Hailey
advertisement
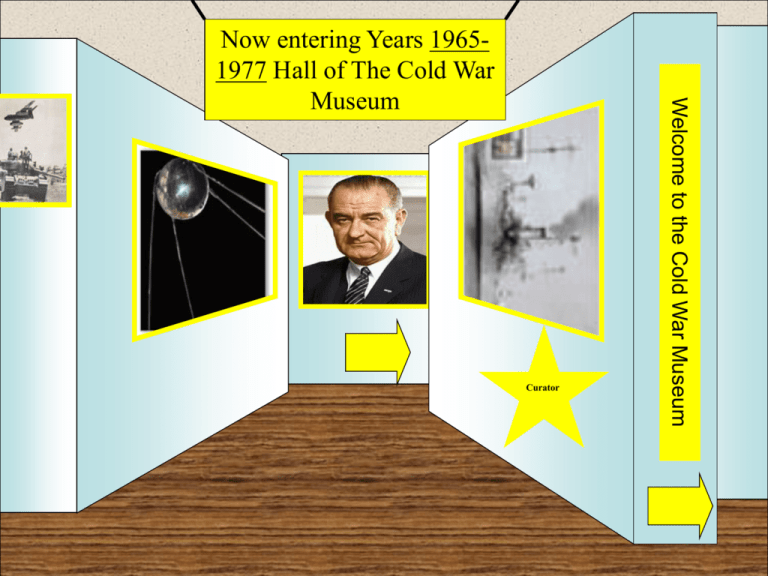
Museum Entrance Curator Welcome to the Cold War Museum Now entering Years 19651977 Hall of The Cold War Museum Room 3 Museum Entrance Artifact 1: Six Day War • Egyptian President, Gamel Abdel Nassar, was still angry about Egyptian defeat in the Suez-Sinai War in 1956. His feelings caused him to gather his allies and plan an invasion on Israel. He ordered the removal of all United Nations troops from areas surrounding Israel, the Sinai Peninsula, the Gaza Strip, Golan Heights, and West Bank, and replaced them with Palestinian troops. On June 5, 1967, before Nassar had a chance to command his troops to attack, Israel attacked Egypt. Israel had foreseen an attack and wanted the war on Arab soil, instead of their own. On the first day of war, over 90% of Egyptian aircraft were destroyed and Egyptian units in the Gaza Strip and Sinai Peninsula were defeated. Image acquired at: Wikipedia. Wikimedia Foundation, 21 Apr. 2014. Web. 21 Apr. 2014. Return to Room Artifact 2: Space Race USSR continued its lead in space exploration with the first person in space, cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin who orbited earth in Vostok 1, April 12, 1961. Less than a month later Allan Shepard became the first American in space. That same month, President Kennedy created the Apollo program designed to land a person on the moon “before the decade is out. Image acquired at: Wikipedia. Wikimedia Foundation, 21 Apr. 2014. Web. 21 Apr. 2014. Return to Room Artifact 3: Lyndon B. Johnson Johnson’s foreign policy, of course, remains best known for his handling of the Vietnam War. Throughout his presidency, he remained faithful to one basic goal: doing the minimum possible to ensure that South Vietnam did not become a Communist state. Unfortunately for the President, the “minimum possible” grew to dangerous extremes-U.S. troop totals, around 16,000 when Johnson entered the White House, peaked at 532,000 in early 1968. Johnson’s policies brought the United States no closer to victory in Vietnam, but badly divided the liberal movement at home, paving the way for his decision not to run for reelection in 1968 Image acquired at: Wikipedia. Wikimedia Foundation, 21 Apr. 2014. Web. 21 Apr. 2014. Return to Room Artifact 4: Bombing of USS Liberty • • On the fourth day of the 1967 Arab-Israeli War, the intelligence ship USS Liberty was steaming slowly in international waters, 14 miles off the Sinai Peninsula. Israeli armored forces were racing deep into the Sinai in hot pursuit of the retreating Egyptian Army At 0800 hrs, 8 June, 1967, eight Israeli recon flights flew over Liberty, which was flying a large American flag. At 1400, waves of Israeli Mystere and Mirage-III fighter-bombers attacked with rockets, napalm, and cannon, concentrating on the ship’s antennae and electronic dishes. Liberty was left afire, listing. Eight of her crew lay dead, 100 wounded, including Commander William McGonagle. Image acquired at: The Cold War Museum." Cold War Museum. N.p., n.d. Web. 22 Apr. 2014. Return to Room Artifact 5: Attack on South Vietnam On January 21, 1968, the North Vietnamese coordinated with the Viet Cong to plan a surprise attack on the South Vietnamese and the U.S. troops. This was the first of two major surprise attacks. On January 21, the North Vietnamese and the Viet Cong bombed a few important American bases in South Vietnam. This was a total shock to America and was a major blow to its confidence. The North Vietnamese destroyed much of the American artillery and supplies. However, this attack was actually a decoy in order to distract the South for an upcoming attack which would be much more destructive Image acquired at: "Vietnamese Family Tries to Escape Fighting, 1968." Most Read. N.p., n.d. Web. 22 Apr. 2014. Return to Room Artifact 6: Czechoslovakia Uprising • • Image acquired at: "Alexander Dubcek." Alexander Dubcek. N.p., n.d. Web. 22 Apr. 2014. The communist party, in addition to being burdened with a failing economy, was being toward apart by a conflict revolving around the extent to which the liberalization should be applied and an effort within the Slovak community for greater autonomy. In 1968, with their political, economic and social problems reaching critical mass, the communist party of Czechoslovakia replaced Novotny as Party Leader with Alexander Dubcek. Dubcek pushed practical reforms across the board, not only for Czechoslovakia but for the Warsaw Pact (the Soviet answer to NATO) as well. Dubcek’s reforms would, as he put it, put “a human face” on socialism Return to Room Artifact 7: Siege of Khe Sahn • After seventy-seven days under full-scale siege at Khe Sanh, the frantically distraught American Forces were finally able to retake a strategically essential transportation path known as Route 9 to end the battle. Due to this newly safe passage, transportable American units were able to swarm the base by June 1968 and relieve the anxious soldiers from their defense station. After an apprehensive battle of attrition and sacrifice of life and nerves, United States General Westmoreland ordered the hard fought for base of Khe Sanh to not only be deserted but also destroyed. This was the longest single battle of the Vietnam war. Image acquired at: POLAPA STUDIOS." POLAPA STUDIOS. N.p., n.d. Web. 22 Apr. 2014 Return to Room Artifact 8: The Fall of Saigon • • Neither North nor South Vietnam was to be stopped by the words on the peace treaty, both determined to fight to the death on the battlefield. The end came two years later with the fall of Saigon. The peace accords in 1973 called a ceasefire and put in place provisions for the protection of the freedom of South Vietnam. Additionally it provided that if the North violated any of these agreements, U.S. troops would return to the aid of the South Vietnamese. Being well aware of the domestic problems following the Watergate Scandal and Nixon’s resignation, the North Vietnamese highly doubted the U.S.’s final promise and drafted a two year plan for the conquering of the South and reuniting the country under communist control. This assumption was confirmed when the United States Congress passed the Foreign Assistance Act in December of 1974 Image acquired at: "Fall of Saigon." Wikipedia. Wikimedia Foundation, 19 Apr. 2014. Web. 22 Apr. 2014. Return to Room Artifact 9: Operation Babylift • The horrific war left terns of thousands of children orphaned and homeless. In the final days of the war both Catholic and Buddhist Sisters could be seen running with armfuls of abandoned children to boats fleeing the country. Humanitarian groups in Vietnam urged the American government to take action, the most influential being Cherie Clark, the Friends of Children of Viet Nam (FCVN) representative in Vietnam. On April 3 President Gerald Ford announced in a mission deemed Operation Babylift, the U.S. military would fly 70,000 orphans out of Vietnam. Return to Room Image acquired at: "Operation Babylift. Mass Evacuation of Orphans from South Vietnam. 1975. - War Photos, Famous History Photos, World War Images, History Images." War Photos, Famous History Photos, World War Images, History Images. N.p., n.d. Web. 22 Apr. 2014. Artifact 10:The Khmer Rouge • In the 1960’s and 1970’s Cambodia was being pulled in many different directions. They were in the middle of a civil war and, at the same time were being drawn into the conflict in Vietnam. Cambodia is a small country, made up of mostly Buddhists. Prince Sihanouk was in the middle of a military coup, and was being overthrown by General Lon Nol, the president of the Khmer Republic. Prince Sihanouk eventually joined forces with a communist organization called the Khmer Rouge. Civil war began wreaking havoc across the country. While this civil war was going on, the Vietnam War was happening right next door. Americans killed over 750,000 Cambodians in the effort to destroy the North Vietnamese. It is estimated that over 150,000 Cambodians died in the civil war, most of them civilians. Image acquired at: Penh, Kevin Doyle/Phnom. "Putting the Khmer Rouge on Trial." Time. Time Inc., 26 July 2007. Web. 22 Apr. 2014. Return to Room Artifact 11: Jimmy Carter • • He was elected President on November 2, 1976. Jimmy Carter served as President from January 20, 1977 to January 20, 1981. Noteworthy foreign policy accomplishments of his administration, including the Panama Canal treaties, the Camp David Accords, the treaty of peace between Egypt and Israel, the SALT II treaty with the Soviet Union, and the establishment of U.S. diplomatic relations with the People’s Republic of China. He championed human rights throughout the world. Image acquired at: "Jimmy Carter." Wikipedia. Wikimedia Foundation, 21 Apr. 2014. Web. 22 Apr. 2014. Return to Room Artifact 12: The Ogaden War • In a blink of an eye, everything can change. It happened when Mengistu Haile Mariam was appointed to chairman of the military and head of state of Ethiopia on February 11, 1977. Throughout the rest of Mariam’s first year of reign, Ethiopia tried to suppress its opponents and enemies. Maxamed Siyaad Barre, president of Somalia, realized that Ethiopia was having major opposition against its own military and government, causing a lot of confusion and warfare. Image acquired at: War Between Somalia and Ethiopia." War Between Somalia and Ethiopia. N.p., n.d. Web. 22 Apr. 2014. Return to Room Hailey Nussbaum Hailey is currently enrolled at Clear springs high school, and is involved in the Student United Way program. She enjoys helping people learn from her mistakes and teaching people new things. Contact: Hailey Nusssbaum Return to Room

![vietnam[1].](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005329784_1-42b2e9fc4f7c73463c31fd4de82c4fa3-300x300.png)




