connective tissues
advertisement
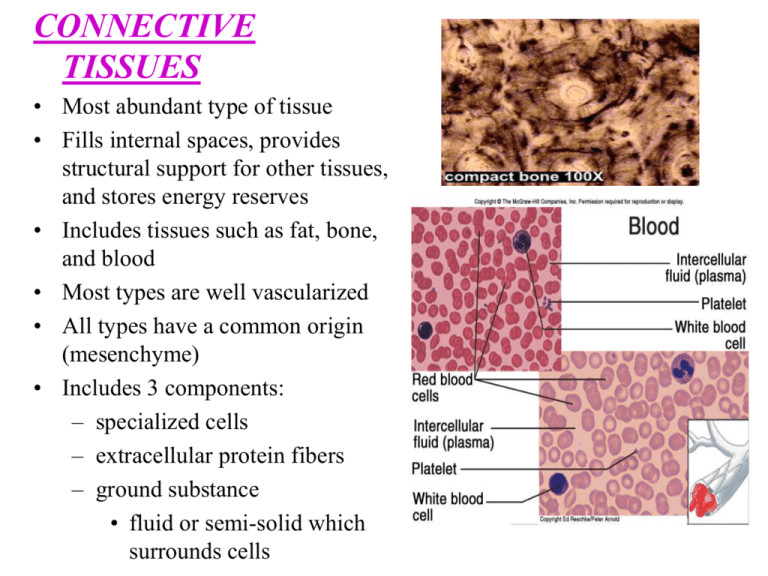
CONNECTIVE TISSUES • Most abundant type of tissue • Fills internal spaces, provides structural support for other tissues, and stores energy reserves • Includes tissues such as fat, bone, and blood • Most types are well vascularized • All types have a common origin (mesenchyme) • Includes 3 components: – specialized cells – extracellular protein fibers – ground substance • fluid or semi-solid which surrounds cells 3 Major Cell Types 1. Fibroblast – Most common fixed cell – Large, star shaped – Produces fibers by secreting protein into matrix 2. Macrophages • • • Wandering Cells that originate as WBC’s Function as scavengers that clear foreign particles Phagocytosis Also, play a role in immunity by allerting other WBC’s of foreign particles 3. Mast Cells • Large, widely distributed cells • Associated with inflammation • Releases heparin and histamine CLASSIFICATION • 3 CATEGORIES: • Connective tissue proper • tissue with many types of cells and extracellular fibers in a syrupy ground substance ex. Adipose tissue • Fluid connective tissue • cells suspended in a watery matrix that contains dissolved proteins ex. Blood • Supporting connective tissue • low diverse cell population and a matrix of closely packed fibers ex. Bone and cartilage CONNECTIVE TISSUE PROPER • Composed of many kinds of cells – Fibroblasts, Macrophages, Adipocytes • 3 types of fibers – Collagen - long, straight unbranched; flexible but strong ex: tendons, ligaments – Reticular – cells suspended in a watery matrix that contains dissolved proteins Bone & Cartilage: stabilizes cells & vessels – Elastic - contains the protein “elastin”. Branched, wavy, will contract after stretching ex: elastic ligaments • Ground Tissue – high viscosity; slows the spread of pathogens to make them easier for phagocytes to catch Real life apps Connective Tissue Proper • Loose connective tissue (areolar) – characterized by white and yellow fibers between fibroblasts – packing material of the body, cushions, attaches skin to the body, supports blood vessels • Adipose tissue – dominated by adipocytes – energy storage, brown fat in infants (highly vascularized) – each cell consists of large vacuole filled with triglycerides • Reticular Connective Tissue – complex open framework of reticular fibers • supports walls of organs such as liver and spleen • Dense Connective Tissue – consists of many closely packed collagen fibers, elastin fibers, and few fibroblasts • regular - collagen fibers are parallel to each other – tendons, ligaments • irregular - collagen fibers are randomly arranged and interwoven : provides strength to resist forces applied from many directions; interwoven meshwork – dermis Elastic Connective Tissue • - consists of mainly yellow elastic fibers – parallel or branching – walls of hollow organs, large arteries, heart etc. FLUID CONNECTIVE TISSUES • Ground substance – plasma • Blood contains formed elements: Erythrocytes, leukocytes, Platelets • Arteries carry blood from heart to capillaries, water and solutes move into interstitial fluid, Veins • Erythrocytes: carry oxygen (confined to vessels) • Leukocytes: fight infection (wander) • Platelets: blood clotting Supportive Connective Tissue Bone & Cartilage • I. – – – – Cartilage Cells: Chondrocytes Matrix: Firm gel of proteoglycans Avascular: heals slowly Covering: Perichondrium: Composed of 2 layers • Outer layer: dense irregular tissue • Inner layer: cells – Growth: Interstitial & Appositional • Appositional: undergoes extensive remodeling on a regular basis • Interstitial: – 3 main types Hyaline - Tightly packed collagen fibers – Most Common Type – Looks like white glass – Functions: Reduces friction, important in growth and repair of bones – Locations: Between bone surfaces, nose, trachea, intercostal cartilage • Elastic - Numerous elastic fibers – flexible – Functions: Provides support but distorts without damage – Locations: Ears, nose, epiglottis • Fibrocartilage - matrix dominated by collagen fibers – Extremely durable – Functions: Resists compression, limits movement – Locations: Between vertebrae, pads within knee joints • II. Bone - Most rigid connective tissue – Cells - Osteocytes – Matrix - 1/3 collagen fibers & mixture of calcium salts – Vascularized - caniculi - extensive blood vessels in matrix for exchange of materials – Covering - Periosteum (2 layers) • fibrous outer layer • cellular inner layer – Growth - Appositional • undergoes extensive remodeling on a regular basis • responds to stresses: grow thicker & stronger = exercise