Integumentary System
advertisement

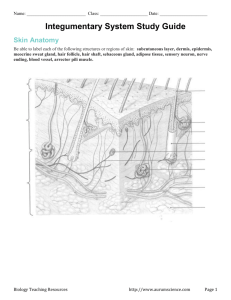
Chapter 5 Integument/Integument system: Debated as to whether or not your skin is an organ or organ system Accounts for 16% of body weight 2 Major Components: 1-Skin or Cutaneous Membrane Epidermis Dermis Hypodermis 2-Accessory Structures Nails Exocrine glands Protection Excretion (salts, water, organic wastes) Maintenance of body temp Synthesis of vitamin D3 Storage of nutrients (adipocytes) Detection of touch, pressure, pain, etc. Skin Epidermis (superficial) Dermis Hypodermis (deep) Thin skin=made of 4 layers of stratified Squamous tissue Most of body Thick skin=made of 5 layers Hands and feet Made of Stratified Squamous epithelium Stratum Stratum Stratum Stratum Stratum Corneum (superficial) Lucidum Granulosum Spinosum Basale or Germinativum (deep) Cells eventually pass through all layers or can eventually be found Surface skin (most superficial) Highly keratinized: thick, interwoven 15-30 days to get from stratum basale to stratum corneum Stay at stratum corneum for 2 weeks b/f shed Loose 500 mL (1 pint) water a day through skin Blisters: water retention between dermis/epidermis under high stress Found in thick skin Glassy, tough Filled with keratin Fibrous proteins—make up your hair and nails Layer missing in “thin” areas “Grainy 3-5 Layer” layers Have stopped dividing at this time High in keratin Makes cells flatter and thinner “Spiny Layer” 8-10 layers Langerhans Cells =participate in immune response Innermost Closest to basement membrane Sends projections into dermis (below basement membrane) Called epidermal ridges Give skin the whorls of fingertips Basal cells =stem cells to make more skin Merkel Cells =sense touch where no hair is present Melanocytes =skin tone Due to interaction of Epidermal Pigmentation and Dermal Circulation 2 Pigments that control your skin color 1-Carotene (orange-yellow) Found in stratum corneum 2-Melanin (brown, yellow-brown, black) Found in stratum basale protects us from UV radiation Melanocytes produce Dark skin = increased amount of Melanin production not increased amount of individual Melanocytes Gives pale or flushed look Better circulation =flushed Reduced circulation=pale Damages DNA of the cell, causing mutations and promoting cancer development Read bottom of 147(Melanocytes-Dermal Circulation) When exposed to sun, epidermal cells make D3, then the liver converts D3, and the kidney makes calcitriol. Calcitriol=ability to absorb calcium and phosphorous (no calcitriol=impaired bone maintenance and growth) Freckles Areas where melanocytes are producing a higher than normal rate of melanin. Birthmarks Non-vascular Overgrowth of melanocytes Tattoo’s Papillary Layer Areolar tissue, capillaries, sensory neurons Supplies epidermis 2. Reticular Layer Collagen and elastic fiber 1. Collagen fibers=strong, resists stretching BUT bend easily Elastic fibers=stretch and return =flexible, elastic dermis Aging, hormones, and excess UV = weakened fibers Wrinkles Excessive stretching past fibers capabilities lead to damaged fibers=stretch marks Caused by: pregnancy, major weight loss/gain SOLUTION: Retin-A from vitamin A increases blood flow to dermis which increases chances for repair 5 million hairs 98% not on head Hair Follicle=organ when hair is grown Hair Root=anchors hair to skin Hair Shaft=part you see Is hair living? No-Comprised of non-living cells Hair follicles are How is color determined? Pigment produced by melanocytes The biochemistry of these structures is affected by DNA Hormonal/Environmental affects Protection (eye lashes, head, sensory, ears, nose) Root hair plexus=sensory nerve around each hair follicle Arrector Pilli-smooth muscle attached to hair follicle=when stimulated, contracts, causes “goose bumps” Stimulated by emotional states, response to cold Hair growth cycle=2-5 years .33mm/day Hair loss occurs when the follicle becomes inactive and shrinks Over time, the connection breaks=hair loss The old hole sheds, new one forms Male Pattern Baldness Decrease in hormones circulating in the blood Alopecia 1 in every 100,000 Complete hair loss all over body Genetic Causes death of hair follicles Sebaceous Share a duct with hair Waxy, oil secretions Apocrine groin) Sweat Glands (armpits, around the nipples, Odorous, sticky Through hair follicle Begin at puberty Merocrine (Oil Glands-Holocrine) Sweat Glands (all other sweat) 2-5 million High numbers in palms/soles Provides protection to finger Nail Body cover nail bed Production at nail root Lunala is pale=lack of blood vessels Is dead, tightly compressed keratin packed cells Not part of integument but important for stabilization Areolar/Adipose tissue Elastic Area for injections