pH=2.46
advertisement
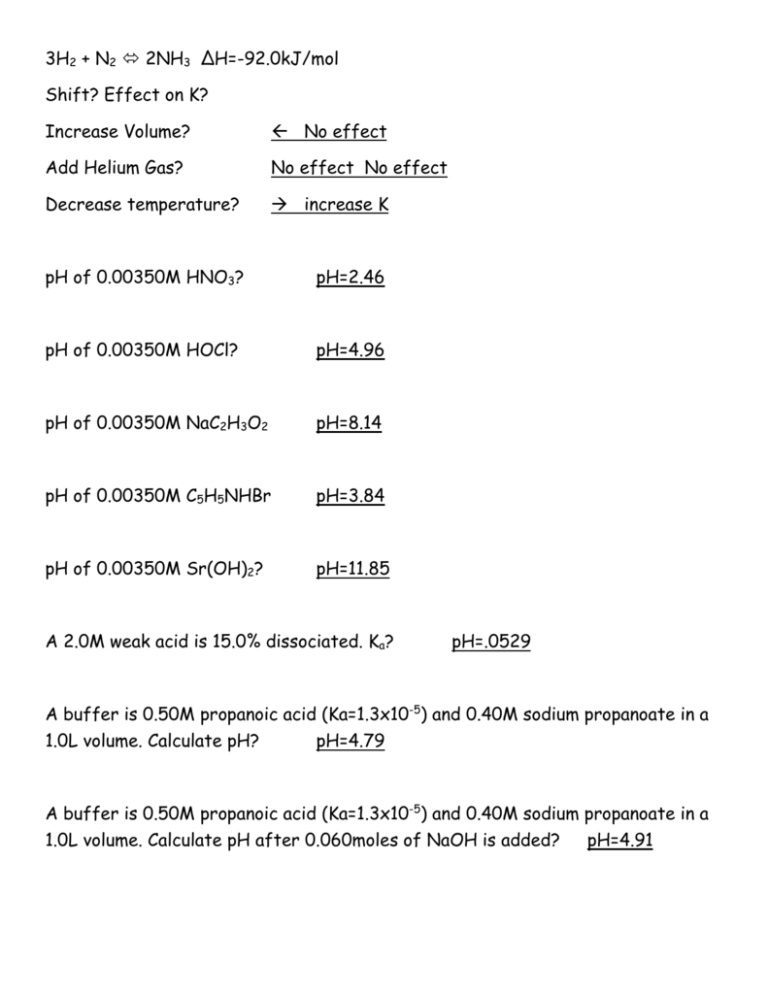
3H2 + N2 2NH3 ΔH=-92.0kJ/mol Shift? Effect on K? Increase Volume? No effect Add Helium Gas? No effect No effect Decrease temperature? increase K pH of 0.00350M HNO3? pH=2.46 pH of 0.00350M HOCl? pH=4.96 pH of 0.00350M NaC2H3O2 pH=8.14 pH of 0.00350M C5H5NHBr pH=3.84 pH of 0.00350M Sr(OH)2? pH=11.85 A 2.0M weak acid is 15.0% dissociated. Ka? pH=.0529 A buffer is 0.50M propanoic acid (Ka=1.3x10-5) and 0.40M sodium propanoate in a 1.0L volume. Calculate pH? pH=4.79 A buffer is 0.50M propanoic acid (Ka=1.3x10-5) and 0.40M sodium propanoate in a 1.0L volume. Calculate pH after 0.060moles of NaOH is added? pH=4.91 A buffer is 0.225M acetic acid(Ka=1.8x10-5) and 0.225M sodium acetate in a 250mL volume. Calculate pH of buffer. pH=4.74 A buffer is 0.225M acetic acid(Ka=1.8x10-5) and 0.225M sodium acetate in a 250mL volume. Calculate pH of buffer after 30.0 mL of 0.100M HCl is added. pH=4.70 Which of the following combinations cannot produce a buffer solution? (a) HNO2 and NaNO2 (b) HCN and NaCN (c) HClO4 and NaClO4 (d) NH3 and (NH4)2SO4 (e) NH3 and NH4Br Calculate the ratio [CH3COOH]/[NaCH3COO] that gives a solution with pH = 5.00? (a) 0.28 (b) 0.36 (c) 0.44 (d) 0.56 (e) 1.82 How many grams of NaF would have to be added to 2.00 L of 0.100 M HF (Ka=7.2x10-4) to yield a solution with a pH = 4.00? (a) 300 g (b) 36 g (c) 0.84 g (d) 6.9 g (e) 60. g Consider the titrations of the pairs of aqueous acids and bases listed on the left. For which pair is the pH at the equivalence point stated incorrectly? Acid-Base Pair pH at Equivalence Point (a) HCl + NH3 less than 7 (b) HNO3 + Ca(OH)2 equal to 7 (c) HClO4 + NaOH equal to 7 (d) HClO + NaOH less than 7 (e) CH3COOH + KOH greater than 7 Which of the following salts give acidic aqueous solutions? Basic? KNO3 KCH3COO NH4NO3 RbI (NH4)ClO4 BaCl2 NaCN KNO2 Acids-NH4NO3 and NH4ClO4 Bases-KCH3COO and NaCN and KNO2 Consider an indicator that ionized as shown below for which its Ka = 1.0 x 10-4 HIn yellow + H2 O H3O+ + Inred Which of the responses are true? (1) The predominant color in its acid range is yellow. (2) In the middle of the pH range of its color change a solution containing the indicator will probably be orange. (3) At pH = 7.00, a solution containing this indicator will be red. (4) At pH = 7.00, most of the indicator is in the un-ionized form. (5) The pH at which the indicator changes color is pH = 4. Ksp Ag2CrO4 9.0 x 10-12 BaCrO4 2.0 x 10-10 PbCrO4 1.8 x 10-14 The chromate that is the most soluble in water at 25oC on a molar basis is: (a) Ag2CrO4 (b) BaCrO4 (c) PbCrO4 The molar solubility of PbBr2 is 2.17 x 10-3 M at a certain temperature. Calculate Ksp for PbBr2. (a) 6.2 x 10-6 (b) 6.4 x 10-7 (c) 4.1 x 10-8 (d) 3.4 x 10-6 (e) 1.4 x 10-5 For Cu(OH)2, Ksp = 1.6 x 10-19. What is the molar solubility of Cu(OH)2? (a) 3.4 x 10-7 M (b) 6.4 x 10-7 M (c) 2.7 x 10-11 M (d) 5.1 x 10-10 M (e) 1.7 x 10-10 M Ag3PO4 (Ksp=1.8x10-18) would be least soluble at 25oC in (a) 0.1 M AgNO3 (b) 0.1 M HNO3 (c) pure water (d) 0.1 M Na3PO4 At 200˚C, the Keq is 550. At 300˚C, the Keq is 0.211. Is the reaction exothermic or endothermic? Exothermic What is the net ionic equation for the aqueous reaction of nitric acid and lithium hydroxide? H+ + OH- H2O Write the reaction when a concentrated solution of ammonia is added to a suspension of zinc hydroxide. Zn(OH)2 + 4NH3 [Zn(NH3)4]2+ + 2OH- Write the reaction when excess concentrated sodium hydroxide solution is added to solid aluminum hydroxide. Al(OH)3 + 3OH- Al(OH)63-







