Earth's Interior notes

Chapter 5.1 Notes
Earth’s Interior
Exploring the Earth
• Geologists use two types of evidence to learn about the Earth’s interior:
-direct evidence from rock samples
-indirect evidence from seismic waves
*the deeper into the Earth you go, the greater the temperature and pressure
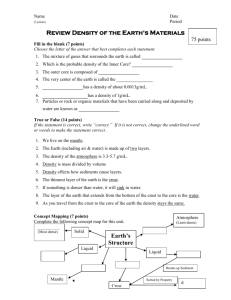
Layers of the Earth
• The Earth is divided into four layers:
-crust
-mantle
-outer core
-inner core
Layers of the Earth
• The crust:
definition – a that includes both
(continental crust)
(oceanic crust) layer of solid rock dry land and the ocean floor
Layers of the Earth
• The crust:
Layers of the Earth
• The crust:
definition – a that includes both
(continental crust) layer of solid rock dry land and the ocean floor
(oceanic crust)
thickness - the crust can range between 5 and 70 kilometers thick
-thickest under mountain ranges
-thinnest under the ocean
composition –
-continental crust mainly made of granite
-oceanic crust mainly made of basalt
Layers of the Earth
• The crust:
Layers of the Earth
• The mantle:
definition – The solid rock that is mantle is made of very hot. It is separated into 3 layers. The lithosphere, the asthenosphere and lower mantle.
thickness – almost 3,000 kilometers
composition – silicon, magnesium and iron
Layers of the Earth
• The mantle:
-lithosphere
– solid rock, similar to the crust
- temperature is between
1400 ° C and 3000 ° C
-the deeper you go, the rock begins to become
“softer”
Layers of the Earth
• The mantle:
-athenosphere – increased temperature and pressure continue to soften the rock
-temperature is at or above 3000 ° C
-convection currents occur in this section
-hotter rock rises and cooler rock sinks
Layers of the Earth
• The mantle:
-lower mantle – solid layer of rock that surrounds the outer core
-temperature reaches almost 4000 ° C
Layers of the Earth
• Outer core:
definition – the layer of liquid around the inner outer core is a rock the moves core
thickness – almost 2,300 kilometers
composition – mainly iron and nickel, some sulfur, oxygen and silicon temperature – between 4000 ° C – 5000 ° C
Layers of the Earth
• Inner core:
definition – The solid ball of extreme pressure.
inner core is a metal, due to the temperature and
thickness – over 1,200 kilometers
composition – mainly iron and nickel, some sulfur, oxygen, carbon and silicon
temperature – between 5000 ° C – 6000 ° C