Skeletal Muscle
advertisement

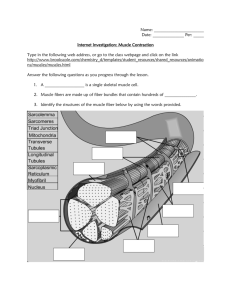
211 ch 9 muscle pt a Chapter 9 Muscles and Muscle Tissue: Part A Muscle Tissue • Three types – Skeletal – Cardiac – Smooth • prefixes for muscle: • Skeletal muscles – Organs attached to bones and skin – Elongated cells called : – Striated: – Voluntary (i.e., conscious control) – Contract rapidly; tire easily; powerful – Require nervous system stimulation • Cardiac muscle – Only in heart; bulk of heart walls – Striated – Can contract without nervous system stimulation – Involuntary – More details in Chapter 18 • Smooth muscle – In walls of hollow organs, e.g., stomach, urinary bladder, and airways – Not : – Involuntary 1 211 ch 9 muscle pt a Special Characteristics of Muscle Tissue • Excitability (responsiveness or irritability): ability to receive and respond to stimuli • Contractility: ability to shorten forcibly when stimulated • Extensibility: ability to be stretched • Elasticity: Muscle Functions • Four important functions – Movement of bones or fluids (e.g., blood) – Maintaining posture and body position – Stabilizing: – Heat generation (especially: ) • Additional functions – Protects organs, forms valves, controls pupil size, causes "goosebumps" Skeletal Muscle • Each muscle served by one artery, one nerve, and one or more veins – Enter/exit near central part and branch through connective tissue sheaths – Every skeletal muscle fiber supplied by nerve ending that controls its activity – Huge nutrient and oxygen need; generates large amount of waste Skeletal Muscle • Connective tissue sheaths of skeletal muscle – Support cells; reinforce whole muscle – External to internal • : dense irregular connective tissue 2 211 ch 9 muscle pt a surrounding entire muscle; may blend with fascia • : fibrous connective tissue surrounding fascicles : : fine areolar connective tissue surrounding each muscle fiber Skeletal Muscle: Attachments • Attach in at least two places – Insertion : – Origin : • Attachments direct or indirect – Direct—epimysium fused to periosteum of bone or perichondrium of cartilage – Indirect—connective tissue wrappings extend beyond muscle as ropelike tendon or sheetlike aponeurosis Microscopic Anatomy of A Skeletal Muscle Fiber • Long, cylindrical cell – 10 to 100 µm in diameter; up to 30 cm long • • • • Multiple peripheral nuclei Sarcolemma = plasma membrane Sarcoplasm = cytoplasm Modified structures: myofibrils, sarcoplasmic reticulum, and T tubules Myofibrils • Densely packed, rodlike (cylindrical) elements • ~80% of cell volume • Contain sarcomeres - contractile units – Sarcomeres contain myofilaments • Exhibit striations - perfectly aligned repeating series of dark A 3 211 ch 9 muscle pt a bands and light I bands Striations • H zone: lighter region in midsection of dark A band where filaments do not overlap • M line: line of protein myomesin bisects H zone • Z disc (line): coin-shaped sheet of proteins on midline of light I band that anchors thin filaments and connects myofibrils to one another • Thick filaments: run entire length of an A band • Thin filaments: run length of I band and partway into A band • Sarcomere: region between two successive Z discs Sarcomere • Smallest contractile unit (functional unit) of muscle fiber • Align along myofibril like boxcars of train • Contains A band with ½ I band at each end • Composed of thick and thin myofilaments made of contractile proteins Myofibril Banding Pattern • Orderly arrangement of actin and myosin myofilaments within sarcomere – Actin myofilaments = thin filaments • Extend across I band and partway in A band • Anchored to Z discs – Myosin myofilaments = thick filaments • Extend length of A band • Connected at M line Ultrastructure of Thick Filament 4 211 ch 9 muscle pt a • Composed of protein myosin • Each composed of 2 heavy and four light polypeptide chains – Myosin tails contain 2 interwoven, heavy polypeptide chains – Myosin heads contain 2 smaller, light polypeptide chains that act as cross bridges during contraction • Binding sites for actin of thin filaments • Binding sites for ATP • ATPase enzymes Ultrastructure of Thin Filament • Twisted double strand of fibrous protein F actin • F actin consists of G (globular) actin subunits • G actin bears active sites for myosin head attachment during contraction • Tropomyosin and troponin - regulatory proteins bound to actin Structure of Myofibril • Elastic filament – Composed of protein titin – Holds thick filaments in place; helps recoil after stretch; resists excessive stretching Sarcoplasmic Reticulum (SR) • Network of smooth endoplasmic reticulum surrounding each myofibril – Most run longitudinally • Pairs of terminal cisternae form perpendicular cross channels • Functions in regulation of intracellular Ca2+ levels – Stores and releases Ca2+ 5 211 ch 9 muscle pt a T Tubules • • • • • Continuations of sarcolemma into muscle fiber Lumen continuous with extracellular space Increase muscle fiber's surface area Penetrate cell's interior at each A band–I band junction Associate with paired terminal cisterns to form triads that encircle each sarcomere Triad Relationships • T tubules conduct impulses deep into muscle fiber; every sarcomere • Integral proteins protrude into intermembrane space from T tubule and SR cistern membranes–act as voltage sensors • SR foot proteins: gated channels that regulate Ca2+ release from SR cisterns Sliding Filament Model of Contraction • Generation of force • Does not necessarily cause shortening of fiber • Shortening occurs when tension generated by cross bridges on thin filaments exceeds forces opposing shortening • In relaxed state, thin and thick filaments overlap only at ends of A band • Sliding filament model of contraction – During contraction, thin filaments slide past thick filaments actin and myosin overlap more – Occurs when myosin heads bind to actin cross bridges • Myosin heads bind to actin; sliding begins • Cross bridges form and break several times, ratcheting thin 6 211 ch 9 muscle pt a filaments toward center of sarcomere – Causes shortening of muscle fiber – Pulls Z discs toward M line • I bands shorten; Z discs closer; H zones disappear; A bands move closer (length stays same) 7