Earth Science - Oceanography
advertisement

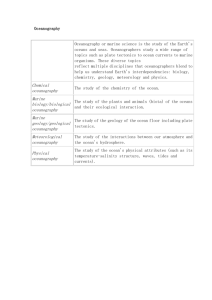
Walk-In Quietly study your notes while roll is being taken. When instructed, put everything away in your backpack, except your pencil and put up your privacy folder Remember to keep your eyes on your own paper! Be sure to use the bolded vocabulary words in your answer for essay question #18 & 19! Write in complete sentences and use proper punctuation! When you are finished, place your test in your privacy folder and fold it up. Put your pencil away and take out your red pen or crayon. Quietly read or rest until everyone is finished Follow the directions for correcting the matching section Hand in your test! Walk-In Copy the question and answer in sentences: How do you think scientists know facts about the ocean and its lifeforms? Possible Answers Scientists have dived below the ocean surface to observe and collect samples. Engineers have created vehicles that can go deep into the ocean to observe. Researchers at the shoreline have observed waves, shore life and weather. What do we know about the oceans? Watch this video clip about the oceans, its mysteries and its lifeforms! How do we know all this?!? The branch of science called… Oceanography (Write this as a title for today’s work!) “Water World” Oceanography “…is the application of science to the study of phenomena in the oceans”. Why Study Oceanography? Oceans comprise (make up) 71% of the Earth’s surface Oceans contain 97% of the water on or near the Earth’s surface Oceans can be a source of food Used for transportation and travel Oceans have a major effect on weather They provide resources near the shoreline (food, plants, minerals). Read: Areas of Study Oceanography has different branches that study the water, rocks at the bottom, wave movement, and life forms. Write down each branch and its main functions… Geological Oceanography (Marine Geology) - Study of rocks and sediments of the ocean floor, and how they form. Physical Oceanography - How and why ocean currents flow, how waves form by the wind, climate, and weather systems. Chemical Oceanography - Composition of sea water, chemicals that change it, and effects of marine pollution. Biological Oceanography (Marine Biology) - Studies organisms that live in the oceans and their relationships to the environment. Ocean Engineering - Design and use of oceanographic instruments and vehicles to explore the ocean. Which branch of oceanography? Look at each slide coming up and decide which part of oceanography is being studied. Which branch studies the temperatures and climate? (Click for answer!) Physical oceanography! Which branch of oceanography focuses on weather systems? Click for answer! Physical oceanography! Which branch studies wave motion? Physical oceanography! Which branch of oceanography studies marine life and food chains? Click for answer Biological oceanography! Which branch of oceanography studies the rocks on the ocean floor? Geological oceanography Which branch observes different kinds of ocean creatures? Biological oceanography Which branch examines the composition of ocean water? Chemical oceanography Which branch develops vehicles to explore the ocean? Oceanographic engineering Exploring the Oceans Researchers use SUBMERSIBLES (small vehicles that can go under water) to explore the ocean and its floor. Submersibles have to withstand very high pressure from the water, and very cold temperatures. They need powerful lights, and a reliable oxygen supply for the researchers. What does a submersible do? Watch this video clip of “Alvin”, a submersible built in 1964 and named after its creator, Allyn Vine. Alvin has made more than 4,700 dives for research! Design and draw a submersible! In your notebook, draw a large diagram of a submersible YOU would design. Label the parts of it, such as lights, seating areas, viewing windows, moveable arms, oxygen tanks, and other things needed to make it work! Summary: What is Oceanography? Broad science focused on the oceans – Geology/geophysics, chemistry, physics, biology, engineering Highly collaborative (work together) We are still exploring (!) but … Feeds also into ocean policy, management, and conservation