Introduction to Human Centered Design
advertisement

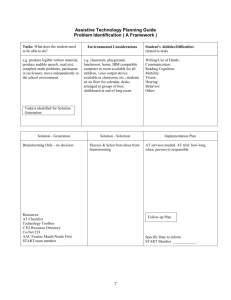
Introduction to HumanCentered Design: Conceptual Design and Prototyping EPICS High School Workshop Tuesday, July 12, 2011 William Oakes and Carla Zoltowski Creativity and Brainstorming Creativity is a divergent thinking skill in which we postpone judgment and try to see a situation from as many different perspectives as possible. Brainstorming is a term used for the creative generation of many ideas. Why Do It? Creativity and brainstorming can be applied in many situations. Certainly important at the beginning of the design process, it can also be applied to any form of problem solving. It is particularly helpful in getting “unstuck” when your problem solving bogs down. It is also applied in trouble-shooting and failure analysis to develop the possible hypotheses that will make up your differential diagnosis. Expanding the Design Space Brainstorming Brainstorming can be done individually or as a team Team brainstorming = Taking advantage of the contributions of the team Sum is greater than the individuals Theory is to stimulate our brains to use our whole brain to expand the options to include the best solution Brainstorming rules Explain the entire procedure to the team Choose one facilitator Records ideas and participates in the generation of ideas. Record ideas that are easily visible to the whole team. Rotate around the group with each person getting to add one idea per rotation. Let members say “pass” Move quickly. NO value judgments. Write ALL ideas down Facilitator treats ALL ideas the same Continue until the entire team is passing Brainstorming – 6-3-5 Group of 6 people Each person writes down 3 ideas Pass to right, next person adds to paper for 5 minutes.. Ideas can be new, extend, or modify original ideas No verbal communication during activity Brainstorming – 6-3-5 Practice Get in groups of 6; select one project from your group Each person writes down 3 ideas Pass to right, next person adds to paper for 5 minutes.. Ideas can be new, extend, or modify original ideas No verbal communication during activity Each group How many different ideas did your group come up with? Did you start running out of new ideas? Triggers Triggers are specific tools to actively bump your brain out of its ruts. They are designed to get you thinking from a different perspective. Many triggers are available (crazy, creative people are always thinking up more), and some are listed below. Other’s Shoes – Reconsider the problem from the perspective of a plumber, civil engineer, physician, child, attorney, basketball player, etc. You can keep this close to your personal comfort level by picking roles you know something about, like plumber perhaps, and then expand to more fanciful ones, like princess. Nature – How does nature deal with this issue, or how would you do it if you were Mother Nature? Opposite – How would you solve the opposite problem (from “cut down a tree” to “grow a tree”)? Or, consider the opposite of some of your ideas (from “cut with a saw” to join with “hot glue”). Random – Use random words, pictures, movie titles, professor names to generate more ideas. More Triggers Analogy – Consider what has similar function but different appearance (automatic clothes washer to washboard), what has similar appearance but different function (washboard to cheese grater), or what has a similar name and different use (bottle cap to baseball cap)? Craziest Idea – take the craziest idea and try use the kernel to get to a practical solution (“Cut down a tree with scissors” to “cut with large hydraulic shears”). Boundaries/Constraints – Remove, adjust, or explore the boundaries of the problem. (If the problem is a better way to wash clothes, what about recycling the old shirt into a new shirt instead of washing? Does it have to be “wash” or can it be “clean” or “deodorize”?) Anthropomorphize – Consider yourself to be the piece of equipment or process. Or consider yourself a molecule flowing through the system. (For “Why is this part failing?” think- “Am I getting hot anywhere, where do I feel the stress?”) Combine – Take different ideas and see what happens if you add them together, or combine them in some other way (Problem: “wash clothes” – combine “spray with a hose” and “pound on a rock” to “spray with wet rocks”) Other – Brainstorm your own trigger or find a trigger in a reference. Brainstorming - SCAMPER Substitute – can you use a different method, device, or material or changed the environment? Combine – can you combine ideas together to produce a better idea? Adapt – what ideas are similar that could be emulated or adapted to fit the current need? Modify, Minify, Magnify – can you change the current idea, make it smaller or larger in some way? Put to other uses – can you use the idea in a new way? Eliminate – are there any ideas that have been shown to not work? Reverse, Rearrange – would an opposing idea give you additional information, or can you interchange the key elements of the idea to form a new one? Looking at nature Innovative vehicle designs often are based on what we think of for a vehicle How many animals have you ever seen that move with wheels? Whack Pack app Explorer Role for discovering resources you’ll use to create new ideas Artist Role for transforming your resources into new ideas Judge Role for evaluating an idea and deciding what to do with it Warrior Role for implementing your idea Heraclitus Insights Practice with Triggers Other’s Shoes Nature Opposite Random Analogy Craziest Idea Boundaries/ Constraints Anthropomorphize Combine Each group Were using the triggers helpful in generating more ideas?