Phylum Porifera
advertisement

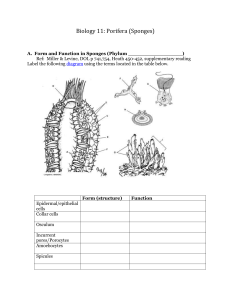
The Sponges General Characteristics Porifera means “full of holes” Sponges are the simplest of animals Live in both freshwater and saltwater. Two cell layers thick, with gel-like substance between them. Do not have tissues, organs, or organ systems. Do have specialized cells and cell structures. Specialized Cell Structures Spicules- needle-like skeleton made of spongin Amoebocytes- cells that carry food to other cells Collar cells- trap food using flagella Obtaining Food and Such Water flow carries Food and Oxygen into the pores and out the osculum. Waste produced are released into the water. Gas exchange occurs through diffusion. No nervous or circulatory system. Reproduction Can occur in three ways: Asexual 1. Regeneration: new organism grows from a piece of the old. 2. Budding: new organism grows on old, falls off, and develops into an adult. Reproduction Sexual: Either sperm is released into the water and carried to a sponge egg where fertilization occurs Or, sperm and eggs are released into the water and fertilization occurs outside the sponge’s body Most sponges are hermaphroditic, meaning they can produce both sperm and eggs. Just not at the same time. Importance of Sponges Natural sponges are used for cleaning or bathing. Sponges are sources of powerful antibiotics. Sponges are homes for other organisms. Food source for some organisms. Works Cited http://www.bio.miami.edu/dana/pix/spongeanatomy.jpg. 318-09. [http://www.bio.miami.edu/dana/pix/spongeanatomy.jpg] http://www.oceanicresearch.org/jpegs/spawning_sponge.jpg. 3-18-09 [http://www.oceanicresearch.org/jpegs/spawning_sponge.jpg ] http://www.mbgnet.net/salt/animals/1sponge.jpg. 3-18-09. [http://www.mbgnet.net/salt/animals/1sponge.jpg]