Works Cited - LHSIBBiology
advertisement
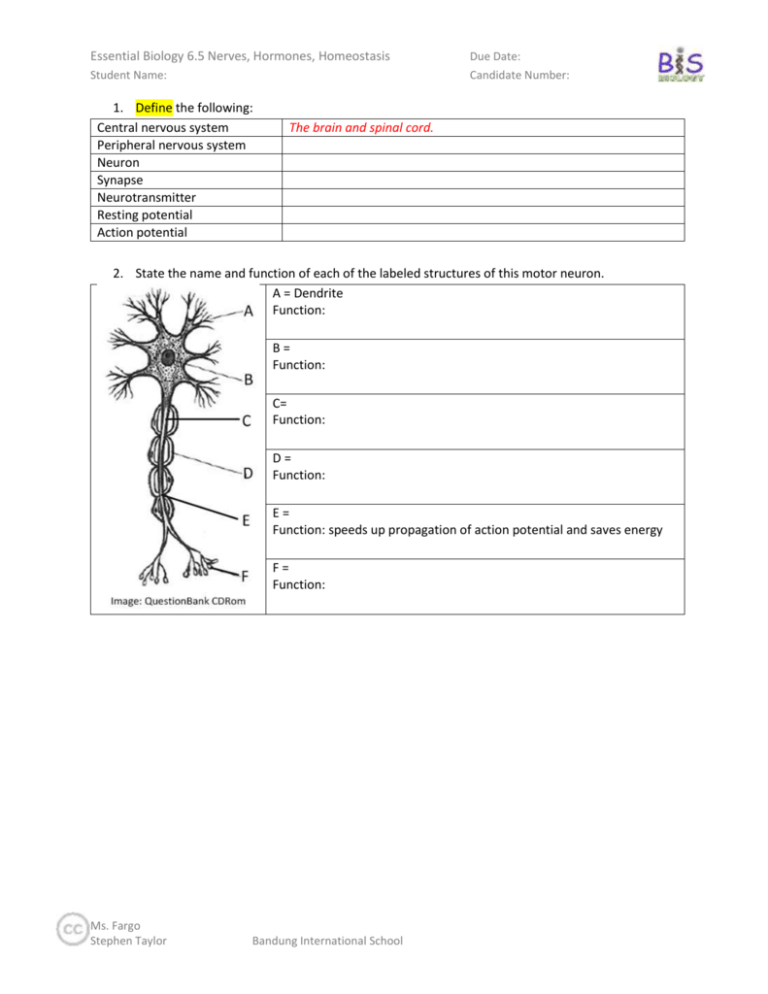
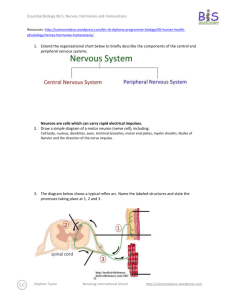
Essential Biology 6.5 Nerves, Hormones, Homeostasis Student Name: 1. Define the following: Central nervous system Peripheral nervous system Neuron Synapse Neurotransmitter Resting potential Action potential Due Date: Candidate Number: The brain and spinal cord. 2. State the name and function of each of the labeled structures of this motor neuron. A = Dendrite Function: B= Function: C= Function: D= Function: E= Function: speeds up propagation of action potential and saves energy F= Function: Ms. Fargo Stephen Taylor Bandung International School Essential Biology 6.5 Nerves, Hormones, Homeostasis Due Date: Candidate Number: Student Name: 3. This diagram shows a simple reflex arc. Identify the structures labeled A-D and state the actions 1-3. A B C D 1 2 3 4. Resting potential is the electrical potential across the membrane of a neuron that is not conducting an impulse. It is used to repolarize (reset) a neuron in between impulses. a. List two ions used in neurons. b. Define electrical potential c. State the specific method of membrane transport used to maintain resting potential d. Explain how a resting potential is maintained, including why it is negative. Sodium ions are pumped out of the neuron By Ms. Fargo Stephen Taylor Bandung International School Essential Biology 6.5 Nerves, Hormones, Homeostasis Due Date: Candidate Number: Student Name: 5. Action potential (AP) is the depolarization and repolarization of the neuron to conduct an electrical impulse. a. Use the following cues to explain how an AP is transmitted along the neuron. Resting potential Is maintained through... Depolarisation Is trigged by… Which causes Voltage-gated Na+ channels “all or nothing response” K+ channels Refractory period b. Explain the significance of the labeled features of this graph, showing an action potential. 1 2 3 4 5 c. Outline how a one-way direction of nerve impulse is maintained. d. Compare resting potential and action potentials. Also known as… Internal potential is… (positive/ negative) Sodium ions are… Potassium ions are… Membrane proteins used (voltage-gated sodium channels or sodium potassium pump?) Ms. Fargo Stephen Taylor Bandung International School Resting potential Action potential -polarisation - polarisation Essential Biology 6.5 Nerves, Hormones, Homeostasis Due Date: Candidate Number: Student Name: 6. A synapse is a junction between neurons. This is a small gap between the terminal end of the pre-synaptic neuron and the dendritic end of the post-synaptic neuron. The electrical signal of the action potential is converted to a chemical signal, which passes across the synapse and stimulates an action potential in the post-synaptic neuron. Whew. a. Label these features of the synapse. A B C D E F G H b. Explain the process of synaptic transmission, referring to all of the labeled structures above. AP reaches terminal end of pre-synaptic neuron This causes voltage-gated Ca2+ channels to open c. Explain the need for high numbers of mitochondria in the pre-synaptic neuron. d. Predict the effect of a drug which acts as a competitive inhibitor of a neurotransmitter. Ms. Fargo Stephen Taylor Bandung International School Essential Biology 6.5 Nerves, Hormones, Homeostasis Student Name: Due Date: Candidate Number: 7. Define the following. Endocrine system Hormone Gland Target cell Homeostasis Negative feedback 8. State the function of the following hormones Insulin Glucagon Adrenalin Testosterone FSH LH Oestrogen Progesterone HCG Oxytocin 9. List five internal conditions in the human body maintained through homeostasis. 10. Explain how homeostasis is based on a system of negative feedback control. Ms. Fargo Stephen Taylor Bandung International School Essential Biology 6.5 Nerves, Hormones, Homeostasis Student Name: Due Date: Candidate Number: 11. Complete the flow chart below to show how the hypothalamus controls body temperature through hormones. What are the body’s responses? 12. Blood glucose levels are maintained by hormones produced in the pancreas. Complete the table to show glucoregulation. High Blood Sugar Pancreatic cells used Low Blood Sugar Beta cells …which secrete… … carried in blood to…. & … causing conversion of.. … to … Overall effect: Ms. Fargo Stephen Taylor Glucose removed from blood Bandung International School Glucose released into blood Essential Biology 6.5 Nerves, Hormones, Homeostasis Student Name: Due Date: Candidate Number: 13. Diabetes mellitus is a disease in which regulation of blood glucose is difficult. Distinguish between type I and type II diabetes. Type I Type II Cause Effect Risk factors Treatment 14. Explain how we can tell from this table that the patient is diabetic. 15. Distinguish between nerves and hormones. Nerves Route Direct from coordinator to effector Hormones Through: From: To: Signal type Chemical Time to take action longer Duration of effects 16. Identify the part of the brain are nerve impulses converted to hormonal signals. Ms. Fargo Stephen Taylor Bandung International School Essential Biology 6.5 Nerves, Hormones, Homeostasis Due Date: Candidate Number: Student Name: 17. Complete the steps below to show how the nervous and endocrine systems work together to regulate body temperature. Stimulus Sensory neuron Relay Effector Hormone 1 Gland Target cells Effect Release of Thyroid hormone Target cells Effect Data-based question practice, from the QuestionBank CDRom 18. The sense of taste is normally caused by the stimulation of chemoreceptors in the taste buds of the tongue. There are four main 'tastes': sweet, salty, bitter and sour. The tongue also has receptors for temperature. It is known that the taste of food can vary according to whether it is cold, warm or hot. Scientists discovered that just warming or cooling parts of the tongue, even when no food was present, also caused a sensation of taste. Scientists experimented with a group of people. They gradually cooled the tips of their tongues and measured the intensity of the taste felt by each member of the group. The experiment was repeated, this time warming the tip of the tongue. The graphs show the average values for the group. Ms. Fargo Stephen Taylor Bandung International School Essential Biology 6.5 Nerves, Hormones, Homeostasis Due Date: Candidate Number: Student Name: Cooling the tongue tip Warming the tongue tip Taste intensity felt / arbitrary units moderate weak just detectable 35 25 35 20 35 15 35 10 35 5 20 25 Decrease in temperature from 35 ºC Key: Salty Bitter 20 30 20 35 20 40 Increase in temperature from 20 ºC Sweet Sour [Source: modified from Cruz and Green, Nature (2003) 403, page 889] (a) Identify which taste was felt most strongly when the tip of the tongue was (i) cooled: (ii) warmed: (1) (b) Compare the effects on the taste of sweetness, of warming and cooling the tip of the tongue. (2) (c) It is important that such experiments use a population sample that is representative. Suggest two biological criteria the scientists would have used to select the people to be tested. (1) Ms. Fargo Stephen Taylor Bandung International School Essential Biology 6.5 Nerves, Hormones, Homeostasis Due Date: Candidate Number: Student Name: (d) Explain whether cooling or warming the tip of the tongue has the greater effect on the sensation of taste. (2) The scientists discovered that there were two types of chemoreceptor in the tongue tip. They called these A and B. They tested these chemoreceptors using solutions of sucrose to find out the type of taste and the intensity felt. The results are shown in the bar chart. moderate weak Taste intensity felt / arbitrary units just detectable sweet detected Key: (e) sour detected A B Compare the effects of sucrose on the A and B chemoreceptors by giving two similarities and two differences. Similarities Differences (4) (Total 10 marks) Ms. Fargo Stephen Taylor Bandung International School Essential Biology 6.5 Nerves, Hormones, Homeostasis Due Date: Candidate Number: Student Name: Works Cited 1. Taylor, Stephen. Nerves, Hormones and Homeostasis (presentation). Science Video Resources. [Online] Wordpress, 2010. http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com/bis-ib-diploma-programme-biology/06human-health-physiology/nerves-hormones-homeostasis/. 2. Allott, Andrew. IB Study Guide: Biology for the IB Diploma. s.l. : Oxford University Press, 2007. 978-019-915143-1. 3. Mindorff, D and Allott, A. Biology Course Companion. Oxford : Oxford University Press, 2007. 978099151240. 4. Clegg, CJ. Biology for the IB Diploma. London : Hodder Murray, 2007. 978-0340926529. 5. Campbell N., Reece J., Taylor M., Simon. E. Biology Concepts and Connections. San Fransisco : Pearson Benjamin Cummings, 2006. 0-8053-7160-5. 6. Burrell, John. Click4Biology. [Online] 2010. http://click4biology.info/. 7. IBO. Biology Subject Guide. [Online] 2007. http://xmltwo.ibo.org/publications/migrated/productionapp2.ibo.org/publication/7/part/2/chapter/1.html. Self Assessment: Essential Biology Criterion Presentation & Organisation Academic Honesty Objective 1 understanding Objective 2 understanding Objective3 understanding Logic, notation, mathematical working Further research Assessment Complete (2) Partially complete (1) NA Complete and neat. All command terms highlighted, tables and diagrams well presented. Sources cited using the CSE (ISO 690 numerical) method, with Works Cited section complete and correct. All answers for the following command terms Most answers for the following command terms correct: correct: Define Draw Label List Measure State Most answers for the following command terms All answers for the following command terms correct: correct: Annotate Apply Calculate Describe Distinguish Estimate Identify Outline Most answers for the following command terms All answers for the following command terms correct: correct: Analyse Comment Compare Construct Deduce Derive Design Determine Discuss Evaluate Explain Predict Show Solve Sketch Suggest Answers are presented in a logical and concise manner. SI units used most times, with correct NA unit symbols and definitions of terms. All mathematical working shown. Evidence is apparent of research and reading beyond the textbook and presentations to find correct answers to challenging questions. If any NA questions are unanswered, this criterion scores zero. NA Total (max 10): Ms. Fargo Stephen Taylor Bandung International School Self MrT Essential Biology 6.5 Nerves, Hormones, Homeostasis Student Name: Ms. Fargo Stephen Taylor Bandung International School Due Date: Candidate Number: