MACROMOLECULES
advertisement

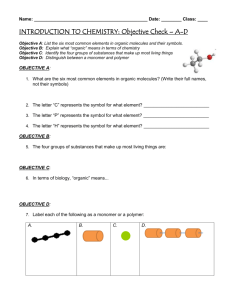
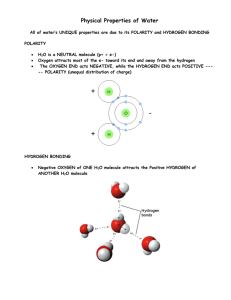
BIO.A.2.2.1: To explain how carbon is uniquely suited to form biological macromolecules Objective: To discuss the unique properties of carbon Warmup: What do you think of when you hear the word organic ? CARBON Carbon’s atomic structure: How many electrons are in carbon’s valence electron level? 4 Is carbon reactive? Yes, it’s not full How many bonds can carbon form? 4 Because carbon can form these bonds, it forms covalent bonds with other carbon atoms to form a variety of carbon backbones (skeletons). Carbon backbones are drawn based on their chemical formulas. For example, which carbon arrangement above matches to: C6H12 straight chain C6H6 ring C6H14 branched Organic molecules contain carbon attached to hydrogen. Oxygen and nitrogen may also be in the molecule. Example: C6H12O6 and C18H34O3 Inorganic molecules contain carbon or hydrogen but not both. They are usually described as being noncarbon based. Example: H2O, NaCl, CO2 Using these definitions, identify the following molecules as either organic (O) or inorganic (I) C5H12 H3PO4 NaCl HCl NH3 CH4 C10H22 CO2 H2O C3H8 = = = = = = = = = = O I I I I O O I I O Organic molecules also contain functional groups. These groups are responsible for organic molecules having specific properties. Common examples are shown below: Elements in each group: oxygen, hydrogen carbon, oxygen oxygen, carbon, hydrogen hydrogen, nitrogen sulfur, hydrogen 1. In order for a molecule to be classified as organic, it must contain hydrogen and ________. A) fat B) water C) carbon D) sugar 2. Atoms of what element form the backbone of large, complex molecules such as sugars and fats? A) Oxygen B) Sodium C) Carbon D) Sulfur 3. Carbon atoms have four electrons in their outer shell. This means that a single carbon atom can form up to_______ bonds with other atoms. A) two B) four C) six D) eight 4. Why can carbon form chains, branches and rings? A) Most organic compounds are ionic B) It has four electrons in its outermost shell C) It only bonds with hydrogen D) Most organic compounds have functional groups 5. Carbon is able to form diversity of organic molecules because of carbon’s A) Ability to bond with up to four other atoms. B) Capacity to form single and double bonds. C) Ability to bond together to form extensive branched, unbranched and ring structures. D) All of the choices are correct. Large molecules in living things are called macromolecules They are also referred to as polymers Each is composed of smaller subunits called monomers Four macromolecules in humans: Macromolecule (Polymer) Monomer Function Example Carbohydrate Monosaccharide Broken down glucose sucrose starch for chemical energy Compose plant cell walls Four macromolecules in humans: Macromolecule (Polymer) Monomer Lipid Glycerol & fatty acid Function Builds membranes Broken down for chemical energy Example Fats Oils Waxes Four macromolecules in humans: Macromolecule (Polymer) Monomer Function Example Proteins Amino acids Controls chemical reactions Albumin Many other jobs Hemoglobin Four macromolecules in humans: Macromolecule (Polymer) Monomer Function Example Nucleic acids Nucleotides Store genetic information DNA Build proteins RNA https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=b7TdWLNhMtM Building Polymers: dehydration synthesis (or condensation) “de” = remove “hydro” = water https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=b7TdWLNhMtM Building Polymers: dehydration synthesis (or condensation) Example: Glucose + C6H6O6 + Fructose Sucrose + H2O C6H6O6 C12H22O11 + H2O Each time a monomer is added to the chain, a H2O molecule is released. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=b7TdWLNhMtM Breaking Polymers: hydrolysis “hydro” = water “lysis” = to break https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=b7TdWLNhMtM Breaking Polymers: hydrolysis Example: Sucrose + H2O Glucose + Fructose C12H22O11 + H2O C6H6O6 + C6H6O6 Bonds are broken in a polymer by adding an H2O molecule to them. 1. Polymers form (breakdown into) monomers with the consumption of which chemical compound? A) ADP B) Water C) Ethane D) Nitrogen 2. Polymers are formed from monomers with the removal of what molecule? A) ADP B) Water C) Ethane D) Nitrogen 3. The diagram above shows a reaction that forms a polymer from two monomers. What is this type of reaction called? A) Glycolysis B) Hydrolysis C) Photosynthesis D) Dehydration synthesis (condensation)