Unit 7 * Cellular respiration
advertisement

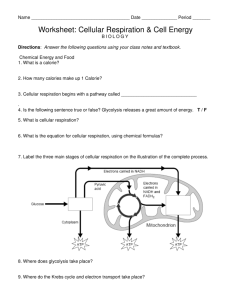
[UNIT 7 – CELLULAR RESPIRATION] Biology Notes Outline 1. Living cells require __________________________________ from outside sources. 2. How do herbivores obtain energy? 3. How do carnivores obtain energy? 4. Energy flows into an ecosystem as _____________________ and leaves as _________________. 5. What does photosynthesis use as an energy source? 6. What does cell respiration use as an energy source? 7. What does ATP stand for? 8. What is the purpose of ATP? 9. What do cells use ATP for? 10. ATP is broken down into ______________. a. This releases ________________. b. ADP can be remade into _______________ when the cell has more ______________. 11. What does NADH do? a. NADH is the ______________ version of the molecule. It carries a _______________ and two _______________________________. b. NAD+ is the ______________ version of the molecule. 12. The breakdown of organic molecules _____________________ energy. 13. Cellular respiration uses _______________ to generate this energy as _____________. Biology Teaching Resources http://www.aurumscience.com/biology.html 1 [UNIT 7 – CELLULAR RESPIRATION] Biology Notes Outline 14. Write the chemical equation for cellular respiration: 15. What is glycolysis? a. Where does it occur? b. During glycolysis, what happens? c. What two molecules are produced? 16. List all of the molecules used up by glycolysis: a. b. c. 17. List all of the molecules produced by glycolysis: a. b. c. 18. Glycolysis produces ATP _________________, which is an advantage when: ___________ ____________________________________. 19. Glycolysis does not require _________________________. 20. Where does pyruvic acid go after glycolysis is over? 21. What enzyme helps transport it there? Biology Teaching Resources http://www.aurumscience.com/biology.html 2 [UNIT 7 – CELLULAR RESPIRATION] Biology Notes Outline 22. What happens during the citric acid cycle? 23. List all of the molecules produced during the citric acid cycle: a. b. c. d. 24. Where does the electron transport chain occur? a. Electrons from ________________ are _______________ along the chain, from one _______________ to another. b. Each time an electron is passed, what happens? c. Electrons drop in _________________ until they reach the final part of the chain, ______________. d. This forms __________________. 25. What has the electron transport chain created? a. H+ then moves _____________________________, into the inner fluid. b. The H+ ions pass through a _____________________ called ____________________. c. The ATP synthase uses this flow of H+ ions to convert __________________________ into ______________________________. 26. Summarize the sequence of cellular respiration Biology Teaching Resources http://www.aurumscience.com/biology.html 3 [UNIT 7 – CELLULAR RESPIRATION] Biology Notes Outline 27. About _______________ of the energy in glucose is transferred to ____________, making __________ total ATP. a. What happens to the other 60%? Fermentation 28. If there is no oxygen present, what can the cell do? 29. Describe the two parts to fermentation: a. b. 30. The two types of fermentation are ____________________ and ______________________. 31. Alcoholic fermentation is used by _________________. a. What does this produce? b. What do we use it for? 32. Humans use _________________________ when they are out of breath. a. The waste product is ______________________. b. This causes _____________________________. 33. What products can be made from this type of fermentation? Biology Teaching Resources http://www.aurumscience.com/biology.html 4