Section 17.1 Summary – pages 443-449
advertisement

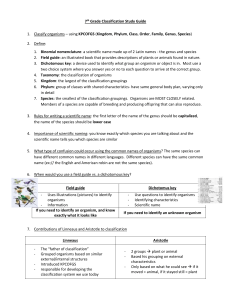
CLASSIFICATION • Biologists want to better understand organisms so they organize them. • One tool that they use to do this is classification—the grouping of objects or information based on similarities. How classification began… • Taxonomy is the branch of biology that groups and names organisms based on studies of their different characteristics. • Biologists who study taxonomy are called taxonomists. Aristotle’s System • The Greek philosopher Aristotle (384-322 B.C.) developed the first widely accepted system of biological classification. • He classified all the organisms he knew into two groups: plants and animals. Aristotle’s System • He subdivided plants into three groups, herbs, shrubs, and trees, depending on the size and structure of a plant. • He grouped animals according to various characteristics, including their habitat and physical differences. Aristotle’s System • According to his system, birds, bats, and flying insects are classified together even though they have little in common besides the ability to fly. • As time passed, more organisms were discovered and some did not fit easily into Aristotle’s groups, but many centuries passed before Aristotle’s system was replaced. Carolus Linnaeus (1707-1778), a Swedish botanist • Linnaeus’s system was based on physical and structural similarities of organisms. He improved the system of naming plants and animals by a two-word name to identify the genus and species. “binomial nomenclature” Linnaeus’ System • Linnaeus’ showed relationships among organisms. • Eventually, some biologists proposed that structural similarities reflect the evolutionary relationships of species. • This way of organizing organisms is the basis of modern classification systems. Species Scientific Names • Modern classification systems use a two-word naming system called binomial nomenclature that Linnaeus developed to identify species. • In this system, the first word identifies the genus of the organism. • A genus (JEE nus) (plural, genera) consists of a group of similar species. • The second word, which sometimes describes a characteristic of the organism, is called the specific epithet. Species Scientific Names • Thus, the scientific name for each species, referred to as the species name, is a combination of the genus name and specific epithet. Homo sapiens Homo = Genus, sapiens = “wise man” Naming Organisms Why do we need to name organisms? What is the name of this organism? Why do scientists not want to use common names? The common name of many animals can be misleading. Ceylon frogmouth (Batrachostomus moniliger) is a bird. Killer whales (Orcinus orca )are the largest member of the dolphin family. Flying fish (Parezocoetus mesogaster) do not fly, but glide. Seahorse (Hippocampus zosterae) is not a horse, but a fish. Why do scientist not use common names? Confusing – more than one common name Misleading – starfish is not a fish Why use a scientific name? There is only one scientific name Felis concolor Species Scientific Names United States and England- Sparrow Spain – gorrion domestico Holland – huismus Scientific name: Passer domesticus Scientific Name What language is used for the scientific naming? LATIN What are the 2 parts of the scientific name? Genus (Latin for group) general description organisms share a major characteristic species exact kind only 1 kind of organism within a genus Recognizing Relationships Tell me something about each of these organisms. Carnegiea gigantea giant saguaro cactus Nymphaea odorata fragrant water lily Canis familiaris domestic dog Peromyscus californicus common California mouse Viola tricolor three color pansy Genus + species names should be used when referring to an organism. Species name alone is not enough. Drosophila melanogaster is a fruit fly. Thamnophis melanogaster is a garter snake. What is the correct way to write the scientific name? drosophila melanogaster Drosophila melanogaster Drosophila melanogaster D. melanogaster * Always capitalize the Genus and not the species. Why are scientific names in Latin? 1. Latin is no longer used in conversation. 2. It’s tradition. 3. Universal. Worksheet: Writing the Scientific Names of Animals COMMONNAME Human Dog Spanish lynx Tiger Jaguar Leopard Bullfrog Cameroon Toad Houston Toad Nile crocodile Caiman Jamaican boa Puerto Rican boa Jamaican iguana Mona iguana Desert monitor Komodo dragon Aquatic box turtle Peregrine falcon Piping plover Audouin's gull Relict gull Tooth cave spider GENUS Homo Canis Felis Panthera Panthera Panthera Rana Bufo Bufo Crocodylus Caiman Epicrates Epicrates Cyclura Cyclura Varanus Varnaus Terrapene Falco Charadrius Larus Larus Leptoneta + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + SPECIES sapiens familiaris pardina tigris onca pardus catesbeiana superciliaris houstonensis niloticus crocodilus subflavus inornatus collei stejnegeri griseus komodoensis coahuila peregrinus melodus audouinii relictus myopica SCIENTIFIC NAME Homo sapiens Canis familiaris Felispardina Panthera tigris Panthera onca P. pardus rana catesbeiana Bufo superciliaris Bufo houstonensis Crocodylus niloticus Caiman crocodilus Epicrates subflavus Epicrates inornatus Cyclura Collei Cyclura stejnegeri Varanus griseus varanus Komodoensis Terrapene coahuila Falco peregrinus Charadrius melodus Larus audouinii Larus relictus Leptoneta myopica Question 4 What is the difference between “classification” and “taxonomy?” Answer Classification is the grouping of objects or information based on similarities. Taxonomy is the branch of biology that classifies and names organisms based on their different characteristics. Question 5 What are the two parts that make up binomial nomenclature? Answer Binomial nomenclature comprises a genus name followed by a specific epithet.