Early American Government The Administrations of
advertisement

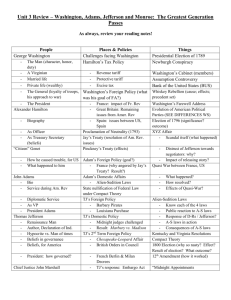
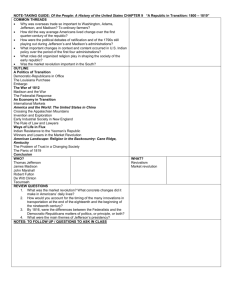
Early American Government The Administrations of Washington, Adams, Jefferson, and Madison George Washington 1789-1797 Washington’s Mount Vernon Virginia Washington’s Oath of Office Washington statue outside Federal Hall New York Jefferson and Hamilton Sec. of State Sec. of the Treasury The Federalist & The Anti-Federalist Hamilton’s Report on the Public Credit Funding Assumption National Bank Excise Tax on Whiskey The French Revolution of 1789 The fall of Louis XVI Political factions favor different countries Federalist favor England Anti-Federalists (Dem-Republicans) favor France The unpopular Jay’s Treaty What of the Native Americans? Thomas Pinckney’s Treaty with Spain The Whiskey Rebellion demonstrates the power of the new government Washington reviewing troops ready to suppress the rebellion Washington’s Farewell 1796 • Avoid political factions • Avoid “entangling foreign alliances” • Friendly to all countries The Presidency of John Adams 1797-1801 Election of 1796 Adams over Jefferson The XYZ Affair “Millions for defense, but not one cent for tribute” John Marshall The Alien and Sedition Acts 1798 A fight in Congress over the Sedition Act Kentucky and Virginia Resolutions Can states nullify federal law? T. Jefferson and J. Madison The Peaceful Revolution The 1800 Election of Democratic Republican Thomas Jefferson • • • • “Smaller Federal Government Reduced Government Spending Smaller Military/Spending Broader participation in Government President Thomas Jefferson 1801-1809 Jefferson’s Montecello Virginia Election of 1800 Louisiana Purchase Treaty • Solving the “Constitutional Dilemma” • 1803 • $15 Million • Doubles the size of the US Livingston, Monroe & Talleyrand • Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte of France Revolt in Haiti Meriwether Lewis and William Clarke • Meriwether Lewis and William Clarke and Sacagawea Lewis and Clark Expedition 1804-1806 The End of Slave Importation 1808 Jefferson’s second term is plagued by foreign affairs problems The Barbary Pirates The shores of Tripoli The Embargo Act of 1807 Troubled relations with England and France (Quasi-War) The death of Alexander Hamilton Weehawken, N.J. 1804 Chief Justice John Marshall’s decision William Marbury vs. James Madison 1803 President James Madison 1809-1817 Madison’s home at Montpellier Virginia The Election of 1808 James Madison America’s Second War for Independence “Mr. Madison’s War” Background Causes • • • • • Impressment The War Hawks Desire to expand into Canada Desire to pacify Native Americans Violation of neutral rights at sea Impressment of U.S Sailors Leading War Hawks Henry Clay and John C. Calhoun First Lady Dolly Madison British burning of the White House The Battle of Fort McHenry 1814 “The Star Spangled Banner” Francis Scott Key The Harford Convention 1814 First threats of Secession The Battle of New Orleans 1815 after the Treaty of Ghent The hero of New Orleans Andrew Jackson The Treaty of Ghent 1814 Status Quo Results/Significance of the War of 1812 • • • • • • American Manufacturing grows The fading of the Federalist party Acceptance of British Canada The emergence of Andrew Jackson and William Henry Harrison Increased US international credibility Growing spirit of “Nationalism”