Computer Science Revision Mind Map
advertisement
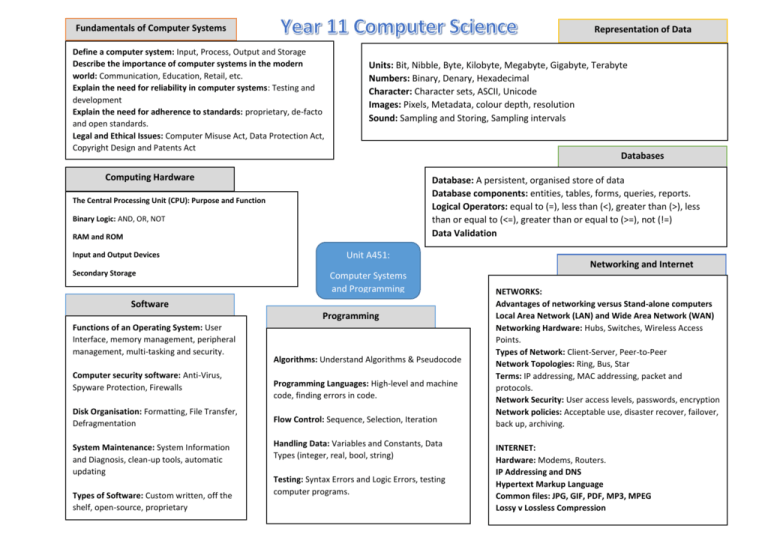
Fundamentals of Computer Systems Representation of Data Define a computer system: Input, Process, Output and Storage Describe the importance of computer systems in the modern world: Communication, Education, Retail, etc. Explain the need for reliability in computer systems: Testing and development Explain the need for adherence to standards: proprietary, de-facto and open standards. Legal and Ethical Issues: Computer Misuse Act, Data Protection Act, Copyright Design and Patents Act Units: Bit, Nibble, Byte, Kilobyte, Megabyte, Gigabyte, Terabyte Numbers: Binary, Denary, Hexadecimal Character: Character sets, ASCII, Unicode Images: Pixels, Metadata, colour depth, resolution Sound: Sampling and Storing, Sampling intervals Databases Computing Hardware Database: A persistent, organised store of data Database components: entities, tables, forms, queries, reports. Logical Operators: equal to (=), less than (<), greater than (>), less than or equal to (<=), greater than or equal to (>=), not (!=) Data Validation The Central Processing Unit (CPU): Purpose and Function Binary Logic: AND, OR, NOT RAM and ROM Input and Output Devices Secondary Storage Unit A451: Computer Systems and Programming Software Programming Functions of an Operating System: User Interface, memory management, peripheral management, multi-tasking and security. Computer security software: Anti-Virus, Spyware Protection, Firewalls Disk Organisation: Formatting, File Transfer, Defragmentation System Maintenance: System Information and Diagnosis, clean-up tools, automatic updating Types of Software: Custom written, off the shelf, open-source, proprietary Algorithms: Understand Algorithms & Pseudocode Programming Languages: High-level and machine code, finding errors in code. Flow Control: Sequence, Selection, Iteration Handling Data: Variables and Constants, Data Types (integer, real, bool, string) Testing: Syntax Errors and Logic Errors, testing computer programs. Networking and Internet NETWORKS: Advantages of networking versus Stand-alone computers Local Area Network (LAN) and Wide Area Network (WAN) Networking Hardware: Hubs, Switches, Wireless Access Points. Types of Network: Client-Server, Peer-to-Peer Network Topologies: Ring, Bus, Star Terms: IP addressing, MAC addressing, packet and protocols. Network Security: User access levels, passwords, encryption Network policies: Acceptable use, disaster recover, failover, back up, archiving. INTERNET: Hardware: Modems, Routers. IP Addressing and DNS Hypertext Markup Language Common files: JPG, GIF, PDF, MP3, MPEG Lossy v Lossless Compression