The Acts of Western Expansion
advertisement

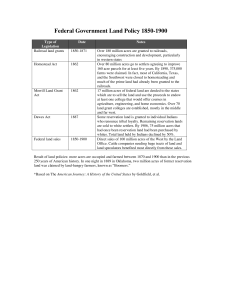
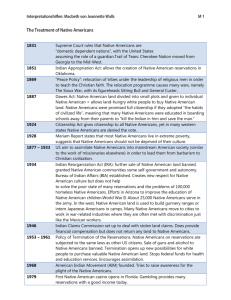
THE ACTS OF WESTERN EXPANSION Semester 2, Day 12 OBJECTIVES Students will be able to Analyze the various acts of Western Expansion and identify how those acts impacted settlement and agriculture Explain what cheap money and inflation could do to a farmer’s income WARM UP In the period from 1860 to 1900, the Federal Government encouraged the settlement of the West by A. passing an increased number of liberal immigration laws B. selling the most fertile public land to Native American Indians C. providing free transportation to settlers moving to the frontier D. granting tracts of land to railroad companies to encourage construction ANSWER D Explanation Much of the western railroad system was encouraged by land grants from the federal government. This system aided the spread of rail lines westward, but was also froth with corruption and scandal as kickbacks and bribes were commonplace in determining where the railroad was to be placed. KANSAS NEBRASKA ACT Passed by Congress on May 30, 1854 allowed people in the territories of Kansas and Nebraska to decide for themselves whether or not to allow slavery within their borders served to repeal the Missouri Compromise of 1820 which prohibited slavery north of latitude 36 °30´ pro-slavery and anti -slavery supporters rushed in to settle Kansas to affect the outcome of the first election held there after the law went into effect. Pro-slavery settlers carried the election but were charged with fraud by anti-slavery settlers, and the results were not accepted by them. The anti-slavery settlers held another election, however pro slavery settlers refused to vote This resulted in the establishment of two opposing legislatures within the Kansas territory. All the violence led to Kansas being referred to Bleeding Kansas PREEMPTION ACT AKA Distribution Preemption Act Passed on September 4, 1841 by Pres. John Tyler The Preemption Act of 1841 permitted "squatters" who were living on federal government owned land to purchase up to 160 acres (65 ha) at a very low price (not less than $1 .25 per acre, or $3.09 per hectare) before the land was to be of fered for sale to the general public. To qualify under the law, the "squatter" had to be : a "head of household"; a single man over 21, or a widow; a citizen of the United States (or an immigrant intending to become naturalized); and a resident of the claimed land for a minimum of 14 months . Helped establish manifest destiny in the US HOMESTEAD ACT Signed into Law by Pres. Lincoln on May 20, 1862 Anyone who had never taken up arms against the U.S. government (including freed slaves and women), was 21 years or older, or the head of a family, could file an application to claim a federal land grant. There was also a residency requirement . Between 1862 and 1934, the federal government granted 1.6 million homesteads and distributed 270,000,000 acres (420,000 sq mi) of federal land for private ownership. This was a total of 10% of all land in the United States 40% who attempted a claim got it ACTS POST 1862 Southern Homestead Act of 1866 Enacted to allow poor tenant farmers and sharecroppers in the south become land owners in the southern United States during reconstruction The Timber Culture Act of 1873 granted up to 160 acres of land to a homesteader who would plant at least 40 acres of trees Kinkaid Amendment of 1904 granted larger homestead tracts, up to 640 acres, to homesteaders in western Nebraska Enlarged Homestead Act of 1909 Gave marginal (dry) land claims 320 acres The Stock-Raising Homestead Act of 1916 640 acres for Ranching purposes PEACE POLICY 1869 – 1881 Pres. U. Grants policy of non -political humane treatment of Native Americans it aimed to place Native Americans on reservations where, in collaboration with Christian Church organizations, the Office of Indian Affairs would provide Native Americans with moral and competent Indian agents, establish churches and schools, teach agriculture and civilized pursuits and provide high -quality supplies at reasonable prices 1872- he allotting of Indian reservations to religious organizations as exclusive religious domains 73 agencies- Methodist, Catholics, Quakers, Baptists, Unitarian, Presbeterian, episcopalian, etc. ended when the government heeded the protests of religious organizations whose missionaries had been removed from reservations on which they had not been assigned TREAT Y OF FORT LARAMIE Aka Sioux Treaty Passed into law on April 29, 1868 Between the US and 3 bands of the Lakota, Yanktonai Dakota, and Arapaho Nation guaranteeing to the Lakota ownership of the Black Hills, and further land and hunting rights in South Dakota, Wyoming, and Montana an article intended to "ensure the civilization" of the Lakota, financial incentives for them to farm land and become competitive, and stipulations that minors should be provided with an "English education" at a "mission building" Gov’t provided teachers, blacksmiths, a farmer, a miller, a carpenter, an engineer and a government agent for the reservation DAWES ACT AKA General Allotment Act or the Dawes Severalty Act Passed into law by congress in 1887 authorized the President of the United States to survey American Indian tribal land and divide it into allotments for individual Indians. Those who accepted allotments and lived separately from the tribe would be granted United States citizenship Amended in 1891 and again in 1906 by the Burke Act the act further provided that citizenship not be granted to Native American individuals until at the time of the final validation of their trust patents, at the end of the probationary period of 25 years CURTIS ACT AKA Act for the Protection of the People of Indian Territory Passed in 1898 an amendment to the United States Dawes Act brought about the allotment process of lands of the Five Civilized Tribes of Indian Territory: the Choctaw, Chickasaw, Muscogee, Cherokee, and Seminole Intended to: establish the concept of individual land holdings new enrollments be performed under the Dawes Act Made large parts of these lands open to settlement by whites provided for the incorporation of towns in Indian Territory establishment of public schools residents could vote for city officials LAND REVISION ACT 1891 gave the president the authority to "set aside and reserve...any part of the public lands wholly or partly covered with timber or undergrowth, whether of commercial value or not.“ did not explicitly authorize the use or development of resources on Reservations lightening irrigation requirements, and extended from 6 to 14 months the time needed to commute a homestead claim into a preemption right under which title could be bought for $1 .25 an acre. FEELINGS CHECK Did we achieve the objective? Students will be able to Analyze the various acts of Western Expansion and identify how those acts impacted settlement and agriculture CHEAP MONEY ACTIVIT Y For the remainder of class I would like you to do Parts A and B of the Farmers Demand Cheap Money Activity. I will be collecting this on Friday 2/6 with the DBQ. This assignment was not originally on your syllabus. My bad. Each section will get 2 points for my flub! IF you do part C I will allot you 5 bonus points to the over all score on your DBQ, but only if it is turned in on Friday!!!!