Indiana Weather, Currents, and Climate
advertisement

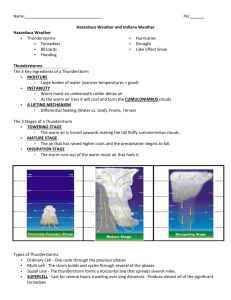
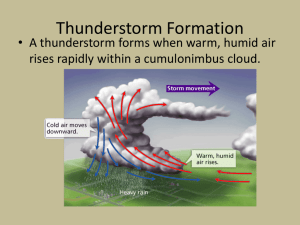
Blizzard of 1978 Greenwood Floodinging – June 08 Special Weather Events There are many types of hazardous weather • Tornadoes • Blizzards • Thunderstorms • Flooding • Hurricanes • Drought Thunderstorms • The 3 Key Ingredients of a Thunderstorm ▫ MOISTURE Large bodies of water (warmer temperatures = good) ▫ INSTABILITY Warm moist air underneath colder dense air As the warm air rises it will cool and form the CUMULONIMBUS clouds ▫ A LIFTING MECHANISM Differential heating (Water vs. land), Fronts, Terrain Thunderstorms • The 3 Stages of a Thunderstorm ▫ TOWERING STAGE The warm air is forced upwards making the tall fluffy cumulonimbus clouds. ▫ MATURE STAGE The air that has raised higher cools and the precipitation begins to fall. ▫ DISSIPATION STAGE The storm runs out of the warm moist air that fuels it. Towering Phase Mature Phase • “Anvil” Shaped Top Mature Phase • “Anvil” Shaped Top Dissipation Stage Types of Thunderstorms • Ordinary Cell ▫ One cycle through the previous phases • Multi-cell ▫ The storm builds and cycles through several of the phases • Squall Line ▫ The thunderstorm forms a horizontal line that spreads several miles. • Supercell ▫ Last for several hours traveling over long distances. Produce almost all of the significant tornadoes Supercell Thunderstorm Thunderstorm Hazards • Hail • Damaging Winds ▫ Indiana State Fair • Tornadoes • Flash-Floods (Greatest cause of death in Thunderstorms) Tornado • A violently rotating column of air descending from a thunderstorm and touching the ground. Formation • Most tornadoes are spawned from supercell thunderstorms. Supercell thunderstorms are characterized by a persistent rotating updraft and form in environments of strong vertical wind shear. • The exact processes for the formation of a funnel are not known yet. Enhance Fujita Scale EF scale Class EF0 EF1 EF2 EF3 EF4 EF5 weak weak strong strong violent violent Wind speed mph km/h 65-85 105-137 86-110 138-177 111-135 178-217 136-165 218-266 166-200 267-322 > 200 > 322 Description Gale Moderate Significant Severe Devastating Incredible What’s more dangerous than a tornado? • The Fire Whirl Flooding • Basics – Too much water in, not enough water out. • Water “Out” sources – rivers, lakes, INFILTRATION, CSO’s. • Dangers People underestimate how powerful moving water can be. Even at low levels moving water is strong. Dangers of moving Water • Of the three deaths which occurred as a result of the Fort Worth tornado, March 28, 2000, one death was due to flooding. The man who drowned was a passenger in a car with his girlfriend, the driver. They approached a low spot with water flowing over the road due to very heavy rain. Flooding was a common occurrence at this location with heavy rains and the danger was well marked. • As the driver drove her car into the water she became frightened as the water rose higher and higher around her vehicle. She backed out to higher ground. The passenger said the water was NOT too deep and he would prove it by walking across to the other side. He never made it. Lake Effect Snow • is produced during cooler atmospheric conditions when COLD winds move across long expanses of WARMER LAKE WATER, providing energy and picking up water vapor which freezes and is deposited on the opposite shores. Lake Effect Snow