Review questions The speed of light in a liquid is 2.25 x 108 m/s
advertisement

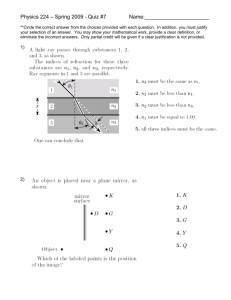
Review questions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. The speed of light in a liquid is 2.25 x 108 m/s. what is a) The refractive index of the liquid? 1.33 b) The liquid (check table in text if unsure) water What is the speed of light in Lucite if its refractive index is 1.51? 1.99 x 108 m/s The angle of incidence is 30o and the angle of refraction is 24o. Draw a diagram and calculate the index of refraction of the second medium if the first is air (n= 1.00) n = 1.23 What is the critical angle? What total internal reflection? The critical angle is the unique angle of incidence between two materials that occurs when the angle of refraction is 90o. The first medium must have a higher index of refraction than the second for this to occur (n1 > n2). (example water to air but not air to water) What is the critical angle of water (with air)? 49o If the critical angle of a medium with air is 40.5o what is the medium’s index of refraction?1.54 7. An object is located 30.0 cm from a converging mirror with a radius of curvature of 10.0 cm. a) at what distance from the mirror will the image be formed? b) if the object is 4.0 cm tall, how tall is its image? a) f = 5.0 cm di = 6.0 cm b) -0.80cm hi is negative, the image is inverted 8. A diverging mirror with a focal length of -5.0 cm produces an image of an object located 15.0 cm from the mirror. What is the distance of the image from the mirror? What is the magnification? di = -3.8 cm , M = 0.25 (positive M means the image is upright, virtual) 9. A lens has a focal length of +20cm and the magnification of an image is +4. How far apart are the object and the image? 45 cm (Hint: if the image Is upright it is virtual and the image distance is negative, the object and the image are on the same side of the lens: the object is 15 cm from the lens and the image is -60 cm ( virtual images have negative distances) so they are on the same side and 45 cm apart.) 10. What mirror offers the largest field of vision? Diverging mirror (convex) 11. When drawing ray diagrams for field of vision, we measure both the angle of incidence and the angle of reflection from which line? Normal line 12. How do we draw the normal line on a) a plane (flat =) mirror? It is at 90o to the surface. For field of vision we draw it at both endpoints b) a curved (spherical) mirror? The normal is 90o to the tangent of the surface at the point of incidence. We draw this by drawing a line from the C, the center of curvature and extend it straight through the mirror at the point of incidence. This line becomes the normal. diagrams p. 141 13. A velocity vector is 15.0 m/s at 220o. What are its two components (x and y)? Vx = 15m/s cos 220o = -11.5 m/s Vy = 15m/s sin 220o = -9.64 m/s 14. Two displacement vectors are given. 15.0m [W 10o S] and 22.0m [E 70o S] What is the resultant vector if we add these 2 vectors together? Vector 15.0m [W 10o S] 22m [E 70o S] total X component -15m(cos 10o)= -14.8m +22m(cos 70o) = +7.52 m VR = 24.4 m [W 72.6o S] Remember diagrams will help with direction Y component -15m(sin10o )= -2.60m -22m(sin 70o) = -20.7m -7.28 -23.3m 15. Use a ruler to create a scale 1 cm = 100 N (the diagram below was drawn to scale and then shrunk, so it is proportional but perhaps the scale is off) 16. The position time graph below shows the motion of a delivery truck whose driver is trying to find a house on a long straight street. a) what is the trucks position at the end of 30s? (at the top of A the truck is at 300m) b) when does the truck stop and how long is he stopped for? At 30s and it stops for 30 s. c) when does he reverse direction? At the end of C, 80s d)What is his average speed? V ave = total distance/total time: 300 + 0 + 200 + 400 = 900m /120s = 7.5 m/s (displacement is 300 + 0 + 200 – 400 = 100m) e)What is his speed in each part? (A, B, C, D) the slope of the line in each part A: 10m/s B: 0 m/s C: 10m/s D: -10m/s Velocity time graph a) What is the velocity in each section (A, B, C) A: -10 m/s B: 0 m/s C: 20m/s b) How far does the truck travel in total? c) To find displacement: the area under the curve To find distance take the absolute value of each displacement. A: -10m/s *30s = -300m (backed up 300m) B: 0m/s * 20s = 0 m (stopped) C: +20m/s * 50 s = 1000m. total distance 1300 m d) How long does it take? t = 100s e) What is the Vave? Total distance/ total time = 1300m/100s = 13m/s f) What is the final displacement? A: -10m/s *30s = -300m (backed up 300m) B: 0m/s * 20s = 0 m (stopped) C: +20m/s * 50 s = 1000m. -300m + 0m + 1000m = 700m.