Sc8 Section 3.2 Factors Affecting Immune System
advertisement
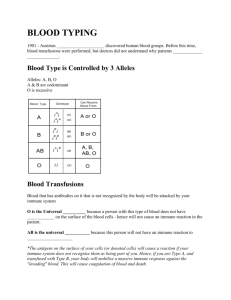
The (First Day Back) Plan… 2 April 2013 • Welcome back… We need to clear up some of those Spring Break cobwebs • A few tasks to accomplish: Review Ch2 Test & Assessment Hopefully this goes “smoother” Mark Osmosis Jones Handout • Quick Review of where we’re at 3.1 – The Immune System • Start 3.2 – Factors Affecting the Immune System (c) McGraw Hill Ryerson 2007 3.1 Immune System Review • Tell me what this is: • Pathogen: • Second Line also involves: B-Cells Produce antibodies to combat antigens Germs or disease-causing invaders • First Line of Defence: Skin & Linings of all internal body systems (Examples?) T-Cells Helper: activates B cells Killer: kill antigens on their own i.e. sweat and oil on skin, mucus and cilia in nose & gastric juices in stomach • Second Line of Defence: Includes “innate immune system” Born with (Examples?) Includes inflammation, white blood cells Also “acquired immune response” Battles antigen (body doesn’t recognize) • Active Immunity Memory to combat future infection • Questions? (c) McGraw Hill Ryerson 2007 3.2 Factors Affecting the Immune System • Vaccines are weakened versions of a disease pathogen that are given to people to protect them from getting the disease later. • Vaccines allow your body to create antibodies against the disease. • Boosters are needed for some vaccines to extend the immune system’s memory. See pages 110 - 111 (c) McGraw Hill Ryerson 2007 Disorders of the Immune System Allergies • An allergy is an unusually high sensitivity to some substance. • Any substance that causes an allergic reaction is called an allergen. Common allergens are: milk, pollen, and dust. • Body releases chemical called histamine to fight allergen. Common symptoms include a runny nose and watery eyes. Dust Mite • Severe allergies can cause an anaphylactic shock. See pages 112 - 113 (c) McGraw Hill Ryerson 2007 Disorders of the Immune System AIDS – Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome • AIDS is caused by a virus called HIV • HIV attacks the immune system by infecting Helper T Cells. When other pathogens or antigens enter the body the immune system can’t activiate Killer T cells or B cells. • AIDS is transmitted by blood and semen. Illustration of HIV See pages 113 - 114 (c) McGraw Hill Ryerson 2007 Taking Care of Your Immune System Important steps you can take to help your immune system stay healthy. See page 114 (c) McGraw Hill Ryerson 2007 Tomorrow and beyond… • Tomorrow’s task: Review 3.2 Handout CYU P.117 # 2-12, 15-17 • Thursday: Review CYU P.117 Chapter Review Day Chapter Review in Text Chapter Summary Sheets Tie up lose ends: Vocab Missed Assignments etc. (Bill Nye…) • Friday: Ch 3 Unit Test… (c) McGraw Hill Ryerson 2007