Piezoelectric Accelerometer
advertisement

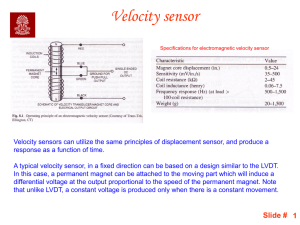
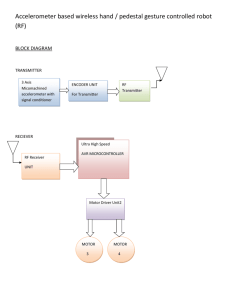
Piezoelectric Accelerometers Theory & Application Metra Mess- und Frequenztechnik Radebeul / Germany www.MMF.de 1 Piezoelectric Effect • Piezoceramics or Quartz generate a charge output when subjected to force. F q q = d.F F q d piezo disk force charge piezo constant F Metra Mess- und Frequenztechnik Radebeul / Germany www.MMF.de 2 Piezoelectric Accelerometer • • A piezoelectric accelerometer consists of a piezoelectric material and a seismic mass. The charge output is proportional to acceleration. q Seismic mass m charge sensitivity: q Bqa = a Piezoceramics Acceleration a Metra Mess- und Frequenztechnik Radebeul / Germany F = m.a www.MMF.de 3 Accelerometer Design • • Example: Shear type accelerometer with ring-shaped piezoceramics. The inertial force of a seismic mass generates an electric signal at the electrodes of the piezo material. Ring-shaped piezo ceramics: shear force Cover Seismic mass Piezo ceramics Post Socket Base Metra Mess- und Frequenztechnik Radebeul / Germany www.MMF.de 4 Other Types of Vibration Sensors Comparison with piezoelectric accelerometers: Sensor Type Advantages Disadvantages Piezoresistive (strain gauge) • Measures static acceleration • Robust • Limited Electrodynamic • Measures • Only Capacitive • Measures • Low static acceleration static acceleration • Cheap manufacturing by semiconductor process Metra Mess- und Frequenztechnik Radebeul / Germany resolution • Only up to some kHz • Power supply required for low frequencies resolution • Fragile www.MMF.de 5 Advantages of Piezoelectric Accelerometers Extremely wide dynamic range, almost free of noise suitable for shock measurement as well as for almost imperceptible vibration Excellent linearity over full dynamic range Wide frequency range, high frequencies can be measured Compact yet highly sensitive No moving parts – long service life Self-generating - no external power required But … they cannot measure static acceleration. Metra Mess- und Frequenztechnik Radebeul / Germany www.MMF.de 6 Charge Mode and ICP Accelerometers • Charge mode accelerometers provide the direct charge output of the piezo material. Disadvantage of charge output: Maximum cable length 10 m, special low-noise cables required. • ICP compatible accelerometers have a built-in amplifier. Advantage of ICP: Cables of several hundred meters length possible, standard coaxial cables can be used. Metra Mess- und Frequenztechnik Radebeul / Germany www.MMF.de 7 Characteristics: Sensitivity • The sensitivity of charge mode accelerometers is measured in pC per m/s² or pC per g. Typical range: 0.1 – 100 pC/ms² or 1 –1000 pC/g • The sensitivity of ICP compatible accelerometers is measured in mV per m/s² or mV per g. Typical range: 1 - 1000 mV/ms² or 10 – 10 000 mV/g • Sensitivity stated in the data sheet is usually calibrated at 80 Hz. Metra Mess- und Frequenztechnik Radebeul / Germany www.MMF.de 8 Characteristics: Frequency Response • • A typical accelerometer has a resonance at 10 – 30 kHz For 3 dB accuracy it can be used up to approx. 50 % of this resonant frequency. fr rel. Ampl. 1,30 1,10 30 % Error 10 % Error 1,00 +/- 3 dB Frequency Range 0,7 fl 0,5fr f r 0,3f r Metra Mess- und Frequenztechnik Radebeul / Germany f www.MMF.de 9 Selecting an Accelerometer Model (1) Acceleration to be measured: • Examples: Very low Seismic Accelerometers (...µm/s² to 1 m/s² KB12 • Medium Standard Accelerometers (1 to 10 000 m/s²) KS76 • Very high Shock Accelerometers (> 10 000 m/s²) KD93 Metra Mess- und Frequenztechnik Radebeul / Germany www.MMF.de 10 Selecting an Accelerometer Model (2) Weight: The weight of an accelerometer should not exceed 10 % of the test object weight. Examples: • Very light Miniature Accelerometers (weight < 5 grams) KS91 KS94 Metra Mess- und Frequenztechnik Radebeul / Germany www.MMF.de 11 Selecting an Accelerometer Model (3) Environmental Conditions: • Humidity and Dust Example: Industrial Accelerometers (with protection grade IP67 and higher) • Grounding Problems / Ground Loops Industrial Accelerometers (with insulated case) Metra Mess- und Frequenztechnik Radebeul / Germany www.MMF.de KS80 12 Accelerometer Mounting Methods Stud Mounting Performance: Max. Frequency: Direct Adhesive Adhesive Pad Insulating Flange Magnetic Base Probe poor good > 20 kHz Metra Mess- und Frequenztechnik Radebeul / Germany < 5 kHz www.MMF.de < 1 kHz 13 Typical Mounting Errors • • For best performance, particularly at high frequencies, the accelerometer base and the test object should have clean, flat, smooth, unscratched and burr-free surfaces. A stiff mechanical connection between the sensor and the test object is important. Sheet metal or plastic parts and other thin and flexible components are unsuited for accelerometer mounting. Uneven surface Rough surface Metra Mess- und Frequenztechnik Radebeul / Germany Flexible coupling www.MMF.de F 14 Instrumentation for Charge Mode Sensors • Charge mode accelerometers require a charge amplifier input. • A charge amplifier is a differential amplifier with Rf capacitive feedback. qf q in Sensor Cf vout + GND Metra Mess- und Frequenztechnik Radebeul / Germany www.MMF.de 15 Instrumentation for ICPAccelerometers Accelerometers with integrated ICP electronics require a constant current supply of 2 - 20 mA via the sensor output. • The constant current source can be part of the instrument or a separate unit. • ICP® Compatible Transducer Constant current source Integrated Charge Converter Piezo System Q U I const coaxial cable, over 100 m long Instrument Cc Decoupling Metra Mess- und Frequenztechnik Radebeul / Germany www.MMF.de 16 Signal Conditioners from Metra M108/116 multichannel ICP conditioners M32 ICP conditioner M68 series charge & ICP conditioners Metra Mess- und Frequenztechnik Radebeul / Germany M28 ICP supply www.MMF.de 17 Accelerometers with TEDS to IEEE1451.4 TEDS = Transducer Electronic Data Sheet New feature for ICP compatible accelerometers. The accelerometer contains a memory chip which stores: Model and version number Serial number Manufacturer Type of transducer, physical quantity Sensitivity Last calibration date Identification of the measuring point Metra Mess- und Frequenztechnik Radebeul / Germany www.MMF.de 18 Advantages of TEDS Transducers Easier sensor identification, particularly at large channel number. No cable tracking and marking. • Automatic calibration of the measuring system. No manual setup of serial number, measured quantity, sensitivity etc. • Sensor replacement without setup ("plug & play"). • Sensor can be used, even if the printed calibration data sheet is just not at hand. • Metra Mess- und Frequenztechnik Radebeul / Germany www.MMF.de 19 Accelerometer Calibration Vibration Calibrators from Metra Model VC10 • Fixed frequency: 159,2 Hz • Vibration level: 10 m/s² • Max. sensor weight: 500 gr. • Battery powered Model VC100 • Frequency range: 70 - 10000 Hz • Vibration level: 1 m/s² • Max. sensor weight: 400 gr. • Sensitivity display • PC controlled • Frequency sweeps Metra Mess- und Frequenztechnik Radebeul / Germany www.MMF.de 20