.
When antibodies are obtained from the serum of an immune human or animal donor, you are receiving (active/passive) humoral immunity.
27.
Active humoral immunity is (artificially/naturally) acquired when we receive vaccines.
28.
Active humoral immunity is (artificially/naturally) acquired during bacterial and viral infections.
29.
Passive humoral immunity occurs (artificially/naturally) when a fetus receives the mother’s antibodies across the placenta or through breast feeding.
30.
Passive humoral immunity occurs (artificially/naturally) when one receives an immune serum such as antivenom or a tetanus shot.
31.
Vaccines treat (bacterial/viral) infections, while antibiotics treat (bacterial/viral) infections.
32.
Explain how each of the following treatments work to prevent disease. a.
Vaccines-______________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________ b.
Antibiotics-____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
A&P 2
nd
Semester Course Review 11
Unit 14: Respiratory System
1.
Label the diagram below of the respiratory system with the following terms:
A.
Diaphragm B. Epiglottis C. Larynx D. Lt main bronchus
F.
K.
Nares
Rt main bronchus
G. Nasal cavity
L. Trachea
H. Oral cavity
M. Uvula
I. Pharynx
E. Lungs (use twice)
J. Pleural membrane
2.
Fill in the blanks for the pathway air takes through the respiratory tract.
Nares
______________ __________________ Larynx ______________ ____________ Bronchioles Alveoli
Match the statements below with the parts of the respiratory system.
3.
____ Prevents food from going into the nasal cavity
4.
____ Food passageway posterior to the trachea
5.
____ Closes off larynx during swallowing
6.
____ C-shaped ring passageway for air only
7.
____ Actual site of gas exchanges
8.
____ Conducting passageway takes air to alveoli
9.
____ First site where air is warmed, moistened and filtered
10.
____ Contains vocal folds, plays role in speech
11.
____Common passageway for food and air
A. Alveoli
B. Bronchioles
C. Epiglottis
D. Esophagus
E. Larynx
F. Nasal cavity
G. Pharynx
H. Trachea
I. Uvula
12.
Fill in the chart below regarding the histology of the respiratory system (HONORS)
Tissue/Organ Structure/Histology Function
A&P 2
nd
Semester Course Review 12
Location in respiratory tract
Nasal cavity
Tracheal/Bronchi cartilage
Bronchioles
Alveoli
13.
The process of air moving into and out of the lungs is called pulmonary (expiration/ventilation). Air flowing into the lungs is called (expiration/inspiration). Air leaving the lungs is called (expiration/inspiration). This mechanical process depends on
(surface area/volume) changes occurring in the thoracic cavity which results in changes in pressure. Air will always move from a (high/low) pressure to a (high/low) pressure gradient.
14.
Pulmonary Ventilation Chart
Activity of diaphragm
Internal volume of thorax (increase or decrease)
Internal pressure of thorax (increase or decrease)
Size of lungs
(increase or decrease)
Direction of air flow (into body or out of body)
Inspiration or expiration?
Contracted, moves downward
Relaxed, moves superiorly
15.
Gas exchange between the pulmonary blood and alveoli is called (external/internal) respiration. Gas exchange between blood and cells is called (external/internal) respiration. Gases move according to the laws of (diffusion/osmosis) which states that gases will passively move from a (high/low) concentration to a (high/low) concentration. Once oxygen moves into the bloodstream it is transported by (bicarbonate ions/hemoglobin) inside red blood cells to body cells. Carbon dioxide is transported as (bicarbonate ions/hemoglobin) in plasma.
16.
Explain how each of the following structures control respiration.
a.
Medulla-______________________________________________________________________________________ b.
Pons-_________________________________________________________________________________________ c.
Phrenic nerve-__________________________________________________________________________________ d.
Intercostal nerve-_______________________________________________________________________________
17.
What is the relationship between blood pH and carbon dioxide levels? ___________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________
18.
How does the pH of blood influence the rate of breathing? _____________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________
A&P 2
nd
Semester Course Review 13
Unit 15: Digestive System
1.
Label the diagram of the digestive system using the following words: Anus, Duodenum, Esophagus, Gallbladder, Ileum,
Jejunum, Large intestine, Liver, Oral cavity, Pancreas, Pharynx, Salivary Glands, Stomach, Tongue
2.
Once the diagram is labeled use colored pencils and organs that are involved in mechanical digestion color green, organs involved in chemical digestion color blue, organs involved in absorption color red. If an organ does more than one function color the word half and half.
A&P 2
nd
Semester Course Review 14
3.
Fill in the blanks below on the pathway foods takes through the digestive tract.
Oral cavity __________ ___________ ____________ Duodenum ____________ ____________ ___________ Anus
Match the digestive structure on the right with the statements on the left.
4.
___ Propels foodstuff through the digestive tract
5.
___Involves the enzymatic breakdown of food particles
6.
___Includes chewing and the muscular contractions of the stomach.
7.
___Transport of nutrients from the lumen into bloodstream.
8.
___ Mechanical digestion in the small intestines.
9.
___Structure where the majority of chemical digestion takes place.
10.
___Structure where the absorption of water takes place.
11.
Chemical Digestion Chart
Enzyme Where enzyme is produced Where enzyme is secreted
A. Absorption
B. Chemical digestion
C. Large intestine
D. Mechanical digestion
E. Peristalsis
F. Segmentation
G. Small intestine
Chemicals needed to activate the enzyme?
Macromolecule it breaks down
Lipase
Nuclease
Pancreatic amylase
Pepsin
Salivary amylase
Trypsin
12.
The (gallbladder/liver) produces bile, while the (gallbladder/liver) stores and secretes bile into the (duodenum/jejunum) along with (pancreatic/stomach) juice.
13.
Digestive system activity is controlled by reflexes via the (parasympathetic/sympathetic) division of the (autonomic/motor) nervous system which is all part of the (central/peripheral) nervous system.
14.
Hormonal regulation of Digestive System Chart
Hormone Source of secretion
Gastrin
Secretin
Cholecystokinin
Action on digestive system
Matching: Match the layer of the alimentary canal on the right with descriptions on the left (HONORS).
15.
___ The secretory and absorptive layer
16.
___Layer composed of at least two muscle layers
17.
___Connective tissue layer, containing blood, lymph vessels, and nerves
18.
___Outermost layer of the wall
A. Mucosa
C. Serosa
B. Muscularis externa
D. Submucosa
19.
Why does the small intestine have villi (HONORS)?____________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________
20.
Histology of Accessory Organs Chart (HONORS)
Accessory Organ Structure Function
Tongue
Salivary Glands
Salivary Glands
Pancrea
Pancreas
Skeletal muscle
Serous cells
Mucous cells
Exocrine gland
Endocrine gland
Unit 16: Urinary System
1.
Use the word bank to label the following structures on the urinary system.
A.
Kidney B. Renal artery C. Renal vein D. Urethra E. Ureters
A&P 2
nd
Semester Course Review 15
F. Urinary bladder
Use the letters of the structures in question 1 to match with the descriptions below on the structures of the urinary system.
2.
___ Filter blood of wastes and excess ions in the form of urine and regulates water balance.
3.
___ Smooth, collapsible muscular sac that stores urine.
4.
___Takes filtered blood drained from the kidneys.
5.
___Thin walled tube that carries urine by peristalsis from the bladder to the outside of body.
6.
___Carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
7.
___Carries oxygen rich blood to the kidneys.
8.
What is the name of the structure within the kidney that is responsible for urine formation?__________________________
9.
Briefly explain the three processes that a nephron in the kidney performs in urine formation. a.
Glomerular filtration-____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________ b.
Tubular reabsorption-____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________ c.
Tubular secretion-_______________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
10.
What is the role of smooth muscle in moving urine through the urinary system (Honors Extension)?____________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________
A&P 2
nd
Semester Course Review 16
Unit 17: Reproductive System
1.
Use the word bank to label the diagram of the male reproductive system below:
A.
Testes B. Scrotum C. Epididymis D. Ductus (vas) deferens
E.
Seminal vesicles F. Prostate G.Bulbourethral glands H. Urethra I. Penis
MATCHING: Use the letters in the diagram above and match to their function below (answers may be used more than once).
2.
___Organ that delivers semen to the female reproductive tract.
3.
___Site of testosterone production.
4.
___ Passageway from the epididymis to the ejaculatory duct.
5.
___Conveys both sperm and urine down the length of the penis.
6.
___Organs that contribute to the formation of semen (more than one answer).
7.
___External skin sac that houses the testes.
8.
___Tubular storage site for sperm.
9.
___Produces a milky fluid that activates sperm.
10.
___Produces substances that nourish and activate the sperm passing through the tract.
11.
___Produces lubricating mucus that cleanses the urethra.
12.
Summarize each of the functions of the male reproductive system below. a.
Spermatogenesis-_______________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
1.
Testosterone production-_________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
A&P 2
nd
Semester Course Review 17
13.
Use the word bank to label the two diagrams of the female reproductive system below.
A.
Ovaries B. Uterine (fallopian) tubes C. Uterus D. Cervix E. Vagina.
MATCHING: Use the letters in the diagram above and match to their function below (answers may be used more than once).
14.
___Chamber that houses the developing fetus.
15.
___Canal that receives the penis during sexual intercourse.
16.
___Usual site of fertilization.
17.
___Duct through which the ovum travels to reach the uterus.
18.
___Primary female reproductive organ that produces sex hormones.
19.
___Acts as a sphincter for the uterus and provides lubrication for the vaginal canal.
20.
What is the function of the endometrium? __________________________________________________________________
21.
(Oogenesis/Spermatogenesis) is the production of oocyte (egg) in the ovary and is activated at puberty by FSH and LH to mature.
22.
(Luteinizing hormone/Progesterone)
causes ovulation of oocyte into uterine tube.
23.
(Estrogen/
Progesterone) allows for the development of the endometrium when fertilization of the egg takes place.
24.
(Follicle Stimulating Hormone/Luteinizing hormone)
stimulates an oocyte to develop in the ovary.
25.
(
Estrogen/Progesterone) creates female secondary sex characteristics and encourages development of the oocyte.
MATCHING: Match the terms on the right with the statements on the left regarding pregnancy (HONORS).
26.
___The fertilized egg.
27.
___Forms the placenta when the blastocyst implants
28.
___The embryo after 8 weeks
29.
___The organ that delivers nutrients to and disposes of wastes for the fetus
30.
___Occurs when a sperm’s chromosomes combine to form with those of an egg
31.
___A period of fairly rapid mitotic divisions of the zygote
32.
33.
___A fluid filled hollow sphere composed of a cluster of cells that can now implant
___Hormone that stimulates the development of the placenta
34.
___Developmental stage extending from fertilization to end of 8 th week
A. Blastocyst
B. Cleavage
C. Endometrium
D. Embryo
E. Fetus
F. Fertilization
G. hCG
H. Placenta
I. Zygote
35.
The process of cellular migrations that ultimately transform a blastocyst into a three-layered embryo is called
___________________________ (HONORS)
36.
The formation of body organs and systems is called ________________________________________ (HONORS).
37.
For the three layers of the embryo listed below explain what systems they differentiate into (HONORS).
a.
Ectoderm-_____________________________________________________________________________________ b.
Endoderm-____________________________________________________________________________________ c.
Mesoderm-____________________________________________________________________________________
A&P 2
nd
Semester Course Review 18
MATCHING: Match the period on the right with the correct major fetal development on the left (HONORS)
38.
___Eyes open
39.
___Distinct bone structure
40.
___Heartbeat, embryo become s fetus
41.
___Development of pink skin tone
42.
___Sex determined
43.
___Fetal position
A. 8 weeks
B. 3 months
C. 4 months
D. 5 months
E. 6-7 months
F. 8-9 months