Chapter 12 Section 3 pg. 422-433
advertisement

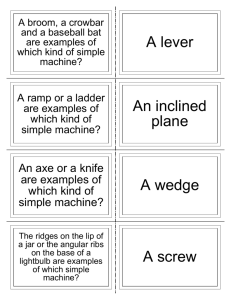
Chapter 14 Section 3 Simple Machines There are 6 basic types of simple machines. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. The inclined plane The wedge The screw The lever The wheel and axle The pulley Inclined Plane Inclined plane is a flat, sloped surface. 1. 2. It allows you to exert your input force over a longer distance. Mechanical Advantage = Length of incline Height of incline Wedge 1. 2. A wedge is a device that is thick at one end and tapers to a thin edge at the other end. When you use a wedge, instead of moving an object along the inclined plane, you move the inclined plane itself. Mechanical Advantage=Length of wedge width of wedge Screws A screw can be thought of as an inclined plane wrapped around a cylinder. 1. The threads of a screw act like an inclined plane to increase the distance over which you exert the input force. 2. The closer together the threads of a screw are, the greater the mechanical advantage. 1. Think of the length around the threads as the length of the inclined plane. Levers A lever is a rigid bar that is free to pivot, or rotate, on a fixed point (fulcrum). 1. Think about opening a paint can. Pg. 426. 2. Mechanical Advantage = Distance from fulcrum to input force ÷ distance from fulcrum to output force. Classes of Levers 1. First-Class Levers – always change the direction of the input force. Ex. Scissors, pliers, seesaws. 1. Second-Class Levers – increase force, but do not change direction of the input force. Ex. Doors, nutcrackers, bottle openers. Third-Class Levers – increase distance, but do not change the direction of the input force. Ex. Fishing poles, shovels, baseball bats Wheel and Axle A wheel and axle is made of two circular or cylindrical objects fastened together that rotate about a common axis. The larger radius is the wheel The smaller radius is the axle Ex. Screwdriver, doorknob, steering wheel. Wheel and Axle How It Works pg. 428 Mechanical Advantage = Radius of wheel Radius of axle Pulley A pulley is made of a grooved wheel with a rope or cable wrapped around it. 1. decreases the amount of input force needed and changes direction of input force. Ex. flagpoles Types of Pulleys 1. Fixed Pulley – does not change amount of force. Only changes the direction of force. 1. Movable Pulley – increases output force. Does not change direction. Block and Tackle – made up of both a fixed and moveable pulley. SEE PAGE 431 1. Compound Machines A machine that utilizes two or more simple machines.