Industry Structure 5 forces 2008
advertisement

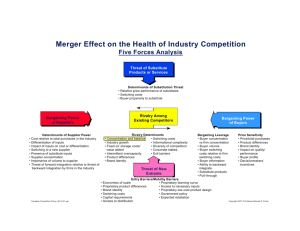
Industry Structure— Porter’s 5 forces Paul C. Godfrey Marriott School of Management Brigham Young University 14 March 2016 The Importance of Industry Structure • Industry structure creates the context in which competition occurs • Industry structure can be intrinsic—due to the nature of the product or process (e.g., commodities) • Industry structure can be derived—by the competitive actions of industry players (e.g., branding power) A Map of Industry Structure Barriers To Entry Supplier Power Competitive Rivalry Substitute Products Buyer Power Barriers to Entry • What are the economic drivers of barriers to entry? • What are the practical sources of barriers to entry? • What barriers to entry exist in the professional sports industry? Barriers to Entry: The Economics • Monopolistic competition allows increased profitability • Limit pricing precludes entry P S P** P* • High barriers to entry create an attractive industry D Q** Q* Q Barriers to Entry: Sources • Economies of Scale • Access to Distribution • Proprietary Product Differences • Absolute Cost Advantages • • • – Learning Curves – Input Lock-up Brand Identity – Product Design Switching Costs Capital Requirements • Government Policy • Expected Retaliation Supplier and Buyer Power • What are the economic drivers of supplier and buyer power? • What are the practical sources of supplier and buyer power? • What types of supplier and buyer power exist in professional sports industries? Supplier/Buyer Power: The Economics P • Supplier power is determined by price elasticity of demand for the product • Supplier power forces bargaining and hold-up • The question: Who gets most of the value added? • Strong supplier power makes an industry less attractive De Di Q Supplier Power: Sources • Differentiation of inputs • • Switching costs of suppliers and firms Cost relative to total purchases • Impact of inputs on buyers cost or differentiation • Threat of forward or backward integration • Presence of substitutes • Supplier concentration • Importance of volume to buyer Buyer Power: Sources • Buyer concentration vs. firm • Buyer volume • Buyer switching costs • Buyer information • Ability to backward integrate • Substitutes • Pull-through • Price Sensitivity – – – – Price/ total purchases Product differences Brand identity Impact on quality/ performance – Buyer profits – Decision maker’s incentives Substitute Products • What are the economic drivers of the power of substitution? • What are the practical sources of power for substitute products? • What substitute products exist within the professional sports industry? Substitute Products: The Economics Inelastic • Cross-elasticity of demand • Competitors need to think broadly about substitutes • Competitors need to link to complements where ever possible • Threat of substitution dampens profitability in the industry P1 Substitute Complement Q2 Substitute Products: Sources • Relative price performance of substitutes • Linking of intangibles to products and services • Switching costs • Buyer propensity to substitute Competitive Rivalry • What are the economic drivers of competitive rivalry? • What are the practical sources of competitive rivalry? • What factors create/ maintain competitive rivalry in professional sports industries? Competitive Rivalry: The Economics P • Classical competition drives the force • The effect of rivalry is uncertain • High degrees of rivalry turn into destructive price competition • Moderate degrees of rivalry improve industry performance S P* D Q* Q Competitive Rivalry: Sources • Industry growth • Concentration and balance • Fixed costs/ value added • Informational complexity • Capacity utilization • Diversity of competitors • Product differences • Corporate stakes • Switching costs • Exit barriers The 5 Forces: Summary “Optimal” Industry Structure Barriers to Entry High Supplier Power Low Buyer Power Low Competitive Rivalry Moderate Threat of Substitution Low • “Optimal” industry structure varies – An industry that is too attractive is often stagnant • The five forces must be viewed in a dynamic context – How are the forces changing?