Chapter 7- Notes
advertisement
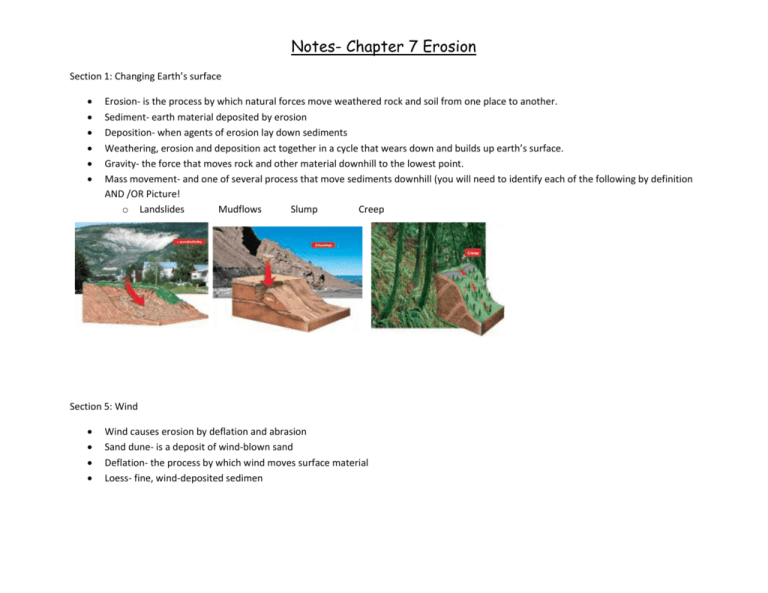
Notes- Chapter 7 Erosion Section 1: Changing Earth’s surface Erosion- is the process by which natural forces move weathered rock and soil from one place to another. Sediment- earth material deposited by erosion Deposition- when agents of erosion lay down sediments Weathering, erosion and deposition act together in a cycle that wears down and builds up earth’s surface. Gravity- the force that moves rock and other material downhill to the lowest point. Mass movement- and one of several process that move sediments downhill (you will need to identify each of the following by definition AND /OR Picture! o Landslides Mudflows Slump Creep Section 5: Wind Wind causes erosion by deflation and abrasion Sand dune- is a deposit of wind-blown sand Deflation- the process by which wind moves surface material Loess- fine, wind-deposited sedimen Notes- Chapter 7 Erosion Section 2: Water Erosion *You will need to be able to identify them by their definition and/or picture. Runoff- water that moves over earth’s surface Rill- tiny groves in soil made by flowing water Gully- a large channel in soil formed by erosion Stream- a channel in which water is continuously flowing downhill Tributary- a stream or smaller river that feeds into a main river Flood plains- a wide valley though which a river flows Meander- a loop-like bend in the course of a river Oxbow Lakes- a meander cut off from the river Alluvial fan- a wide slopping deposit of sediments formed where a stream leaves a mountain range Delta- a landform made of sediment that is deposited where a river flows into an ocean or lake Ground water- water that fills in the spaces and cracks in underground soil and rock layers Stalactite- a cone shaped calcite deposit that forms from the roof of a cave Stalagmite-a cone shaped calcite deposit that forms from the floor of a cave Karst topography- a region in which a layer of limestone close to the surface creates deep valleys, caverns and sinkholes Notes- Chapter 7 Erosion Notes- Chapter 7 Erosion Section 3: Glacier Erosion *you will need to be able to identify them by their definition and/or picture. Glacier- any large mass of ice that moves slowly over land Continental glacier- any glacier that covers much of a continent Ice age- when continental glaciers covered much of the earths surface Valley glacier- is a long, narrow glacier that form when snow and ice builds up high in a mountain valley. How glacier erode and shape land: Plucking and abrasion o Plucking- when a glacier picks up rock one place and puts them down in a different place o Abrasion- the rock that remain at the bottom of a glacier and drag across the ground Glacial Landformo Fiord- form when the level of the sea rises and fills a valley once filled by a glacier o Horn- when glacier carve away the sides of a mountain, the result is a horn, a sharpened peak o Cirque- a bowl shaped hollow eroded by a glacier o Arête- a shaped ridge separated by two cirques o Glacial Lakes- when a glacier leave behind large lakes in long basins o Moraine- where a glacier deposits mounds or ridged of till o U-Shaped Valley- a flowing glacier scoops out a U-shaped Valley o Drumlin- a long mound of till that is smothered in the direction of the glacier flow o Kettle Lake- forms when a depression left in a till by melting ice fills with water Notes- Chapter 7 Erosion Section 4: Waves *You will need to be able to identify them by their definition and/or picture. The energy in wave come from the wind that blows across the water’s surface Waves shape the coast through erosion by breaking down rock and transporting sand and other sediments Headland- is a part of the shore that sticks out into the ocean Landforms- created by wave erosiono Sea-cave- forms as wave action hollows out the cliff o Sea-arch- forms when sea caves on either side of a headland join o Sea-stack- left standing when a sea arch collapses Landforms formed by depositiono Beach- formed as waves pile up sand along the shore o Spit- formed as long shore drift deposits sand along the shore o Sandbar- formed by wave action bringing sediment and sand into one pile away from the shore









