The Digestive System
advertisement

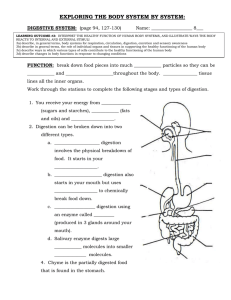
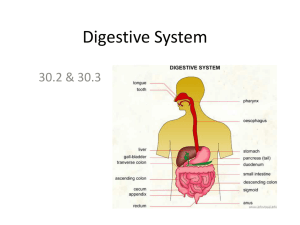
The Digestive System Chapter 45 Animals are heterotrophs • Require fuel – Chemical energy is obtained from the oxidation of complex organic molecules • Require essential nutrients – Chemicals an animal requires but cannot synthesize – varies from species to species – Essential amino acids – human adults can produce 12 of the 20, making 8 essential – Essential fatty acids – deficiencies are very rare – Vitamins and minerals (required in small amounts) Food Processing • Ingestion – The act of eating • Digestion – Breaking down food into smaller molecules – Polymers monomers – Mechanical digestion: physically breaks food up and increases its surface area – Chemical digestion: enzymatic hydrolysis uses water to break bonds in polymers • Absorption – The uptake of small molecules into the body • Elimination – Undigested material passes out of the body The Mammalian Digestive System • The oral cavity – Begins both physical and chemical digestion • Teeth + saliva produce bolus • The pharynx – Epiglottis helps prevent food in trachea • The esophagus – Peristalsis – rhythmic contractions that move food; starts as voluntary and changes to involuntary The Mammalian Digestive System… • The stomach – Stores food and performs preliminary digestion • Churning to mix food into chyme • Gastric juice works mainly on proteins • The small intestine – – – – Most enzymatic hydrolysis of food and absorption of nutrients Also involved: pancreas, liver, gall bladder Huge surface area provided by villi and microvilli Nutrients cross into bloodstream by diffusion and active transport • The large intestine – Reclaiming water from feces is the major job – Intestinal bacteria live on organic material – produce vitamin K