The Circular Flow of Economics
advertisement
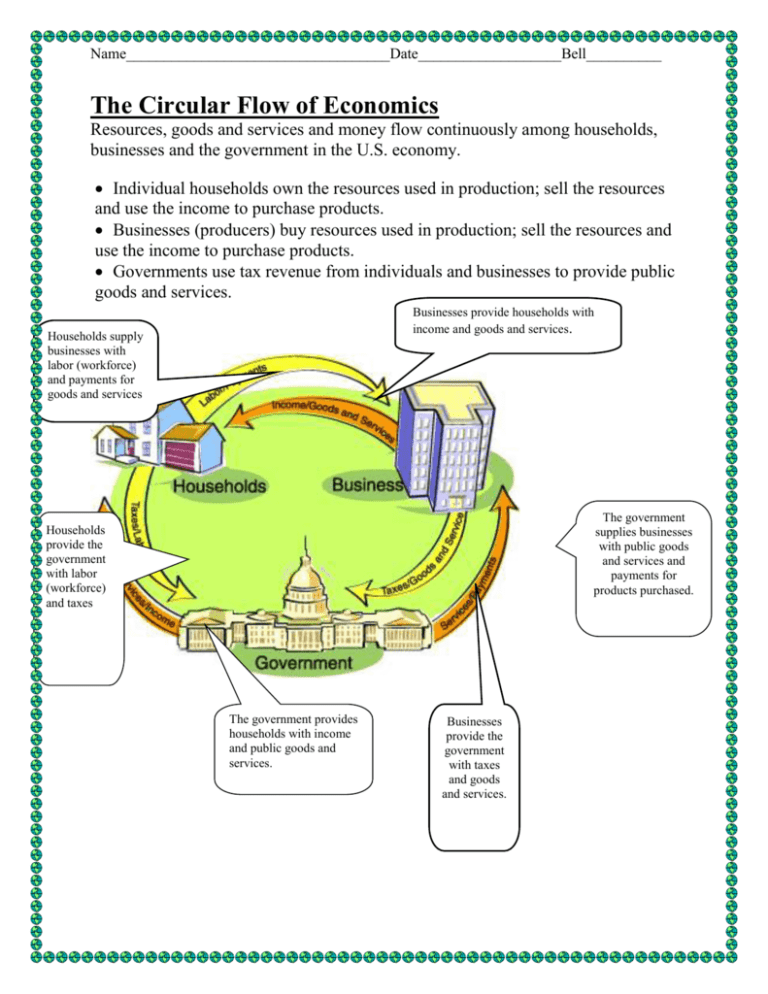
Name___________________________________Date___________________Bell__________ The Circular Flow of Economics Resources, goods and services and money flow continuously among households, businesses and the government in the U.S. economy. Individual households own the resources used in production; sell the resources and use the income to purchase products. Businesses (producers) buy resources used in production; sell the resources and use the income to purchase products. Governments use tax revenue from individuals and businesses to provide public goods and services. Businesses provide households with income and goods and services. Households supply businesses with labor (workforce) and payments for goods and services The government supplies businesses with public goods and services and payments for products purchased. Households provide the government with labor (workforce) and taxes The government provides households with income and public goods and services. Businesses provide the government with taxes and goods and services. Name___________________________________Date___________________Bell__________ Production, Consumption & Distribution Four Questions All Economic Systems Must Address 1. WHAT is produced? 2. HOW should these goods be produced? Production Goods and services must satisfy the consumers wants and desires Factors of Production Combine the factors of production to make or produce the goods and services Capital Entrepreneurship Land Labor Distribution 3. For WHOM are the goods and services produced? 4. HOW MANY goods and services should be produced? Getting the goods and services from producer to consumer Consumption Make enough to have a large profit and still have consumer demand. How many is determined by supply and demand. Name___________________________________Date___________________Bell__________ Unit 7a: Economics Supply and Demand Scarcity is the inability to satisfy all wants at the same time due to limited resources Choices must be made as to what to produce, how much to produce and who will receive what is produced. PRICE: Mechanism to decide who gets goods and services. The amount that satisfies both producers for profit and consumers for value. Supply and Demand determine price through their interaction. DEMAND: is the amount of a good or service that consumers are willing and able to buy at a certain price SUPPLY: is the amount of a good or service that producers are willing and able to sell at a certain price. LAW OF SUPPLY Businesses will provide more products when they can sell them at higher prices LAW OF DEMAND Buyers will demand more products when they can buy them at lower prices INCENTIVES Incite or motivate Change economic behavior Something that spurs someone into action: sale, coupons, etc. Name___________________________________Date___________________Bell__________ Resources, Scarcity & Opportunity Cost Good Anything that can be grown or manufactured (made) Food Clothes Cars Service Something a person does for someone else in exchange for money or value. doctor hairdresser waiter Natural Human Capital Combine to make goods and services Resources Our Basic Economic Problem: People have Unlimited Wants Food, clothing, shelter, schools, hospitals, cars, transportation But Resources are Limited Land, soil, minerals, fuels, people, money, technology SCARCITY The inability to satisfy all wants at the same time; the NEEDS are greater than the RESOURCES Since resources are LIMITED consumers and producers must make CHOICES CHOICE: selecting from a set of alternatives OPPORTUNITY COST: what is given up when the choice is made. Scarcity forces us to choose which needs and wants to satisfy with available resources. Scarcity affects decisions concerning what and how much to produce, how goods and services will be produced and who will get what is produced. Combining resources to make goods and services. Production (Sellers) Available resources and consumer preference determine what is produced Consumption (Buyers) Using goods and services Consumer preference and price determine what is purchased. Name___________________________________Date___________________Bell__________ Challenges in a Free Market Vocabulary Terms Economic Proposition Scarcity Alternatives Choice Trade-offs Opportunity Cost In English Lesson for Life You can't have everything you Acceptance of scarcity will help you make want. more reasoned choices. Different options from which you can choose. There are many different ways to allocate resources and to solve problems. Because you can't have everything you want, you have to make choices from a list of alternatives. When policy-makers decide on a particular resource allocation, recognize that a choice had to be made due to scarcity. You may not like the alternative chosen, you may question the choice, but the villain is scarcity. Choices involve giving up You are responsible for the consequences something to get something. of your choices. Since you make choices, All choices have consequences, you can't be a victim. both positive and negative. What is given up when a choice is made. All choices have opportunity costs. A good idea is only a good idea if its value is greater than the value of its opportunity cost. Voters must always identify the opportunity cost of a particular policy. Economic Systems The type of economy a country has is based on the amount of government involvement in economic decisions. Command Economy The central government makes decisions and determines how resources will be used. The central government owns property and resources. Businesses are not run for profit. No competition Lack of consumer choice The government sets the prices of goods and services. China, North Korea, Cuba Free Market Economy Also known as capitalism or free enterprise Private ownership of property and resources (owned by individuals) Individuals and businesses make profits Individuals and businesses compete Economic decisions are made by supply and demand Profit is a motivator for productivity Name___________________________________Date___________________Bell__________ No government involvement Consumer sovereignty: buyers determine what is produced Mixed Economy Most common type of economic system Government and individuals share the decision making process Individuals and businesses make decisions for the private sector Individuals own the means of production Government makes plans for the public sector Government guides and regulates production of goods and services offered. A greater government role than in a free market economy Most effective economy for providing goods and services U.S. and most Western European countries are mixed economies. Who owns the resources and how are they allocated? Who makes the decisions about what to make and sell? Free Market Economy Resources own privately; allocated according to price Consumer and producers Mixed Economy Private individuals and the government Command Economy Central government owns and allocates Consumers and producers for the private sector; government for the public sector Central Government Technology How are prices determined? Advanced Supply and demand Advanced Competition or set by government Advanced or developing Set by government Factors of Production Factors of Production Anything that goes into the making of a good or service Capital tools machinery money technology Name___________________________________Date___________________Bell__________ Entrepreneur Business owner and risk taker combines the factors of production Land Natural resources Labor Workers and their time and energy Business Organizations The 15 million businesses in the U.S. fall into three categories: sole proprietorships, owned by a single individual, partnerships, with more than one owner sharing the risks and profits and corporations, owned by their stockholders. Sole Proprietorship 1 owner The owner takes all the risks Supplies capital, hires help, pays taxes The owner makes all the profits The owner is solely responsible for losses b Partnership More than one owner (2+) Corporation Owned by stockholders Risks are shared amongst the owners Profits are shared amongst the owners Often more successful than sole proprietorships Responsibilities are shared Authorized to act as a legal person regardless of the number of owners Owners share the profits Liability is limited to investment (you can only loose as much as you put in) Raise money by selling stocks No one is responsible for corporation’s debt if it fails Name___________________________________Date___________________Bell__________ Sole proprietorships Advantages Partnerships Advantages Corporations Advantages Disadvantages Disadvantages Disadvantages The U.S. Economy The U.S. Economy is a MIXED economy where individuals, businesses and the government make economic . decisions Money left over after all business expenses have been paid. Profit Free Markets Markets are allowed to operate without undue interference from the government. Money, goods and services flow continuously among individual households, businesses and the government Competition The U.S. Economy is a MIXED Economy Consumer Sovereignty Consumers determine what goods and services are produced by what they buy. Rivalry between businesses for the same customers; results in better quality. Private Property Individuals can own the means of production & property without undue government interference. Name___________________________________Date___________________Bell__________







