Group Dynamics presentation on transition stage
advertisement

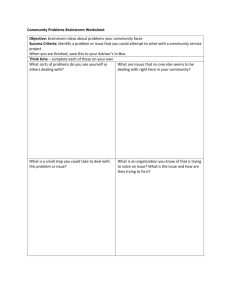
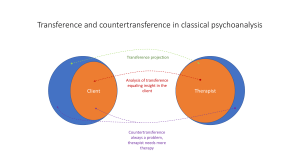
Group Dynamics: “Transition Stage” of Group SOPHIE KILLIP, ANSLEY LOVETT, MATTHEW LACHMAN, AND EMILY NEFF (MEMBERS OF THE “FANTASTIC RANGERS”). Let’s Review the Transition Stage! Characteristics of the Transition Stage: Establishing Trust, Defensiveness/Reluctance, Common Fears, Conflict, Confrontation, and Challenges to the Leader Problem Behaviors/ Difficult Group Members: Silence/ Lack of Participation, Monopolistic Behavior, Storytelling, Questioning, Offering “Pseudosupport”, Hostile Behavior, Acting Superior, Members Becoming Assistant Leaders Scenario: Dealing with Defensive Behavior Therapeutically: Group Member: "I don't want to be here" Responses: "Where would you rather be?" or "What makes it difficult for you to be here?" Group Member: "I'm afraid to talk more about this" Responses: "What do you fear would happen if you say more?" or "What would it take for you to feel safer in here?" Review Continued Dealing with Transference/ Countertransference: -Transference: The feelings that clients project onto the counselor -Countertransference: When counselors project their own unresolved conflicts onto the client -What kind of transference leads to my countertransference? -Many leaders imagine that they will be respected, needed, admired, or seen as an expert...this is not always the case. Our countertransference reactions are inevitable. Unconscious "soft are real. spots" Coleader Issues at the Transition Stage: Negative reactions toward one leader, Challenges to both leaders, Dealing with problem behaviors, Dealing with countertransference. Salient Theme: "Dealing With Avoidance by the Whole Group" Application to other Settings Clinical Treatment teams Psychiatrist VS. Psychologist Counselors VS. Social Workers Community Sports Teams 1. Forming 2. Storming* 3. Norming* 4. Performing Reflection on an Issue: Resistance What is Resistance? “Behavior that keeps us from exploring personal conflicts.” Labeling behavior as resistant could imply a lack of autonomy and become a self-fulfilling prophecy. Many writers have reconceptualized resistance and instead place emphasis on the therapeutic relationship and reflective listening (e.g. Winslade, Crocket, & Monk, 1997). Reflection on an Issue: Resistance The traditional view of resistance mostly blames the client and disregards the counselors responsibility (DeShazer, 1984). Later conceptualizations appear to view resistance in a more positive way. Collaboration between client and counselor is more important than identifying behaviors that can block the connection. Progress is more likely to occur by respecting and understanding defensive behavior. Supporting Resource Importance of cohesion - Therapist (counselor) - Group members - Group as a whole Impact of cohesion - Predictor of outcome - Deeper self-disclosures of group members - More feedback - Navigate through resistance and anxiety Aspects to pay attention to: - Therapeutic style - Screening - Length of group Final Points to Remember! The Transition Stage is characterized by feelings of anxiety and defenses. The members role is to recognize and deal with their defensiveness. e.g. the struggle of playing it safe of the risk of getting involved. e.g. express feelings to avoid a climate of distrust. The leaders task is to encourage and challenge members to resolve conflicts and negative reactions. e.g. provide a model for dealing directly with challenges. Activity Time! Activity: At your table, use a dry erase marker (or paper and pen) to write down the following: 2 pieces of information you learned from this presentation on the “transition stage” of group. 1 strategy you can use to help facilitate a smooth transition in the stage of group processing. Optional: 1 question you have as a table that we can discuss as a class.