Retailing
advertisement

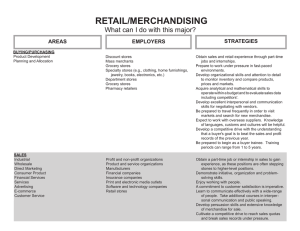
Retailing Includes the business activities involved with the sale of goods and service to the final consumer for personal, family, or household use Final step in the distribution channel Types of retailers by ownership Independent Corporate (retail) chain Franchise Leased department Independent store Operates only one outlet Personal service Good location Close customer contact Attracts entrepreneurs Corporate (retail) chain Multiple outlets Centralized purchasing and decision making More complex organizations Franchising Contractual agreement between a franchisor and a retail franchisee Franchisee runs a certain form of business under an established name and according to specific rules Leased department Section of a store rented to an outside party Operates under store rules Pays a percentage of sales as rent Types of Retailer by strategy Convenience store Conventional supermarket Food-based supermarket Combination store Specialty store Category killer Traditional department store Full-line discount store Warehouse club Convenience store Well-situated Food oriented Limited assortment Low service High prices Conventional supermarket Departmentalized food store Food Related products Food-based superstore Broad range of food and non-food items Combination store (supercenter/hypermart) General merchandise and grocery items General merchandise25-40% of sales Efficient operations Increased impulse purchases Greater number of transactions Specialty store Limited variety Great depth Usually one product line, or several related product lines Category killer “discount specialty store” Especially large specialty store Traditional Department Store Great variety Depth of assortment varies by department Often anchor stores Average to above average prices Full- line discount store Low prices Low service Broad variety Shallow assortment Lower rent locations Warehouse club Wholesale and retail consumers Pay yearly dues for membership Non-store retailers Direct marketing Vending machine Direct selling Direct marketing Consumer is exposed to a good or service by a non-personal medium Order by mail, phone or PC Vending machine Coin or card operated machinery to dispense goods or services Require intensive training Cards and electronic tracking Direct selling Involves personal contact with consumers in their homes and other non-store locations and phone solicitations Phone Referrals Party method Considerations Location Atmosphere Scrambled merchandising Location Isolated Unplanned business district Planned shopping center Atmosphere Physical attributes of a retailer that are used to develop an image and draw customers Exterior General interior Store layout Display Scrambled merchandising Adding goods and services that are unrelated to each other and the firm’s original business One stop shopping Increased traffic High profits Increases competition Technological advances Computerized POP Self-checkout Video kiosks Site selection software Networking distribution Anti-theft developments Computerized reorder