Meiosis

Meiosis
• The ability to pass on traits is called heredity.
– This ability is one of the unifying themes of biology as individual units of heredity (genes) are passed from one generation to the next in reproductive cells called gametes.
– Organisms can reproduce in 2 basic ways; sexually and asexually.
Genetic Variation
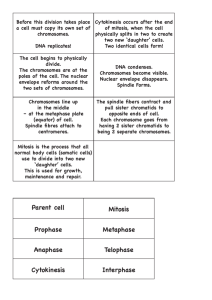
• Meiosis reduces the number of chromosomes and produces haploid
(1n) cells from diploid cells (2n).
– n = # of each chromosome
• Interphase
– DNA is replicated and sister chromatids are joined at the centromere regions
Stages of Meiosis - I
• Prophase I
– chromosomes condense and pair
• Forms a tetrad… complex of 4 sister chromatids
• crossing-over may occur as DNA segments are exchanged between homologous chromosomes
– Increases genetic variability
– the rest is the same as in mitosis
Stages of Meiosis -
I
• Metaphase I
– tetrads are now aligned at the metaphase plate
– rest like mitosis
• Anaphase I
– chromosome pairs (sister chromatids) move toward the poles
– rest like mitosis
• Telophase I (cytokinesis)
– each cell is now haploid but still consists of pairs of sister chromatids
– cytokinesis splits the cell and cells are now haploid at 2n = 46
• Prophase II
– spindle fibers again grow and sister chromatid pairs move toward the metaphase plate
• Metaphase II
– chromosomes are now at the metaphase plate but are not genetically identical due to crossing over
• Anaphase II
– sister chromatid pairs separate at the centromere region and move toward opposite poles
• Telophase II (cytokinesis)
– nuclei begin to form and DNA begins to uncondense
– cytokinesis separates divides the cell
– there are now 4 haploid cells
(n=23)
– each daughter cell is genetically unique
Stages of Meiosis - II
Sexual Reproduction
• Fertilization - union of gametes from 2 different parents
– gametes are produced via meiosis and each have 1/2 the
DNA of the somatic cells from which they were derived
Genetic Variation
• Genetic variation is made possible through the following processes:
– Independent assortment of chromosomes
• because the arrangement at the metaphase plate is random, each haploid has a 50% chance that it will receive a parental chromosome
– Crossing over
• creates recombinant chromosomes that are a mix or both parental chromosomes
– Random fertilization
• because of random fertilization each individual contains a genetically unique compliment of chromosomes and genes