ppt
advertisement

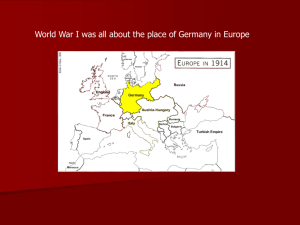
The Great War, 1914-1918 Otto Dix, “Flanders” (painted: 1934-36) Why is the Great War seminal? • Eventually involved most of the world • 65 million troops fought • Germany and France mobilized 80 percent of males (aged 15-49) • 18.4 million perished (soldiers and civilians) • 23 million wounded • Destroyed four empires (Hohenzollern/German, Habsburg, Ottoman, Russian/Romanov) • Sparked communist revolution in Russia (and elsewhere) • Helped Hitler rise to power • Began de-colonization • Improved many women’s situation Causes of the Great War 1. Alliance system: Triple Alliance: Germany Austria-Hungary Italy Triple Entente: Britain France Russia Alliance system (cont.) • KEY: 1871: German unification upset balance • 1879-1918: Austro-German Alliance • 1881-1887: Alliance of Three Emperors • Germany • Austria-Hungary • Russia • Triple Alliance, 1882-1915 • Germany • Austria-Hungary • Italy • 1887-1890: Russian-German Reinsurance Treaty William (Wilhelm) II (b. 1859; r. 1888-1918) • Grandson of William I • Wanted to be a “Warrior King” • Lame • 1890: Forced resignation of (irreplaceable) Bismarck • Lost Russia 1890 France courts Russia • 1891: Republican France and Autocratic Russia sign alliance (to 1917) • “Marseillaise”, the hymn of the revolution British Empire • “Splendid Isolation” • 1900: Germany starts building large navy • Boer War, 1899-1902 • 1904: Anglo-French Entente (Entente Cordiale): Britain got Egypt France got Morocco • 1907: Anglo-Russian Agreement 2. Imperialism • 1905-6: First Moroccan Crisis • 1911: Second Moroccan Crisis • German Panther at Agadir on July 1, 1911 • British called Germany’s bluff • Resolved peacefully 3. Nationalism • • • • Serbian Austrian Russian France vs. Germany • 1871 and AlsaceLorraine • Germany vs. Britain • Naval Race 4. Short memory • No major wars since 1815 • War as adventure • Schoolbooks • Intellectuals: Europe was decadent, needed a war for renewal. 5. Military Plans • Germany’s Schlieffen Plan • Russia to mobilize against Germany and Austria-Hungary • Planning made it more inevitable Immediate catalysts 1908: Austria-Hungary formally annexed Bosnia and Herzegovina 1912: First Balkan War, the Balkan League (Serbia, Greece, Montenegro and Bulgaria) took Macedonia from Ottoman Empire 1913: Second Balkan war, Bulgaria attacked Serbia, leading A-H to intervene Immediate catalysts (cont.) 28 June 1914: Archduke Franz Ferdinand is assassinated Black Hand Gavrilo Princip Gavrilo Princip, 1894-1918 Immediate catalysts (cont.) A-H decides to teach Serbia a lesson Franz Joseph asks Germany for support William II sends “Blank Check” (Austria could “rely on Germany’s full support.”) 23 July 1914: A-H presents ultimatum to Serbia Immediate catalysts (cont.) • 28 July 1914: A-H declares war on Serbia – Tsar Nicholas II orders partial mobilization against A-H • 29 July 1914: Russia orders full mobilization against A-H and Germany • 2 August 1914: German General von Moltke demands that Belgium permit German armies to march through it • 4 August 1914: Britain and France declared war on Germany • 11 November 1914: Ottoman Empire declared war on Britain, France, and Russia.