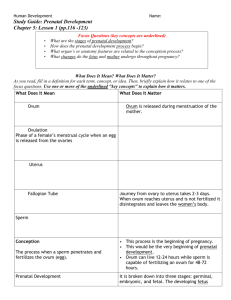
Conception
advertisement

• Conception is when sperm and egg meet and fertilization occurs • Sperm - one of the tiniest cells in the human body • Conception occurs in the outer third of the fallopian tube • Zygote - fertilized egg 1 Improving the Chances of Conception • Time intercourse so it occurs around time of ovulation • Sperm live inside a woman’s body for up to 5 days • Egg is capable of being fertilized for about the first 12 to 24 hours after ovulation • Position during and after intercourse is important 2 Symptoms of Pregnancy • Missed menstrual period • Breast tenderness • Morning sickness • More frequent urination 3 Diagnostic Signs of Pregnancy • Presumptive Signs: breast changes, amenorrhea, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, frequent urination • Probable Signs: Positive pregnancy test, physical changes in the uterus • Positive Signs: Ultrasound or X-ray of fetus, fetal heartbeat, fetal movement 4 Pregnancy Tests Physician tests: – Immunologic test based on detection of hCG – Beta-hCG radioimmunoassay • Home pregnancy tests 5 Development of the Conceptus • Nine months of pregnancy are divided into three equal periods of three months - called trimesters – First trimester - months 1 to 3 – Second trimester - months 4 to 6 – Third trimester - months 7 to 9 6 The Embryo and Its Support Systems • Placenta - an organ formed on the wall of the uterus through which the fetus receives oxygen and nutrients and gets rid of waste products • Human chorionic gonadotropin - a hormone secreted by the placenta; it is the substance detected in pregnancy tests 7 The Embryo and Its Support Systems • Umbilical cord - the tube that connects the fetus to the placenta • Amniotic fluid - the watery fluid surrounding a developing fetus in the uterus 8 Fetal Development During the First Trimester • Develops into a fetus with most of the major organ systems present • 4th to 8th week - external body parts develop 9 Fetal Development During the First Trimester • 7th week - liver, lungs, pancreas, kidneys, and intestines have formed and begun limited functioning • End of 12th week - 10 centimeters long; weighs 19 grams 10 Fetal Development During the Second Trimester • Quickening occurs - women becomes aware of fetal movements – around the end of the 14th week • Fetal heart beat can be detected • Fetus opens its eyes 11 Fetal Development During the Third Trimester • Fetus’s skin is wrinkled and covered with downlike hair • Fetus turns in uterus to assume a head-down position • Fetus experiences rapid growth 12 Physical Changes: First Trimester • Large increase in levels of hormones • Breasts swell and tingle; development of mammary glands • Need to urinate • Morning sickness • Vaginal discharges may increase • Feelings of fatigue and sleepiness 13 Psychological Changes • Depression is common • Negative emotions • Positive feelings 14 Physical Changes: Second Trimester • Morning sickness disappears • Constipation and nosebleeds sometimes occur • Edema - water retention and swelling • Colostrum may come out of the nipple 15 Psychological Changes • Psychological well-being is greater among women who have social support • Depression higher in some studies 16 The Father’s Role in Pregnancy • Couvade syndrome - male pregnancy Symptoms(a condition in which a man experiences some of the same symptoms and behavior of an expectant mother.) • The father-to-be - many choose to be actively involved • Diversity in the contexts of pregnancy there are lots of various family contexts that exist today 17 Sex During Pregnancy • Intercourse can continue safely until 4 weeks before the baby is due 18 Nutrition During Pregnancy • Diet during is extremely important • Woman must get enough protein, folic acid, calcium, magnesium and vitamin A • The fetus comes first – it draws the nutrients it needs first, and whatever is left is for mom 19 Nutrition Deficiencies • Calcium – future risk of bone and tooth loss • Folic acid – (folate) much higher risk of neural tube defects. (decreases risk by 50%) • Zinc – malformations of the central nervous system 20 Effects of Drugs Taken During Pregnancy • Teratogens - a substance that produces defects in a fetus • Antibiotics - may damage fetus • Alcohol - may cause fetal alcohol syndrome • Cocaine - increased risk of premature birth 21 Effects of Drugs Taken During Pregnancy • Steroids - can cause masculinization of a female fetus and other fetal damages • Other drugs - check with physician and “when in doubt, don’t” • Dads and drugs – drugs can damage sperm and their genetic content 22 Birth: The Beginning of Labor • Bloody show(During pregnancy, your cervical opening becomes blocked with a thick plug of mucus that prevents bacteria from entering the uterus. When your cervix begins to loosen, this mucous plug is dislodged.) • Amniotic sac ruptures • Progesterone-withdrawal theory 23 The Stages of Labor • Labor divided into 3 stages • Parturition - whole process of childbirth 24 First-Stage Labor • Regular contraction of uterus muscles • Effacement • Dilation • Divided into 3 stages: – Early first-stage labor (0-5 cm) – Late first-stage labor (5-8 cm) – Transition phase (8-10cm) 25 Second-Stage Labor: Delivery • Begins when cervix is fully dilated • Urge to push or bear down • Crowning – top of the head is visible • Episiotomy may be performed – incision that is sometimes made at the vaginal entrance during birth • Baby is born 26 Third-Stage Labor • Placenta detaches from walls of the uterus • Afterbirth is expelled • Several contractions may accompany placental expulsion • Episiotomy and tears are sewn up 27 Cesarean Section • A method of delivering a baby surgically, by an incision in the abdomen • Reasons to have a C Section: – Baby is too large, mother’s pelvis is too small – Cervix is not dilating – Umbilical cord prolapses(comes out of place) – Excessive bleeding – Placenta previa(blocks cervix) 28 After the Baby is Born: The Postpartum Period • Physical changes – Hormones levels return to normal – Woman may feel exhausted – Discomfort from episiotomy • Psychological changes – Postpartum depression 29 Attachment to the Baby • Bonding can occur before baby is born • Critical period of bonding occurs in minutes and hours immediately after birth 30 Sex During Postpartum • Couple should wait at least 2 weeks before resuming intercourse • If woman had an episiotomy, she may experience vaginal discomfort Sex may not be resumed for up to 6 weeks in some cases. 31 Breast-Feeding Biological mechanisms – Prolactin - stimulates breasts to produce milk – Oxytocin - stimulates breasts to eject milk • Physical and mental health – Breast feeding is encouraged 32 Problem Pregnancies • Ectopic pregnancy - fertilized egg implants somewhere other than the uterus • Pseudocyesis - false pregnancy • Pregnancy-induced hypertension – too much stress for mother to be able to handle. 33 Problem Pregnancies • Viral illness during pregnancy • Birth defects • Rh incompatibility • Miscarriage - spontaneous abortion • Preterm birth 34 Infertility • Refers to a woman’s inability to conceive and give birth to a living child, or a man’s inability to impregnate a woman • Causes - can be either female factors or male factors 35 Causes in the Female • Pelvic inflammatory disease • Failure to ovulate • Blockage of the fallopian tubes • Hostile mucus 36 Causes in the Male • Infections in the reproductive system caused by sexually transmitted diseases • Low sperm count • Low motility of the sperm 37 Combined Factors • Immunologic response • Lack of knowledge 38 Psychological Aspects of Infertility • Couple subjected to psychological stress • Man may feel that his masculinity or virility is in question 39 Treatment of Infertility • Fertility drugs • Microsurgery • New reproductive technologies 40 Assisted Reproductive Technologies • Artificial insemination - sperm are placed into vagina by means other than sexual intercourse • Sperm banks • Embryo transfer - embryo is transferred into uterus, usually from the lab. 41 New Reproductive Technologies • Test-tube babies - in vitro fertilization - egg is fertilized by sperm in a laboratory dish • GIFT - gamete intra-fallopian transfer • ZIFT - zygote intra-fallopian transfer • Cloning • Gender selection 42