SYSTEMS AND FUNCTIONS
advertisement

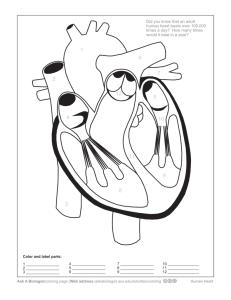
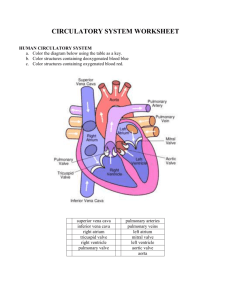
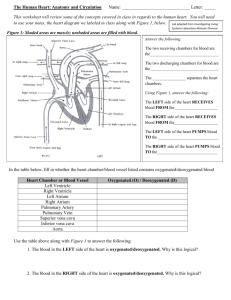
Seng Lily Moua Hour 1 Anatomy and Physiology SYSTEMS AND FUNCTIONS Digestive System: (20) Liver- cleanses the blood and processes nutritional molecules, which distributed to the tissue. (34) Stomach- storage compartment enables 2 or 3 meals a day. (13)Gall Bladder- active storage shed, which absorbs mineral salts and water received from the liver and convert into thick, mucus called “bile”, to be released when food is in the stomach. (33 Spleen- valuable organs which produce some of the white blood cells, filters blood, destroy old, worn-out red blood cells and returns needed iron to the blood, disposing of the rest as waste. (31)Small Intestine- is where the remaining nutrients are absorbed before moving into the large intestine. (19)Large Intestine (colon) - “bowel” is sometimes called the “garbage dump” of the body, because the materials that reach it are of very small use to the body and are sent on to be dispose of. (11)Epididymis- is upright and allows air to pass through the larynx and into the rest of the respiratory system. (36)Trachea- forms the trunk of an upside-down tree and is flexible, like a vacuum tube, so that the head and neck may twist and bend during the process of breathing. (4) Cecum- pouch like structure located in the lower right abdomen that absorbs water from the waste, returning fluid to the body and consolidating the waste for its journey through the end stage of digestion. (38) Umbilical Cord- is to carry nourishment and oxygen from the placenta to your baby and return waste products to the placenta from the fetus. (30) Pyloric Valve- regulates the flow of chime out of the stomach into the duodenum. Endocrine System: (27)Ovary- producing eggs or “ova,” the ovaries produce female sex hormones called estrogen and progesterone. (35)Testes- the testicle lays inside the scrotum and produces as many as 12 trillion sperm in a male’s lifetime, about 400 million of which are ejaculated in one average intercourse. Reproductive System: (28)Penis- is the external sex organ of the male through which both urine and semen pass. (42)Uterus- or “womb” is a hollow, muscular organ in which a fertilized egg, called the “zygote,” becomes embedded and in which the egg is nourished and allowed to develop until birth. (43)Vagina- is a muscular passage which forms a part of the female sex organs which connects to the neck of the uterus (called the “cervix”) with the external genitals. (15) Horn of Uterus- defines the entrance of the uterine tubes into the uterus. (40) Urogenital Opening- the opening where waste and reproductive fluid is expelled. (41) Urogenital Papilla- is a tube extending from the urogenital opening that deposits eggs or sperm. (44) Vas Deferens- a tube that transfers sperm from the epididymis to the prostate upon ejaculation. Nervous System: (32)Spinal Cord- provide a two-way communication system between the spinal cord and parts of the arms, legs, neck and trunk of the body. (6) Cerebellum- helps provide smooth, coordinated body movement. (7) Cerebrum- it is the part of the brain that controls thought, memory and the sense. (22) Longitudinal Cerebral Fissures- is the deep groove that separates the two hemisphere of the vertebrate brain. (24) Mammary Papillae- each teat has streak canals which is where the milk is delivered to the end of the teat for drinking by her young, aka piglets. (26) Medulla- is responsible for regulating your rat of breathing, your heart rate, blood pressure, circulation and digestive system activity. Cardiovascular System: (5)Carotid Artery-two specialized regions: the carotid sinus, which monitors the blood pressure, and the carotid body, which monitors the oxygen content in the blood and helps regulate breathing. (29)Pulmonary Artery- when the muscular wall of the right ventricle contacts, the blood inside the heart chamber is put under more press, and the tricuspid valve closes. (2) Aorta- carries and distributes oxygen rich blood to all arteries. (3)Atrium- it receives de-oxygenated blood from the superior and inferior vena cavae and the coronary sinus, and pumps into the right ventricle through the tricuspid. (8) Coronary Artery- first blood vessels that branches off the ascending aorta. (37) Umbilical Artery- is a paired artery (with one for each half of the body) that is found in the abdominal and pelvic region. (45) Vena Cava (superior and inferior)- The inferior vena cava is one of two veins which carries deoxygenated blood from the body into the right atrium of the heart, the other vein is the superior vena cava: inferior deals with blood coming from body areas below the heart, superior deals with blood coming from above the heart. (46) Ventricle (left or right)- do the heavy pumping. The right ventricle pumps blood from the heart to the lungs. The left ventricle takes the blood that has been collected from the lungs and pumps it out to the body. Urinary System: (16)Kidneys- they are the balancers of internal fluids, so if we overeat or overdrink one day and diet the next, or if we have active, “sweaty” day, the kidnesy will compensate and see that these fluctuations in fluid, salt and glucose are leveled out. (17) Kidney Cortex (Renal)- filter blood and remove waste product inside your body (18) Kidney Pelvis (Renal)- act as a funnel for urine flowing to the ureter. (39) Urinary Bladder- as a temporary reservoir for urine. The bladder possesses features that enable urine to enter, be stored, and later be released for evacuation from the body. Skeletal System: (10)Digit- each finger may flex and extend, abduct and adduct, and so also circumduct. (1)Ankle- is needed to walk with a smooth and nearly effortless gait. Respiratory System: (9) Diaphragm- small openings in the diaphragm allow structures such as the aorta, inferior vena cava and esophagus pass through. (12) Epiglottis- is to block off food and liquids form entering the trachea (windpipe). It allows air to pass through larynx into the rest of the respiratory system. (14) Hard Palate- to help form speech sounds, and to allow food to be chewed while breathing continues. (20) Larynx- ensures that the airways are open, which means we get to breathe. (23) Lung- is to transport oxygen from the atmosphere into bloodstream, and ot release carbon dioxide form the bloodstream into the atmosphere. Muscular System: (25) Masseter Muscle- These muscles help mainly in the movement of the mandible and not the maxilla as maxilla is an Integra part of the skull and the mandible being the only movable bone in the skull.