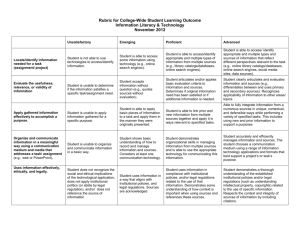
Web Based Research
advertisement
Laying the Foundation Mining the Web Fr. Jomar Legaspi Learning Milestones • • • • • • • Internet / World Wide Web Search Engines Fundamentals of Search Mathematics Search Strategies Evaluating Web Resources Citing Web Resources Web Search Exercise Internet • How it happened? – need to connect scientists / experts from diverse locations to fast track space exploration project – ARPANET – explosive growth – browser • How big is the Internet? – approximate – 40 million networks – 200 M users connected to it – 5 M websites – quadruples by 2005 – 1 billion web documents (IDC – Internet Data Corporation – 1998) • Internet revolution: – democratization of information – convergence of technology Search Engines – Mining the Internet • Individual Search Engines: compile their own searchable databases – Index words or terms in web based documents – Directories – classify web documents or locations in arbitrary classifications or taxonomy • e.g. Yahoo, Google, Altavista • Metasearch engines – gateway to databases from multiple search engines – Advantages: fast, more relevant but not that comprehensive vs individual search engines • e. g. Metacrawler Mining the Internet – Search Engines • Subject Directories – maintained by human editors rather than by spiders or web robots – Types: • • • • • General Academic Commercial Portals = Gateway Vortals – subject specific – Strengths and weaknesses • Cumbersome – process entails going through several layers of categories / steps • High quality content – less instances of out of context search results • Active links – When to use: • General search / general topic – Examples: • Yahoo • LookSmart • Magellan Mining the Internet – Search Engines • Gateways and Vortals – Gateways / portals: collection of databases and information websites categorized by subjects assembled, reviewed, recommended by content specialists or experts. Excellent for academic research • Internet Public Library: www.ipl.org • Argus Clearinghouse: www.clearinghouse.net • WWW Virtual Library: www.vlib.org – Vortals (vertical portals) – dedicated to a single subject • Eric Clearinghouse: http://www.eric.ed.gov. • The Big Hub: www.thebighub.com • Complete Planet: www.completeplanet.com Mining the Internet – Search Engines • Deep Web or the “Invisible Web” – approximately 60% - 80% of the web remains invisible to search spiders / robots. – Information in secured private networks / databases – Gateways and vortals = the best way to gain access and exploit the Deep Web / Invisible Web Mathematics of Search Engines • Use + or – signs before a keyword to force their inclusion / inclusion in the search. • “” – keywords are searched in exact order / sequence – “information technology strategies” • Combination of all the symbols – “information technology strategies”-businessgovernment +schools Search Strategies • Articulate what you need to search. Formulate the key concepts as specific at they could be. • Critical success factor: KEYWORDS • Keywords = use NOUNS / OBJECTS rather than verbs and adjectives • Avoid use of propositions, conjunctions, or common verbs – most search engines will disregard them • Most powerful keywords = “phrase” Separating diamonds from dirt… • • • • • Tool – CARS by Robert Harris Credibility – Trustworthiness of the author = authority and credibility • Author’s name • Qualification • Affiliations • Publisher / Sponsor • Address, tel. Nos. • Email address Accuracy – Objective, correct, up-to-date, comprehensive, exact. The information is appropriate to the audience it was intended for. • Date of publication • Last date when the site was updated • Email address • Link to questions and comments Reasonableness – Balance, objectivity, and consistent; tone of the language – moderate / absence of motherhood statements / grandstanding – Watch out who is the sponsor Support – Sources of information / knowledge – Corroboration • Citations of sources: bibliography Resources • Ellen Chamberlain, Bare Bones 101: A Basic Tutorial on Searching the Web, University of Southern California Beufort Library, http://www.sc.edu/beaufort/library/bones.html, January 2000, February 10, 2002 • Craig Branham, A Student’s Guide to Research in the WWW, St. Louis University, Illinois, http://www.slu.edu/departments/english/research/, March 27, 1997, February 10, 2002 • BrightPlanet Corp., Guide to Effective Searching of the Internet, http://www.brightplanet.com/deepcontent/tutorials/search/index.asp, 2000 – 2002, March 1, 2002 Your school recently subscribed to the services of a local Internet Service Provider. Initially it was decided that Internet access will be available in the library where 15 computers were installed. Your school principal understood that the Internet can exponentially increase the number of learning resources available to the students which before where simply limited to print media. The principal wrote a memo asking all teachers to develop an online resource center as a way to assist students to search for quality information in the web. Your task: 1. define your audience 2. define the subject area / content / discipline 3. search the web for at least 10 online resources 4. give a brief description of each site