Notes 3.4
advertisement
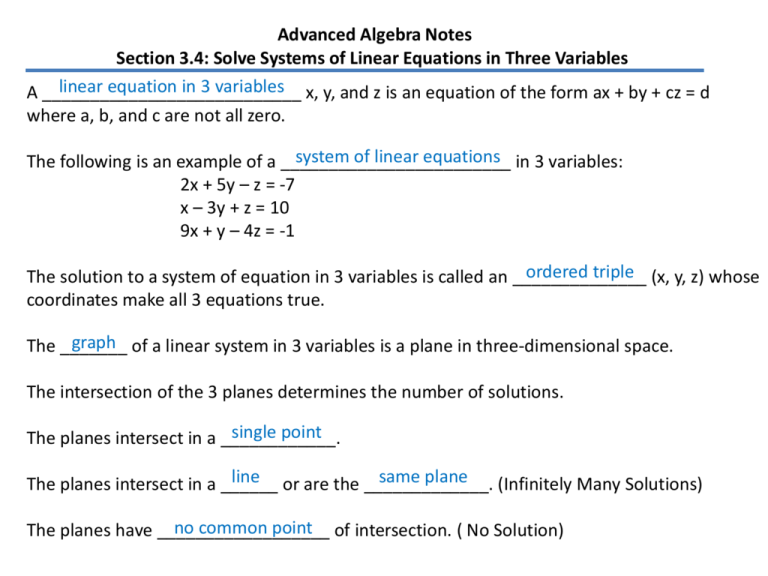
Advanced Algebra Notes Section 3.4: Solve Systems of Linear Equations in Three Variables linear equation in 3 variables x, y, and z is an equation of the form ax + by + cz = d A ___________________________ where a, b, and c are not all zero. system of linear equations in 3 variables: The following is an example of a ________________________ 2x + 5y – z = -7 x – 3y + z = 10 9x + y – 4z = -1 ordered triple (x, y, z) whose The solution to a system of equation in 3 variables is called an ______________ coordinates make all 3 equations true. graph of a linear system in 3 variables is a plane in three-dimensional space. The _______ The intersection of the 3 planes determines the number of solutions. single point The planes intersect in a ____________. line or are the _____________. same plane The planes intersect in a ______ (Infinitely Many Solutions) no common point of intersection. ( No Solution) The planes have __________________ Steps: 1. Rewrite 2 of the equations in 3 variables as equations in 2 variables using substitution or elimination. 2. Solve those 2 equations for both variables like you were taught in section 3.2. 3. Once you get the values from step 2, substitute them in to one of the original equations and solve for the 3rd value. Then write your ordered triple. ** If the variables disappear and you get a false statement -3 = 0, then the system has no solutions. ** If the variables disappear and you get a true statement 0 = 0, then the system has infinitely many ordered triple solutions. Examples: 1. -y = -2x – 6z – 4 y = 2x + 6z + 4 2x – y + 6z = -4 6x + 4y – 5z = -7 -4x – 2y + 5z = 9 6x + 4(2x + 6z + 4) – 5z = -7 6x + 8x + 24z + 16 – 5z = -7 14x + 19z = - 23 -4x – 2(2x + 6z + 4) + 5z = 9 -4x – 4x – 12z – 8 + 5z = 9 -8x – 7z = 17 14 x 19 z 23 4(14 x 19 z ) (23)4 56 x 76 z 92 8 x 7 z 17 7(8 x 7 z ) (17)7 56 x 49 z 119 27 z 27 8 x 7 z 17 8 x 7(1) 17 8 x 7 17 8 x 24 x3 y 2x 6z 4 z 1 y 2(3) 6(1) 4 y 664 y 4 3, 4,1 2. 3x + y – 2z = 10 6x – 2y + z = -2 x + 4y + 3z = 7 3x y 2 z 10 3x y 2 z 10 2(6 x 2 y z ) 2(2) 12 x 4 y 2 z 4 15 x 3 y 6 3(6 x 2 y z ) (2) 3 x 4 y 3z 7 18 x 6 y 3 z 6 x 4 y 3 z 7 17 x 10 y 13 15 x 3 y 6 15(1) 3 y 6 15 3 y 6 3y 9 10(15 x3 y ) (6)10 150 x 30 y 60 3( 17 x 10 y ) (13)3 51x 30 y 39 99 x 99 x 1 (1,3, 2) y 3 6x 2 y z 2 6(1) 2(3) z 2 66 z 2 z 2 3. x+y–z=2 3x + 3y – 3z = 8 2x – y + 4z = 7 3( x y z ) (2) 3 3 x 3 y 3 z 6 3 x 3 y 3 z 8 3 x 3 y 3 z 8 02 4. x+y+z=6 x–y+z=6 4x + y + 4z = 24 x y z 6 x y z 6 x y z 6 4 x y 4 z 24 2 x 2 z 12 5 x 5 z 30 5(2 x 2 z ) (12)5 10 x 10 z 60 2(5 x 5 z ) (30) 2 10 x 10 z 60 00 Infinite # of ordered triples