BIOS 1300 SI WORKSHEET 7 SI Leader: Merrin Jeffries (email
advertisement

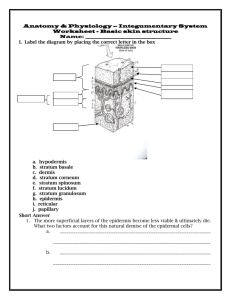
BIOS 1300 SI WORKSHEET 7 SI Leader: Merrin Jeffries (email: mj983011@ohio.edu ) 23 September 2014 1. A major function of the skin is protection from: a. abrasion b. UV light c. entry of microorganisms d. dehydration e. all of the above 2. The layer of the skin that is composed of dense connective tissue and has projections called papillae is the: a. dermis b. hypodermis c. stratum corneum d. stratum basale e. stratum lucidum 3. This layer contains loose connective tissue and has about half of the body’s stored fat: a. dermis b. hypodermis c. stratum corneum d. stratum basale e. stratum lucidum 4. The specific layer that shapes the ridges for fingerprints and footprints is the: a. hypodermis b. papillary layer of the dermis c. reticular layer of the dermis d. underlying muscle layer e. superficial bony layer 5. The epidermis is nourished by diffusion from capillaries in the a. epidermis b. reticular layer of the dermis c. papillary layer of the dermis d. hypodermis e. subcutaneous tissue 6. Cell division occurs in which layer of the epidermis? a. stratum basale b. stratum corneum c. stratum granulosum d. stratum lucidum e. stratum reticularis 7. The stratum germinativum includes both the stratum basale and the a. stratum corneum b. stratum granulosum c. stratum lucidum d. stratum reticularis e. stratum spinosum 8. The _______________ consists of many layers of dead squamous cells surrounded by lipids. a. dermis b. hypodermis c. stratum corneum d. stratum basale e. stratum spinosum 9. In which of these layers are melanocytes found? a. dermis b. hypodermis c. stratum corneum d. stratum basale e. stratum lucidum 10. Thick skin: a. usually lacks the stratum lucidum b. is typically found on the back c. does not produce hair d. (unlike thin skin) develops calluses and corns e. all of these 11. Most of the cells of the epidermis are a. fibroblasts b. keratinocytes c. Langerhans cells d. macrophages e. melanocytes 12. Which of these statements is true regarding keratinization? a. the deepest cells are located in the stratum corneum b. epithelial cells eventually die and produce an outer layer of cells c. the stratum corneum has cuboidal or columnar cells that undergo mitotic division d. the stratum basale can thicken to produce a callus e. the newest cells are found in the outer layer of cells 13. Melanin a. production occurs in melanocytes and keratinocytes b. is packaged into vesicles called melanosomes c. is present in large quantities on soles of the feet d. is responsible for skin color, but no hair color e. all of these 14. All of these conditions increase the amount of melanin in the skin EXCEPT: a. exposure to UV light b. pregnancy c. Addison’s disease d. vitiligo e. freckles 15. Which glands of the skin possess all of the following characteristics? 1. Secrete oily, white substance rich in lipids. 2. Open into a hair follicle. 3. During secretion, lysis and death of secretory cells a. apocrine sweat glands b. merocrine sweat glands c. sebaceous glands 16. Which of these parts of the body have the most merocrine sweat glands? a. margins of the lips b. soles of the feet c. forearm d. leg e. back of neck 17. Apocrine sweat glands a. are found everywhere in the body except the palms of the hands b. produce secretions that are metabolized by bacteria to produce odor c. are function even in babies d. are located in the external auditory meatus e. produce cerumen 18. As a result of aging, the skin: a. increases the amount of elastin fibers in the dermis b. becomes thicker c. has decreased blood flow d. has increased activity of the sebaceous glands e. generally increases the amount of melanin produced 19. Which of these is not considered to be a cause of acne? a. hormones, especially testosterone b. a diet rich in fatty foods and chocolate c. abnormal keratinization of hair follicles d. an increase in sebum production e. the bacterium Propionibacterium acnes 20. Which of these qualities must a medication possess if it is absorbed from a skin patch? a. lipid soluble b. water soluble c. most contain keratin d. musty be slightly acidic e. must contain melanin 21. Protective functions of the integumentary system include all of these EXCEPT: a. callus formation prevents damage by friction b. nails protect the ends of digits c. hairs in the nose and ears prevent entry of foreign material d. hair protects the head from abrasion and UV light e. skin glands produce alkaline secretions that kill bacteria 22. The embryonic germ layer from which the skin and nervous system are derived is: a. ectoderm b. endoderm c. mesoderm 23. All of these characteristics correctly describe epithelial cells EXCEPT: a. cover surfaces, either outside or inside the body b. usually have a free surface and a basal surface c. have little extracellular material between them d. have specialized cell contracts, such as tight junctions and desmosomes e. capillaries penetrate the basement membrane to provide a good blood supply 24. Tall, thin epithelial cells with only some cells reaching the free surface, but with all cells attached to the basement membrane membrane are called a. simple squamous epithelium b. simple cuboidal epithelium c. simple columnar epithelium d. pseudostratified columnar epithelium e. transitional epithelium 25. Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium is found in the a. lining of the mouth b. lining of the urinary bladder c. lining of the small intestine d. pancreas e. skin 26. Epithelial cells that can stretch from a cuboidal or columnar shape to a squamous shape are called a. simple squamous epithelial b. simple cuboidal epithelium c. simple columnar epithelium d. pseudostratified columnar epithelium e. transitional epithelium 27. In which of these locations would pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium intermixed with goblet cells be found? a. lining of blood vessels b. lining of the nasal cavity and trachea c. lining of serous membranes d. lining of the small intestine e. surface of the skin 28. The lining of blood vessels is covered with a. simple ciliated cuboidal epithelium b. simple squamous epithelium c. transition epithelium d. simple columnar epithelium with microvilli e. simple ciliated columnar epithelium 29. Which of these cell connections attach epithelial cells to the basement membrane? a. desmosomes b. gap junctions c. hemidesmosomes d. tight junctions e. zonula occludens 30. Gap junctions a. are small protein channels between cells b. can function to coordinate movements of cilia c. allow ions and small molecules to pass between cells d. are found in intercalated disks in cardiac muscle cells e. all of the above 31. Glands that produce hormones are a. apocrine glands b. endocrine glands c. exocrine glands d. holocrine glands e. merocrine glands 32. Glands that secrete substances with no actual loss of cellular material are a. apocrine glands b. holocrine glands c. merocrine glands d. sebaceous glands e. all of the above 33. In nerve cells, processes that conduct action potentials away from the cell body are a. axons b. dendrites c. neuroglia d. reticular fibers e. all of these