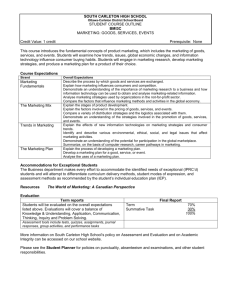
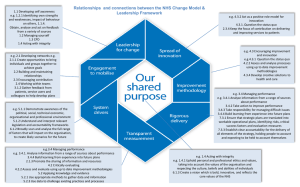
Engaging with Imagery
advertisement

Is a Picture Worth a Thousand Words? Engaging with Visual Culture Outline of Workshop • • • • • • • • Why analyse visual culture? Using Imagery Media and Themes Reading Images Reading a Building Objects and Artefacts What Next? Further reading 1. Why analyse visual culture? 2. Understanding how we tell stories about ourselves and others through images and visual culture ….. 3. Key skills : observation, analyses, identification, description, explanation, argument, awareness, self expression, oral and literacy skills ….. 4. You should treat an image, artefact or building the same as you would any written text: INTERROGATE, QUESTION and ANALYSE. Reference Images are relevant to all subject areas To illustrate Provide data In your presentation Using Imagery Marketing and promotion The focus of discussion Your own imagery Visual planning and brainstorming Evidence of process What ‘media’? • The term media in this context means ‘the agency or means of doing something … the material or form by which something is communicated.’ [Oxford Dictionary] Activity 1: Now we have considered why and how you can use visual culture within your Extended Projects, in pairs jot down all the different types of media which make up visual culture that you can think of. Media Photography Advertising Maps Clothing Packaging Architecture Fine Art Flags Graffiti Themes Race Sexuality Gender Religion Ethnicity The Canon Memory Space and Place Digital/ Cyber Signage Authorship Artefacts Spatial Design Film/ TV Viewer The Gallery Products Family Animation Performance Narrative What theories can you apply? What is it (i.e. media)? Relationship between the image and written documents? What’s its relevance socially, politically, economically? Who made it? When was it created? Reading Images What codes and signifiers are used to generate meaning? Audience? Purpose? Relationship between text and image? Where is it displayed? What is the composition? How is colour used? How is it displayed? Where are you viewing it? What is present in the image? Activity 2: Codes & Signifiers • In pairs discuss the symbolism or associations of the colour ‘red’ • This is a basic example. The meanings generated by this colour would also depend on the other content of the image, and the country or culture it refers to • Do you know of any images, films, posters etc where red has been used effectively? Activity 3: Comparing Images Applying the questions from the Reading Images wheel, in pairs analyse how the graffiti image on the left (by an anonymous artist) has appropriated the Alfred Leete’s World War I Lord Kitchener recruitment poster (1914). Other Visual stimuli Activity 4: Reading a Building • There might be further questions you need to consider if you are reading different types of visual stimuli, other than 2d images, • For instance, consider a building – What questions might you need to consider to analyse or respond to the built environment? Reading a Building Age Stories and narratives Style Inhabitants/ users Ornament or decoration Uses Spaces Location or site Materials used The ‘life cycle’ of an object ……. Object is made/ created/ ‘born’ Object is distributed Object is then purchased Object goes through a process of use Object discarded …. Thrown away/ lost/ given away/ passed on to another Object begins a new life: in landfill/ recycled/in someone else’s property/ waiting to be purchased ….. The ‘life cycle’ of an object ... For an interesting example of the life cycle of an object, watch the 18min film Plastic Bag, directed by Ramin Bahrani (2009). The film can be found on YouTube and Futurestates.tv http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YDBtCb61Sd4, or http://www.futurestates.tv/episodes/plastic-bag Objects and Artefacts Questions: • • • • • • • What is it? Where is it from? What is its age? What is it made of? What is its purpose? What visual details are there? What does it feel like? What Next? • Use the window as a frame – what is the image in that frame? • Analyse the front page of a newspaper or magazine • Evaluate an advertising billboard • Examine a company website • Respond to a personal photograph • Assess the layout and design of a favourite shop • Record the images and objects on your street • Consider the design of food packaging Further Reading Barthes, Roland, Camera Lucida: Reflections on Photography. London: Vintage, 1993. Berger, John, Ways of Seeing. London: Penguin Classics, 2008. Fernie, Eric, ed, Art History and its Methods: A Critical Anthology. London: Phaidon, 1995. Honour, Hugh, Fleming, John, eds, A World History of Art. London: Laurence King, 2009. Howells, Richard, Visual Culture: An Introduction. Cambridge: Polity Press, 2003. Pearce, Susan M, ed, Interpreting Objects and Collections. London: Routledge, 1994. Pointon, Marcia, History of Art: A Student’s Handbook. London: Routledge, 2002. Laneyrie-Dagen, Nadeije, How to Read Paintings. Edinburgh: Chambers, 2004.