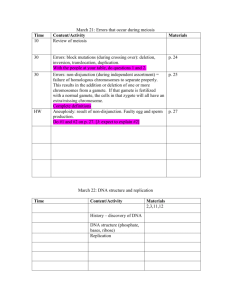
Unit 6 Review

Unit 6 Test
Review
1. Look at the chart. It describes the genes of tomato plants and how the environment may affect the final appearance. What gene seems to be influenced by the environment?
Gene A
2. In lady bugs, a single gene determines the bug’s markings. The pattern allele is dominant to the plain allele. A plain lady bug is crossed with a homozygous patterned lady bug. What percentage of the offspring from this cross are expected to be patterned?
100%
3. Define homozygous.
Carries the same alleles,
2 dominate or 2 recessive
4. Define heterozygous.
Carries different alleles, 1 dominate and 1 recessive.
5. Define genotype
The alleles, or genes, an organism has
6. Define phenotype.
The physical appearance of an organism, descriptive
7. What parents most likely produced the offspring shown in the punnett square?
Tt and Tt
8. How many chromosomes do humans have?
46
9. How many chromosomes do you get from your mother?
23
10. How many chromosomes do you get from your father?
23
11. In fruit flies, the gene for eye color is located on the X chromosome. The red eye allele (R) is dominant to the white eye allele
(r). A female fly with genotype X R X r is mated with a male fly with genotype X R Y. What are the possible percentages of the genotypes of their offspring?
X R X R
X R X r
X R y
X r y
25%
25%
25%
25%
12. Can a person with AB blood type produce a child with O blood?
NO
13. A parent with blood type
A and a parent with blood type B have kids. What are the possible blood types of their kids?
A, B, AB, or O
14. X-linked traits are usually more common in males than females, why?
Males inherit from their mothers because they only have one X chromosome
15. If a mutation occurs on the DNA, what could occur with the mRNA and then the protein that gets produced?
A mutation in the DNA can cause a mutation in the mRNA and then a mutation in the protein.
16. This is a reproductive cell of a parent. What are the possible combinations of alleles this parent could give to their offspring?
ST, St, sT, st
17. What two things does a karyotype show?
Gender and chromosome mutations
18. B=black fur, b=white fur, S=short hair fur, s=long hair fur. Cross a parent that is heterozygous for both traits with a parent that homozygous recessive for both traits. What percentages of their offspring would be white and long fur?
25%
19. Using the gel electrophoresis picture, which suspect do you think committed the crime?
Suspect C
20. What is DNA Fingerprinting?
DNA fingerprinting is a technique in which sequences of bases in
DNA unique to an individual organism are discovered and then compared to other DNA sequences from a different organism of the same species.
21. Why is DNA fingerprinting used?
Solve crimes, discover who someone’s relatives are
22. Attached earlobes is a recessive trait.
Using the clues from the key, determine the genotype of all the individuals in the pedigree in
#22.
Person 1ff, 2Ff, 3F?, 4ff, 5F?,
6F?, 7F?, 8Ff, 9Ff, 10ff, 11ff,
12ff, 13ff, 14ff
23. How many males in the pedigree above have attached earlobes?
4
3
24. How many females in the pedigree above have attached earlobes?
25. What does the word haploid mean?
Half the number of chromosomes
26. What does the word diploid mean?
The full or regular amount of chromosomes
27. What does “2n” and “n” mean?
2n means diploid, n means haploid
28. In what types of cells does meiosis occur?
Gametes or reproductive cells
29. What process is shown in this picture? meiosis
30 . What is crossing over?
When the chromosomes exchange genes
31. When does crossing over occur?
Prophase 1 of meiosis
32. Why does crossing over occur?
So the daughter cells produced are genetically different, increases variation
33. How are the daughter cells in mitosis different from the daughter cells in meiosis?
Mitosis produces 2 genetically identical daughter cells, Meiosis produces 4 genetically different daughter cells