Economics –Foundations Sub-topic SL/HL Core – Assessment
advertisement

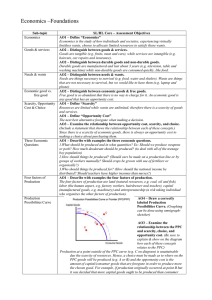
Economics –Foundations Sub-topic Economics Goods & services Needs & wants Economic good vs. free good Scarcity, Opportunity Cost & Choice Three Economic Questions Four factors of Production Production Possibilities Curve SL/HL Core – Assessment Objectives AO1 – Define “Economics” Economics is the study of how individuals and societies, experiencing virtually limitless wants, choose to allocate limited resources to satisfy those wants. AO2 – Distinguish between goods & services. AO2 – Distinguish between durable goods and non-durable goods. AO2 – Distinguish between needs & wants. AO2 – Distinguish between economic goods & free goods. AO1 – Define “Scarcity” AO1 – Define “Opportunity Cost” AO3 – Examine the relationship between opportunity cost, scarcity, and choice. (Include a statement that shows the relationship between each of these concepts.) AO1 – Describe with examples the three economic questions. 1.What should be produced and in what quantities? Ex: Should we produce weapons or pork? How much deodorant should be produced? (to deal with all of the teenage boy population) 2. AO1 – Describe with examples the four factors of production. Utility AO4 – Draw a correctly labeled Production Possibilities Curve. (Graphing can be done using omnigraph-sketcher) AO3 – Examine the relationship between the PPC and scarcity, choice, and opportunity cost. (Be sure to explain & show on the diagram how each of these concepts relates to the PPC) AO1 – Define “potential output,” and relate to PPC (Relate to PPC means show it on the PPC graph and explain its position on the graph in words) AO1 – Define “potential growth,” and relate to PPC AO2 – Distinguish between potential output and actual output, and relate to PPC. AO2 – Distinguish between potential growth and actual growth, and relate to PPC. AO1 – Define “Utility” Margin AO1 – Define the term “Marginal” Microeconomics vs. Macroeconomics Positive vs. Normative Econ Ceteris Paribus AO2 – Distinguish between Microeconomics and Macroeconomics. Circular Flow Model Public vs. Private Sectors Rationing Systems Growth vs. Development AO2 – Distinguish between Positive and Normative Economics with examples. AO1 – Define “Ceteris Paribus” AO1 – Explain the reason Ceteris Paribus is used in economic models. AO4 – Draw a correctly labeled Circular Flow Model. AO2 – Explain the Circular Flow Model. AO3 – Distinguish between the public sector and the private sector with examples. AO2 – Distinguish between a planned economy and a free-market economy. AO3 – Compare and contrast the advantages and disadvantages of planned and free-market economies. AO2 – Distinguish between economic growth and economic development. AO1 – Define “sustainable development”