Reform Mov'ts.revised - Greer-American-History-2
advertisement

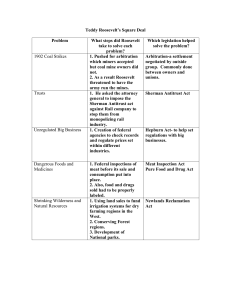
Unit III. The Progressive Era Key Vocabulary 1. 2. 3. Progressivism- Period of dramatic change where reformers set out address major social, political and economic problems. Sherman Anti-Trust Act Ida Tarbell A. Regulating Big Business 1. Benefits of Big Business a. Created new jobs b. New affordable products c. Wealth was used for philanthropy (generosity to charity) - mil. Of $ were donated to libraries, hospitals, the arts, research, universities, 2. Sherman Anti-Trust Act (1890) Law developed to stop trusts and monopolies from using underhanded methods. a. ex. controlling prices, trade or supply 2. Purpose was to protect competition 1. 3. ‘Busting Trusts’ Even though congress tried to fight monopolies in big business w/the Sherman Anti-Trust Act, it was not strictly enforced. b. Pres. Theodore Roosevelt made it his mission to break up trusts & monopolies. a. Monopoly, right, blasts Competition, center. Uncle Sam, far left, readies to fire a tiny cannon from Fort Legislation. Congress passed the Sherman Antitrust Act in 1890. c. Began with Northern Securities Co., the largest railroad trust by having the Justice Dept. file a law suit for violating the anti trust act. d. Ida Tarbell helped to expose the monopolies in the oil busin. e. Both the railroads & oil bus. Were broken up into smaller businesses. f. Roosevelt’s work pushed the idea that gov’t regulation (enforcement of laws) was needed. B. Reform in Politics 1. Political Machines a. organized group that controlled the activities of a political party in a city b. offered services to voters & businesses in exchange for political or financial support. c. People received city jobs, or political appointments in exchange for their votes this is known as patronage or the spoils system d. “Bosses” controlled most aspects of the city (police & fire dept., sanitation, licenses, inspections etc.) & gained citizen support by solving problems in communities 2. Corruption Sparks Reform a. political machines committed voting fraud to win elections. b. took “kickbacks” (illegal payments) for helping companies get contracts. c. accepted bribes to allow for illegal activities. d. William Marcy Tweed A.K.A. “Boss Tweed”- Head of Tammany Hall (NY Democratic Political Machine.) pocketed over $200 mil. e. With the help of political Cartoons by Thomas Nast, Boss Tweed was indicted on 120 counts of fraud & extortion f. Robert La Follette fought for pol. Reform in Wisconsin & influenced other states to reform their corrupt gov’ts. g. Oregon passed: initiative- citizens enact laws by popular vote. Referendum- allowed voters to overturn an existing law. Recall- allowed voter to remove an elected official from office 3. Presidents Attack Political Corruption a. Pres. Rutherford B. Hayes fired useless or corrupt employees b. Pres. James A. Garfieldfought the Stalwarts (ppl that oppossed pol. Reform) & gave jobs to reformers. (later assassinated by lawyers who he turned down for a job) c. Chester A. Arthurpassed the Pendleton Act which called for civil servants to be given jobs based on a merit system C. Social Reformers Mobilize 1. Social Reformers were mostly young educated men & women from the middle class 2. Focused on eliminating poverty especially among immigrants 3. Many were influenced by the Social Gospel Mov’t which preached salvation through service of the poor. 4. Settlement House Movement a. Settlement Housescommunity centers in slum areas that provided educational, cultural & social services b. Jane Adams- founded Hull House in Chicago after living in the 1st English settlement house. D. Workers Rights 1890’s - 1920’s 1. Child Labor Reform a. In the early 1900’s over a million children worked in mines & factories b. Mary Harris Jones (Mother Jones)- led the “March of the Mill Children” to gain support for child labor laws. c. By 1903 43 states passed laws outlawing the hiring of children 2. Improving Adult Working Conditions a. Adult workers also faced poor working conditions with long hours, low pay and dangerous work environments b. States like Oregon passed laws limiting women to a 10 hour work day c. Others like Maryland passed laws to assist workers that had been injured on the job d. Labor unions & reformers helped to get shorter work days, improvements in factory safety. E. Environmental Reform 1. John Muir • The first modern environmentalist • Environmentalism was the idea that we should protect and conserve the countries natural resources • Lived in the Yosemite Valley in California • Saw first hand what loggers, miners and farmers were doing to the land • Began lobbying the federal government to protect the wilderness 2. Theodore Roosevelt Helps the Environment – Increased the national forest from 47 million acres to 195 million acres – Doubled the number of national parks Roosevelt’s conservationism even led the banning of Christmas trees in the White House F. Protecting Health 1. Horror in the Meat Packing Industry a. Upton Sinclair- Wrote “The Jungle” (1906) b. the book exposed the horrible living & working conditions & sanitation conditions of the meat packing industry “…there would be meat that tumbled out on the floor in the dirt & sawdust” Burns Meat Packing Co. c. Sinclair’s work led to the Meat Inspection Act (1906) -called for strict cleanliness requirements & the creation of federal meat inspection programs. "There is one kind of prison where the man is behind bars, and everything that he desires is outside; and there is another kind where things are behind bars, and the man is outside." 2. Pure Food & Drug Act a. Before this law companies falsy advertised & added harmful chemicals to their products. b. PFDA was passed same year as Meat Insp. Act & stopped the sale of contaminated foods & medicines c. called for truth in labeling 1. Women’s Suffrage Movement a. Susan B. Anthony, Alice Paul were leaders in the fight for women’s voting rights. b. Their efforts led to the passage of the 19th amend. (women’s right to vote) H. How the Media Exposed Corruption 1. muckrakers used yellow journalism (writing about scandal & sensation) 2. Ida Tarbell (Rockefeller oil), Lincoln Steffens (political corruption), Henry Demarest Lloyd (Big Business, power of the wealthy) 3. Discussion Questions The Labor Movement – What are your thoughts on the changes that the labor movement brought about? – Do you think government should be involved in the regulation in the work place? Environmentalism – Do you think the ideas behind environmentalism were correct? – How do you think the movement towards preserving the environment has impacted the world you live in today? Read your two primary source documents – How do these two documents connect to each other? – In what ways do the documents represent the fulfillment of the ideals of the progressive era?