Hon. William Dressel (Ret.)
Greg Brown
President
The National Judicial College
Chief Probation Officer
Colorado’s 20th Judicial District
The Appropriate
Evidence Based Sentence
is Determined by:
Applicable Law
Information Available
Community Safety
Victim Responsiveness
Etiology of Adult
Sex Offenders
Etiological Theories
• Single Factor
–
–
–
–
Biological
Behavioral
Socio-cultural
Attachment/intimacy
Biology
• Hormones
– High testosterone levels may lead to
increased sex drive
• Predisposition
– Sexual appetites or preferences
Behavior
• Conditioning - sexual interests are
strengthened through experiences or
reinforcers
– Ex: masturbation to deviant fantasies
• Learning - model aggressive and
hostile attitudes/behavior
– Ex: domestic violence
Socio Cultural
• What role does society and cultural
structures, norms, and messages have?
• Desensitizing messages
– Television, music, video games
– Advertisements, television, and film
• Men socialized to be aggressive or
dominant
Attachment / Intimacy
• Insecurely attached persons want
emotional closeness but avoid it out of
fear of rejection
– “Romantic” relationship with a child is safer
• Dismissive attachment styles have no
desire to be intimate with others
– Negative, angry, hostile feelings
What is the Cause of Offending?
• Critical message - one size does NOT fit all
• Sexual abuse is an extraordinarily
complex multifaceted problem
• No clear explanation
• Management of offenders MUST consider
their vulnerability
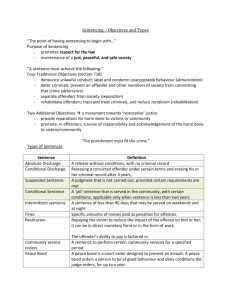
Sentencing Factors
Sentencing Factors
• The Law
– State prison mandatory?
– Mandatory conditions of probation?
• The Crime
– Extreme violence?
– Weapons?
– Multiple victims?
– Impact on victim
Sentencing Factors
(cont.)
• Defendant’s History
– Prior record
• Prior sex crimes?
• Prior crimes of violence, weapons?
– Family history and structure
– Employment history
– Physical health
Sentencing Factors
(cont.)
• Defendant’s Treatment Needs
– Psychological history, adjustment, and
current status
– Intellectual and cognitive functioning
– Substance abuse history
– Sexual attitudes
– Response to prior treatment
Sentencing Factors
(cont.)
• Defendant’s Risk of Re-offending
– Actuarial assessment
• Static-99
• RRASOR
– Clinical
– Psych/sexual evaluation
– Motivation to change
– Community support
Sentencing Factors
(cont.)
– Correctional and treatment resources
• Within institution
• Community-based
• Ability to pay
• Degree of supervision
Pre-sentence
Investigation Reports
What items or information need to be in a
pre-sentence report or investigation?
All of the foregoing factors
Other
Psychosexual Evaluations
5 Components for
Psychosexual Evaluations
• Risk Assessment
• Offense-specific validated instruments
• Psychological Testing
• General
• Offense specific
• Physiological Testing
• Plethysmograph
• Visual reaction time measure
(Abel Assessment of Sexual Interest or Affinity)
• Polygraph
5 Components for
Psychosexual Evaluations
• Collateral information
• Police reports
• Criminal history info
• Victim statements
• Clinical interview
(Cont’d.)
Decision Making
Risk level
Low
High
Risk for what behavior?
Less serious
Most serious
When/How info discovered?
Client offered
New charges
Criteria for
Incarceration
Criteria for Incarceration
• Denial of offense
• Sadistic practices
• High degree of psychopathy measured by
PCL-R
• Use of weapon
• Forcible rape
• Previous failure of offense-specific treatment
• Offenders identified as high risk on validated
sex offender risk assessment instruments
Criteria for
Incarceration or Commitment
• High on the HARE or diagnosed as a psychopath
• Fixated pedophile
Deviant arousal to children
History of molesting
No appropriate arousal
NOT Criteria for
Incarceration or Commitment
• Admits offense
• Extra familial offender
• Admits some previous offenses
• Admits other paraphilias
• Admits fantasy & planning
Victims’ Rights
Victims’ Rights
• Most states have a “Victims’ Rights” statute.
• Defining a “victim” may be problematic. (All
victims are not created equally.)
• If the victim is a minor or is deceased, a
member of a victim’s family or another
person may exercise the rights of the victim.
• Many states permit the victim to be present
during trial and sentencing even though they
may be a witness against the defendant.
Victims’ Rights
(cont.)
• Typically, the victim has the right to prepare
and submit a victim impact statement.
• Also, a victim has the right to make a
statement prior to sentencing and state laws
often require that “the court shall consider” a
victim’s statement.
Victims’ Rights
(cont.)
• Statement to the court or defendant?
– Security concerns
– Oral: Reading? Video?
• Allow questions by defendant?
• Defendant’s right to speak?
Probation Elements
Probation
What Conditions of Probation or Supervision
for Sex Offenders are available?
Treatment
• Participate in & complete treatment program
• Sign release of information
• Submit to all testing
Contact with Others
• No contact with minor males/females
• No contact without direct supervision
• Stay away from places where children
congregate
• No association with sex offenders
• Stay 100 yards from victim and victim’s:
residence, school, & workplace
• No contact with family of victim
Supervision
• Register as sex offender
• Carry registration certificate at all times/
present to law enforcement
• Search and seizure
• Polygraph examination
Residence
• Not within 1 mile of school, park, or
recreation facility
• Not with another sex registrant
• Inform any person living with of status as
sex offender
• No minors in residence
Employment
• No employment that requires entry into
residence
• No employment that regularly has contact
with minors
• Approval of all employment by probation
officer
Travel/Activities
• Not to enter, travel past, or loiter near:
adult bookstores
topless bars
massage parlors
sex shops
• Maintain detailed travel log
• Wear GPS system
• Probation officer approves all recreation
and leisure activities
• Probation officer approves means of travel
and route to work or treatment
Access to Sexual Material
• No possession of children’s/women’s
clothing (for male offenders)
• No possession of pornographic material,
whether involving adults or minors
• No possession of computer/internet access
• No use of 800 or 900 numbers
Substance Abuse
• May not possess or consume alcohol; may
not frequent places where alcohol is
primary item of sale
• May not possess or use narcotics or
controlled substances without medical
prescription
• Drug and alcohol testing
Miscellaneous
• No possession of cameras or video
equipment
• Non-confidential AIDS testing
• No possession of identity concealing items
Available Sanctions
•
•
•
•
•
Treatment
Victim Contact
Driving and Travel
Daily Living
Social/Sexual
Behavior
• Internet
Restrictions
•
•
•
•
Work Restrictions
Alcohol and drugs
Disclosure
Polygraph,
Plethysmograph,
other tests
• Other Technology
Restrictions
Limits
What can a judge do to limit the risk to
the community when placing a sex
offender on probation?
Responses to Limit Risk
• Limiting access to victims
• Electronic monitoring or curfews
• No contact orders
• Restrictions on movement
• Increased monitoring, contact, treatment
• Pre-revocation contracts
• Admissions to violations
Revoking Supervision
•
•
•
•
New criminal conduct
Violations of treatment contract
Establishing pattern of offending behavior
Failure to complete or progress in
treatment
• Violation of probation conditions
• If revoked because of treatment failure &
reinstated, client should go to more
intensive treatment program
Actuarial Risk Factors
for Re-Offending
Risk Factors for Re-Offending
• Deviant sexual preference
• Sexual preoccupation/compulsivity
• Sexualized violence
(including sadistic sexual interests)
• Lifestyle instability/self regulation problems
• Poor coping/problem solving skills
(e.g. sex as coping)
Adapted
from Hanson & Morton-Bourgon, 2004, 2005; Knight
&Thornton, 2007; Doren, 2007, 2008; Thornton, Hanson & Mann, 2007
Risk Factors
(Cont’d.)
• History of previous sex offenses
• Non-sexual criminal history
• High degree of psychopathy
• Male target pedophilia
• Hostile, negative emotionality
(grievance thinking)
• Any previous probation/parole violation
Risk Factors
(Cont’d.)
• Emotional congruence with children
• High degree of impulsivity
• Negative social influences
• DSM-IV personality disorder
• Intimacy deficits
• Non-contact paraphilias
• Victim access
Risk Factors
(Cont’d.)
• Pro-offending beliefs
• Substance abuse
• Lack of concern for others
• Stranger victim
• Male victim
• Offender young, single
Elements of NJC’s
Model Curriculum
• Understanding Sexual Offenders & Sexual
Victimization
• Assessment of Sex Offenders
• Treatment & Supervision of Sex Offenders
• Evidence Based Sentencing including
Conditions to Impose
• Sex Offender Registration & Notification Act
Comprehensive Approach
Victim
Centeredness
Public
Education
Monitoring
and Evaluation
Specialized
Knowledge
and Training
Collaboration
Carter,
Bumby, and Talbot
2004 CSOM Comprehensive
Approach Publication