2x - Miss aguilera
advertisement

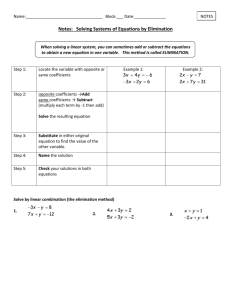
System of Linear Equations Illustrating Elimination Solving Systems of Equations by Elimination Step 1 Write the system so that like terms are aligned. Step 2 Eliminate one of the variables and solve for the other variable. Step 3 Substitute the value of the variable into one of the original equations and solve for the other variable. Step 4 Write the answers from Steps 2 and 3 as an ordered pair, (x, y), and check. Example 1: Elimination Using Addition Solve 3x – 4y = 10 by elimination. x + 4y = –2 Step 1 Step 2 3x – 4y = 10 x + 4y = –2 4x + 0 = 8 4x = 8 4x = 8 4 4 x=2 Write the system so that like terms are aligned. Add the equations to eliminate the y-terms. Simplify and solve for x. Divide both sides by 4. Example 1 Continued Step 3 x + 4y = –2 2 + 4y = –2 –2 –2 4y = –4 4y –4 4 4 y = –1 Step 4 (2, –1) Write one of the original equations. Substitute 2 for x. Subtract 2 from both sides. Divide both sides by 4. Write the solution as an ordered pair. Example 2: Elimination Using Subtraction Solve 2x + y = –5 by elimination. 2x – 5y = 13 Step 1 2x + y = –5 –(2x – 5y = 13) Step 2 2x + y = –5 –2x + 5y = –13 0 + 6y = –18 6y = –18 y = –3 Add the opposite of each term in the second equation. Eliminate the x term. Simplify and solve for y. Example 2 Continued Step 3 2x + y = –5 2x + (–3) = –5 2x – 3 = –5 +3 +3 Write one of the original equations. Substitute –3 for y. 2x Simplify and solve for x. = –2 x = –1 Step 4 (–1, –3) Add 3 to both sides. Write the solution as an ordered pair. Example 3A: Elimination Using Multiplication First Solve the system by elimination. x + 2y = 11 –3x + y = –5 Step 1 Step 2 x + 2y = 11 –2(–3x + y = –5) x + 2y = 11 +(6x –2y = +10) 7x + 0 = 21 7x = 21 x=3 Multiply each term in the second equation by –2 to get opposit y-coefficients. Add the new equation to the first equation. Simplify and solve for x. Example 3A Continued Step 3 x + 2y = 11 3 + 2y = 11 –3 –3 2y = 8 y=4 Step 4 (3, 4) Write one of the original equations. Substitute 3 for x. Subtract 3 from each side. Simplify and solve for y. Write the solution as an ordered pair. Example 3B: Elimination Using Multiplication First Solve the system by elimination. –5x + 2y = 32 2x + 3y = 10 Step 1 2(–5x + 2y = 32) 5(2x + 3y = 10) –10x + 4y = 64 +(10x + 15y = 50) Step 2 19y = 114 y=6 Multiply the first equation by 2 and the second equation by 5 to get opposite x-coefficients Add the new equations. Simplify and solve for y. Example 3B Continued Step 3 2x + 3y = 10 2x + 3(6) = 10 2x + 18 = 10 –18 –18 Step 4 2x = –8 x = –4 (–4, 6) Write one of the original equations. Substitute 6 for y. Subtract 18 from both sides. Simplify and solve for x. Write the solution as an ordered pair. x 2 y 10 2 x 5 y 52 Find a constant that you can multiply the first equation that will get you the opposite of -2x. 2* ( x 2 y 10) 2 x 4 y 20 (6, 8) Elimination x 2(8) 10 x 16 10 x 10 16 2 x 4 y 20 2 x 5 y 52 9 y 72 x6 y 8 Lesson Check Solve each system by elimination. 1. 2x + y = 25 3y = 2x – 13 2. –3x + 4y = –18 x = –2y – 4 (2, –3) 3. –2x + 3y = –15 3x + 2y = –23 (–3, –7) (11, 3)