Data Collection and Analysis
advertisement

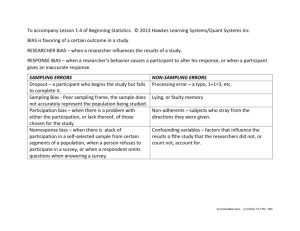
Research Design and Implementation - 2 Data Collection Methods Table 4-2 Relationship between Data Collection Method and Category of Research Category of Research Data Collection Method Exploratory Descriptive Causal Secondary Sources Information System a b Databanks of other a b organizations Syndicated Services a b b Primary Sources Qualitative Research Surveys Experiments a b b a b b a Research Tactics Measurement – Generally what questions do we ask so that we get the information we want Sampling Plan – How do we select a sample for the study such that we maximize its chances of faithfully representing the population of interest Analysis – confirming that all information being obtained is appropriate and adequate for addressing the RQ / hypothesis Errors in Research Design Assume you are interested in knowing what Winthrop undergrad students feel about the quality of the faculty – What is the population? Size? Assume you take a sample of 100 students and find the sample mean – Would your sample mean match the population mean? – If not, what is the difference? Errors in Research Design Assume you get a mean figure of 4.0 on a 1 (low quality) to 5 (high quality) scale The population mean is an unknown figure – Always wise to acknowledge that it may be different from the sample mean – assume it is 4.5 What is the difference between 4.5 and 4.0? Errors in Research design Sampling errors – difference between measure obtained from the sample and true measure obtained from the population from which the sample is drawn (assuming random sampling is used) Non-sampling errors – – – – Design errors Administering errors Response errors Non-response errors Non-sampling errors – Design Errors Selection errors – biased sample selection Population specification error – drawing a sample from the wrong population Non-sampling errors – Design Errors Sampling frame error – using inaccurate sampling frame to create the sample Surrogate information error – difference between information required for the study and what the researcher seeks Non-sampling errors – Design Errors Measurement error – difference between information sought by the researcher and information generated by a particular measurement procedure used by the researcher Non-sampling errors – Design Errors Experimental error – improper experimental design Data Analysis error – e.g. wrong data coding or wrong statistical analysis Non-sampling errors – Administering Errors Questioning error – incorrect phrasing of questions to respondents Recording error – improperly recording the respondents answers Interference error – does not follow the exact procedure while collecting data Non-sampling errors – Response Errors Respondent supplies (intentionally or unintentionally) incorrect answers to questions – Does not understand the question – “Fatigue or boredom Non-sampling errors – Response Errors Unwillingness to give information Social desirability bias Non-sampling errors – Non-Response Errors Respondents who did not respond may think differently on the issue Some members of the sample may have provided incomplete information RESEARCH DESIGN PROCESS Compare Cost and Timing Estimates with Anticipated Value Revise Terminate Implementation Proceed Data Collection and Analysis Data collection Field work Data processing Data analysis Statistical analysis Interpretation Conclusions and Recommendations