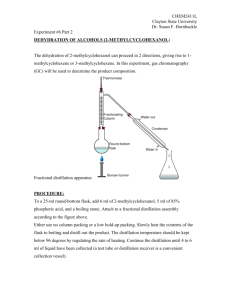
M. TECH IN CHEMICAL
advertisement
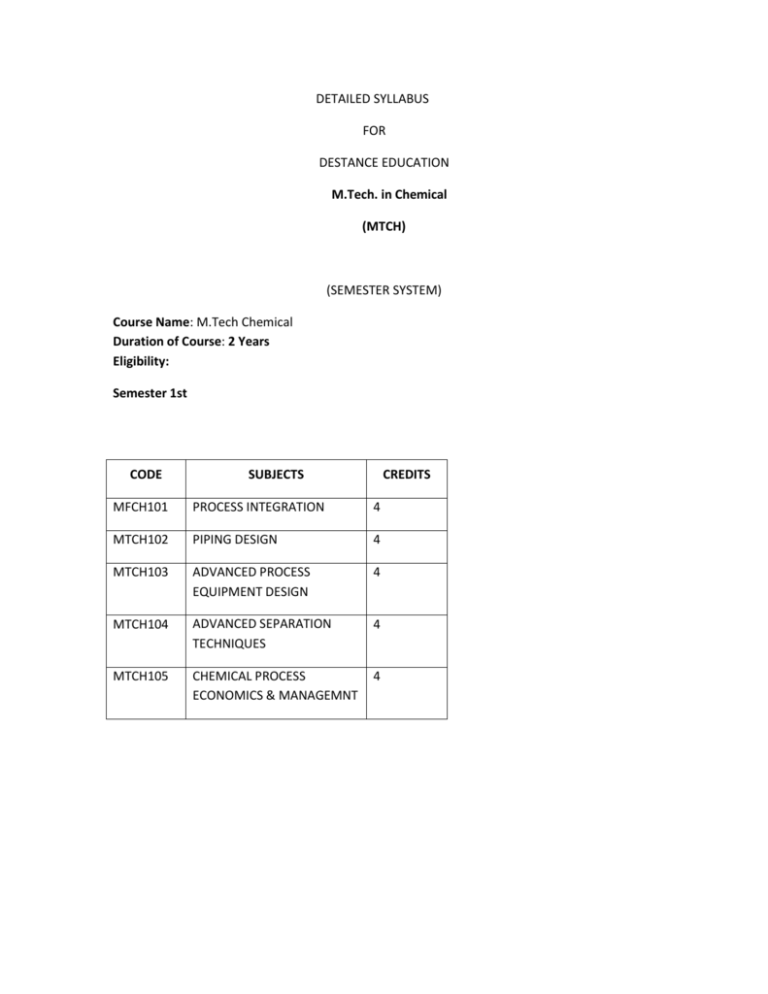
DETAILED SYLLABUS FOR DESTANCE EDUCATION M.Tech. in Chemical (MTCH) (SEMESTER SYSTEM) Course Name: M.Tech Chemical Duration of Course: 2 Years Eligibility: Semester 1st CODE SUBJECTS CREDITS MFCH101 PROCESS INTEGRATION 4 MTCH102 PIPING DESIGN 4 MTCH103 ADVANCED PROCESS EQUIPMENT DESIGN 4 MTCH104 ADVANCED SEPARATION TECHNIQUES 4 MTCH105 CHEMICAL PROCESS ECONOMICS & MANAGEMNT 4 MTCH1 PROCESS INTEGRATION Introduction Introduction to Process Integration. Importance of Process Integration and applications in Chemical Industries. Overview of Process Integration. Heat Exchanger Networking Hot Composite Curve, Cold Composite Curve, Problem Table Algorithm, Grand Composite Curve, Area Targeting by Uniform Bath formula and Unit Targeting by Eulers’ formula, Heuristics for Pinch Design, Maximum Energy Recovery Design, Evolution of Network. Reactor Integration Choice of Idealized reactor model and reactor performance. Reactor configurations: Temperature Control, Gas-Liquid and Liquid Liquid Reactors, Choice of Reactors. Heat Integration characteristics of reactors, Appropriate placements ofreactors. Use of GCC for Heat Integration of reactors. Distillation Integration Distillation sequencing, Heat Integration characteristics of Distillation column, appropriate placement of distillation column, various configurations for heat integration of distillation column. Mass Exchanger Network Synthesis Mass Exchanger Network, Minimum Mass Separating Agents (MSA), Mass exchange networks for minimum external MSA. Minimum Number of Mass Exchangers. Laboratory work: Experiments will be based on the syllabus covered as above. Text-Books: 1. Chemical Process Design and Integration Robin Smith, John Wiley and Sons. Ltd., New Delhi, 2005. 2. Product & Process Design Principles Warren D. Seider, J. D. Seader and Daniel R. Lewin, Wiley Publication. Reference Book: 1. Heat Exchanger Network Synthesis U. V. Shenoy, Gulf Publication. MTCH102 PIPING DESIGN Fundamentals of Piping Engineering Definitions, Piping Components their introduction, applications. Piping MOC, Budget Codes and Standards, Fabrication and Installations of piping. Pipe hydraulics and sizing Pipe sizing based on velocity and pressure drop consideration cost, least annual cost approach, pipe drawing basics, development of piping general arrangement drawing, dimensions and drawing of piping. Plot plan Development of plot plan for different types of fluid storage, equipment layout, process piping layout, utility piping layout. Stress analysis Different types of stresses and its impact on piping, methods of calculation, dynamic analysis, flexibility analysis. Piping support Different types of support based on requirement and its calculation. Transient fluid flow analysis. Heat tracing and thermal insulation of pipe. Typical P&I diagrams for Vessels, Pumps, Compressor and Fire Heaters. Tutorials will be based on the above using standard Software. Text Books: 1. Piping Handbook, 6th edition, M.L. Nayyar, P.E., Mc Graw-Hill, Inc 2. Piping Design Handbook edited by Johan J McKetta, CRC Press, 1992. MTCH103 ADVANCED PROCESS EQUIPMENT DESIGN Introduction to process equipment design Nature of design, types of process, codes and standards, factor of safety, degree of freedom and design variables. Heat Transfer Equipment Design Introduction to design procedure of S & T heat exchangers Detailed design of condensers, reboilers, vaporizers and direct fired furnaces Plate Heat exchangers- Design of gasketed plat heat exchanger, welded plates, plate fines and spiral heat exchangers. Fin tube heat exchangers, air cooled heat exchangers. Heat transfer to vessels-Jacketed vessels, internal coils and agitated vessels. Mass Transfer Equipments Introduction to continuous distillation, process description, design variables, design methods for binary systems. Multicomponent distillation, shortcut methods for stage and reflux requirement, rigorous solution procedure, plate efficiency, plate hydraulic design, other distillation systems including batch distillation, steam distillation and reactive distillation. Packed column- design and principles, packed bed height calculations, column diameter, column internals, wetting rates. Venturi scrubber design and principle. Extractor design Liquid-liquid extraction, Gas liquid separators- settling velocity, vertical and horizontal separators, Gas solid separators- cyclone separators, liquid liquid separators- decanter. Liquid solid separators- drying. Design of Pumps & Turbines Pressure drops in pipe lines, NPSH, characteristic curves, Power Calculations. Mechanical design Fabrication aspects of Pressure vessels, distillation columns and reactors. Material of Construction Selection of MoC. Material properties, mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, protective coatings, linings. Laboratory work: Experiments will be based on the syllabus covered as above. Text Books: 1. Chemical Engineering Design 4th ed., R K Sinnott , Elsevier Publication. 2. Process Equipment Design 3rd ed., M V Joshi, Macmillan India Limited. Reference Book: 1. Introduction to Process Engineering and Design, Shuchen B. Thakore and Bharat I. Bhatt Tata McGraw-Hill Publishing Company Ltd., New Delhi, 2007 MTCH104 ADVANCED SEPARATION TECHNIQUES Separation Processes Industrial Chemical Processes, Mechanism of Separation, Separation by Phase Addition or Creation, Separation by Barrier, Separation by Solid Agent, Separation by External Field or Gradient, Component Recoveries and Product Purities, Separation Power, Selection of feasible Separation Processes. Advanced and Approximate Methods for Multicomponent and Multistage Separations Equilibrium Based Methods for Multicomponent Absorption and Stripping Enhanced Distillation and Supercritical Extraction Distillation Curve Maps, Extractive Distillation, Salt Distillation, Pressure Swing Distillation, Homogeneous Azeotropic Distillation, Heterogeneous Azeotropic Distillation, Reactive Distillation, Supercritical Fluid Extraction Adsorption, Ion Exchange and Chromatography Sorbents, Adsorbents, Ion Exchangers, Sorbents for Chromatography, rations, Ion Exchange Equilibria, Equilibria in Chromatography, Adsorption, Chromatography, Slurry Adsorption, Fixed Bed Adsorption (Percolation), Thermal Swing Adsorption, Pressure Swing Adsorption, Continuous Countercurrent Adsorption systems, Membrane based Separation Overview of Membrane Science and Technology Introduction, Historical Development of Membranes, Types of Membranes and Membrane Processes Membrane Transport Theory Introduction, Solution diffusion Model, Structure Permeability Relationship in Solution diffusion, Pore flow Model, Boundary Layer Film Model, Determination of the Peclet Numer, Concentration Polarization in Liquid and Gas Separation Processes Membrane Preparation and Membrane Modules Isotropic Membranes, Anisotropic Membranes, Metal Membranes and Ceramic Membranes, Liquid Membranes, Hollow Fiber Membranes, Membrane Modules, Crossflow, Co-flow and Counter-flow. Reverse Osmosis, Microfiltration and Ultrafiltration Principle, Theory, Membranes and Materials, Membrane Selectivity, Modules, Concentration Polarization, Membrane Fouling and Cleaning, System Design, Applications Pervaporation and Gas Separation Principle, Theory, Membrane Materials and Structure, Process Design, Applications Dialysis and Electrodialysis Principle, Chemistry of Ion Exchange Membranes, Transport in Electrodialysis Membranes, System Design, Carrier Facilitated Transport: Coupled Transport, Faciliated Transport Miscellaneous Applications of Membranes Membrane Reactor, Membrane Contactors and Membrane Distillation, Hemodialysis, Blood Oxyenators, Controlled Drug Delivery, Donnan Dialysis and Diffusion Dialysis, Charge Mosaic Membranes and Piezodialysis. Text Books: 1. Membrane Technology and Applications, Richard W. Baker, John Wiley & Sons Inc. 2. Separation Process Principles by J. D. Seader and Ernest J. Henley, John Wiley & Sons. Reference Book: 1. Separation Processes by C. Judson King, McGraw Hill Inc MTCH105 CHEMICAL PROCESS ECONOMICS & MANAGEMNT Introduction General remarks on process plant design, Project, Demands on project engineers, Overview of activities Project Planning Product development, Plant type: Location / kind of premises. Capacity / availability / lifespan, Degree of automation, Legal requirements, Costs, Investment, Operating costs. Inquiry/ Invitation to tender, Project controlling, Plant manufacturer: Risk analysis, Basic engineering, Process development, Balancing, Basic and process flow diagram, Materials concept, Main apparatus, Layout, Quotation, Quotation price, Contract negotiations Contract Order basis, Regulations, Labour employment, Subcontractors, Project documentation, Technical part, Contractor’s scope of supply and services, Employer’s scope of supply and services, Commercial part: Deadlines / penalties, Warranties / penalties, Defects / acceptance, Prices / terms of payment/bonds, Alterations/claims,Terminations/suspension, Insurance, Secrecy, Severability clause, Coming into effect, Signature policy Project Management Project Planning and Scheduling, Schematic Representation of Project Management, Pitfalls in Project Planning, Milestones and Milestone Planning, Work Breakdown Structure (WBS), Gantt Chart, Hierarchical Plan, Project Network, Activity Floats, Programme Evaluation & Review Technique (PERT), Critical Path, Project Control, Decision Making, Project Reporting, Project Meetings, Project Failure and Success. How Public Investment in Projects is initiated in India? Steering Committee, Tender Committee, Joint Venture Organizations, Main Contributing Factors For Successful Projects, Management of Projects, Project Management Consultants (PMCs). Orientation, Indian Individuality, Organization Management Functions, Project Management Team, Desirable Characteristics, Competencies of Project Manager, Duties of A Project Manager, Project Team, Problem Areas of Concern. Project execution Project organization: Project structures, Systematic, Project manual, Correspondence system, Revision service, Cost monitoring, Time scheduling/monitoring of dates, Computers in plant manufacturing. Approval planning, Component procurement, Piping and instrumentation diagrams, Electrical, Measurement and Control engineering, Layout and building design, Layout design, Building design, Piping planning, Documentation, Erection, Commissioning Text Books: 1. Process Plant Design – Project Management from Inquiry to Acceptance, Frank Peter Helmus, Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co.. 2. Project management in Emerging Environment of Globalization, Ramaraju Thirumalai, Himalaya Publishing House. Semester 2nd CODE Subjects Credits MTMH201 COMMUNICATION SKILL FOR ENGINEERS 4 MTMH202 PROCESS AND PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT 4 MTMH203 ENVIRONMENT AND SAFETY IN PROCESS INDUSTRIES 4 MTMH201 COMMUNICATION SKILL FOR ENGINEERS 1. Meaning and importance of communication skills, process, types of communication, barriers to effective communication, kinesics (non-verbal communication-proxemics, chronemics). Difference between verbal and non-verbal communication. Psychological and cultural influence on communication. 2. Introduction to technical writing. Characteristics of technical writing. SOTC (Society of Technical Communicators) on good technical communication. 3. Technical-writing-technical discussion, technical instructions (User’s manual). 4. Memorandum, minutes of meetings, correspondence techniques-inviting experts, inviting quotation, complaint letters and letters of regret and adjustment. 5. Summarizing technical material. 6. Writing research papers. References: 1. Basic communication skills for Technology – Andrea J. Rutherford (person) 2. Technical writing process and product- Shron J. Gerson (person) 3. Technical communication – principles and practices – Meenakshi Raman (Oxford) 4. Business correspondence and report writing – R. C. Sharma, Krishna Mohan (Tata McrGraw) MTMH202 PROCESS AND PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT Introduction Goal of industrial research and development, Production structure of Chemical Industry, Task of Process Development, Creative Thinking. Preliminary Database Creation, Preliminary Process Synthesis, Examples. Product Development Development of chemical product on laboratory scale, quality improvement, reproducibility etc. Case studies of products developed. Chemical Production Plant and Its Components Details about Catalyst, Reactors, Product Processing, Pipelines Pumps and Compressors, Product supply and storage, Water Disposal, Measurement and Control Technology, Plant Safety, Material Selection. Process Data Chemical Data, Mass Balance, Physio-chemical data sources and estimation, Patenting and licensing situations, development cost, location, market situation, plant capacity, raw materials, waste disposals Course of Process Development Process development as an iterative process, Drawing up of an initial version of the process, checking the individual steps, Micro Plant: Link between the laboratory and the pilot plant, Testing the entire process on small scale. Scaling up Process Scaling up of process from laboratory to pilot plant and to industrial scale. Process Evaluation Batch Versus Continuous, Equilibrium Limitations, Process alternatives, Preparation of study report Flow sheeting Basic Flow Diagram, P&ID, Development of flow diagram, Flow sheeting. Laboratory work: Experiments will be based on the syllabus covered as above. Text Books: 1. Process Development - From the Initial Ideal to the Chemical Production Plant G H Vogel, Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH, 2005. 2. Conceptual Design of Chemical Process, J M Douglas, Mc GrawHill Book Company. 1998. Reference Books: 1. Chemical Process Development, Jordan, Mc-Graw Hill. 2. Product and Process Design Principles-Synthesis, Analysis and Evaluation, 2nd ed., W D Seider, J D Seader and D R Lewin, John Wiley and Sons. 2004. 3. Analysis, Synthesi and Design of Chemical Processes, R Turton, R C Bailie, W B Whiting, J A Shaeiwitz, Prentice Hall, New Jursey. 1998. MTMH203 ENVIRONMENT AND SAFETY IN PROCESS INDUSTRIES Introduction Resources Management, Clean Development Mechanism, Command and control and Market Based Initiatives for pollution control. Pollution Abatement in Process Industries Types of pollution in process industries, Modes of Surveillance, Evaluation and Techniques for abatement. Design for effluent treatment in specific process Industries such as, Fertilizer, Petroleum, Pulp and Paper, Dairy etc. Environmental Issues in Process Industries Identifying and evaluating the probable environmental consequences of a proposed development project, Methods for Environmental Impact Assessment, Risk Assessment of the project. Uses, advantages and limitations of various environmental management tools. Case studies of Life cycle Assessment, Environmental Audit, Energy Audit and Water Audit. Environmental Regulations: Indian & International Regulations to encourage pollution prevention and cleaner production. International standards on various aspects of environmental management Safe (inherent) Process Design Practices Chemical Process Industry (CPI) Safety Codes. Control technology to reduce accidents in CPI. Process Hazard Evaluation Hazard Evaluation techniques, Qualitative Risk Analysis (QRA) Techniques, Risk Assessment (RA) accident probability, Hazard Operability Studies (HAZOP) Hazard Analysis (HAZAN), Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) and Event Tree Analysis (ETA) Safety Analysis Safety Review, Preconditions and preparations, analytical procedures, analysis of safety related information and safety measures, Integrated approaches for safety management, Case studies in process safety management Text Books: 1. Integrated Environmental Planning, Janes K. Lein , Blackwell Publishing. 2. Safety Assessment for Chemical Processes, J Steinbach , Willey – VCTT. Semester3rd CODE Subjects Credits MSCH1 Advanced Catalytic Engineering 4 MSCH2 Fluidization Engineering 4 MSCH3 Process \Plant Simulation 4 MSCH1 ADVANCED CATALYTIC ENGINEERING Introduction and Fundamentals Catalysis – Emergence of Catalyst Technology, Basic Variables for Control of Chemical Reactions, Importance of Catalysis and Catalyst Technology, Impact on Society and Life Forms, Scope of Catalyst Technology, Fundamental Catalytic Phenomena, Steps in a Heterogeneous Catalytic Reaction, Reaction and Diffusional Resistances for a Catalytic Reaction, Kinetics of Catalytic Surface Reactions, Effects of Surface Structure and Support on Catalytic Activity Catalyst Materials, Properties and Preparation Catalyst Materials: Active Phase, Carriers, Promoters, Molecular Sieves and Zeolites, Catalyst Properties, Catalyst Engineering, Physical, Mechanical and Chemical Properties, Catalyst Preparation methods including novel methods and nanocomposit preparations. New Concepts of Catalysis Design, Design of New Molecular Sieves, Design of Sophisticated Composite Catalysis Based on Nanostructures, Novel catalyst Preparation Methods: The Preparation of Amorphous Metal Powders, Supported Catalysts and Nanocolloids by a Sonochemical Technique Catalyst Characterization and Selection Principles and Objectives of Catalyst Characterization, Determining Physical Properties of Catalysts, Determining Chemical Properties of Catalysts, Catalyst Selection Catalytic fixed Bed Reactor Design and Activity Testing Fundamentals of Reactor Design, Collecting, Analyzing and Reporting Data from Laboratory Reactors, Choosing Reactors in the Laboratory and Plant Design of Adiabatic, Iso-thermal, non-isothermal and non-adiabatic reactors Laboratory work: Experiments will be based on the syllabus covered as above. Text Books: 1. Fundamentals of Industrial Catalytic Processes, 2nd Edition, C. H. Bartholomew, Robert J. Farrauto 2. Catalytic Reactor Design by M. Orhan Tarhan, McGraw Hill Book Company Reference Books: 1. Chemical and Catalytic Reaction Engineering by James J. Carberry, Dover Publications 2. Chemical Reactor Design for Process Plants by H.F. Rase, Wiley-International Publication 3. Chemical Reactor Analysis and Design, G.F. Froment and K.B. Bischoff, Jhon Wiley & Sons MSCH2 FLUIDIZATION ENGINEERING Introduction Phenomenon of Fluidization, Behavior of a Fluidized Bed, Comparison with other contacting methods, Advantages and Disadvantages of Fluidized Beds for Industrial Operations, Fluidization Quality, Selection of a Contacting Mode for a given Application. Industrial Applications of Fluidized Beds Coal Gasification, Gasoline from other Petroleum Fractions, Gasoline from Natural and Synthesis Gases, Synthesis Reactions, Metallurgical and Other Processes, Physical Operations Cracking of Hydrocarbons, Combustion and Incineration, Carbonization and Gasification and Reactions Involving solids, Bio -fluidization Fluidization and Mapping of Regimes Characterization of Fixed Beds of Particles, Fluidization without Carryover of Particles: Minimum Fluidizing Velocity, Pressure Drop-verses-Velocity Diagram, Effect of Pressure and Temp. on Fluidized Behavior, Sintering and Agglomeration of Particles at High Temperature. Type of Gas Fluidization with and without Carryover, Turbulent and Churning Fluidization, Pneumatic Transport of Solids, Fast Fluidization , Voidage Diagrams for all Solid Carryover, Regimes, The Mapping of Fluidization Regimes Bubbles in Dense Beds Single Rising Bubbles: Rise Rate of Bubbles, Evaluation of Models for Gas Flow at Bubbles, The Wake Region and the Movement of Solids at Bubbles, Solids within Bubbles. Coalescence and Splitting Bubbles: Interaction of Two Adjacent Bubbles, Coalescence, Bubble Size and Bubble Frequency, Splitting of Bubbles and Maximum Bubble Size, Bubble Formation above a Distributor, Slug Flow Bubbling Fluidized Beds Emulsion Movement for small and Fine Particles, Emulsion Movement for Large Particles, Emulsion gas Flow and Voidage. Effect of Pressure on Bed Properties. Estimation of Bed Properties: Gas Flow in the Emulsion Phase, Bubble Gas Flow, Bubble Size and Bubble growth, Bubble Rise Velocity, Beds with Internals, Physical Models : Scale up and scale down Flow Models for Bubbling Beds General Interrelationship among Bed Properties, Simple Two-phase Model, K-L Model with its Davidson Bubbles and Wakes High Velocity Fluidization Turbulent Fluidized Beds, Experimental Findings, Fast Fluidization, The Freeboard Entrainment Model Applied to Fast Fluidization, Design Considerations, Pressure Drop in Turbulent and Fast Fluidization Circulation Systems Circuits for the Circulation of Solids, Finding Required Circulation Rates, Flow of GasSolid Mixtures in Downcomers: Downward discharge from a Vertical Pipe, Moving Bed Downflow, Fluidized Downflow, Fluidized Downflow in Tall Downcomers. Flow in Pneumatic Transport Lines: Vertical Upflow of Solids, Horizontal Flow, Safe Gas Velocity for Pneumatic Transport, Pressure Drop in Pneumatic Transport, Pressure drop in Bends, Practical Considerations Design of Catalytic and non-catalytic Fluidized bed Reactors Tutorials will be based on the above using standard Software. Text Book: Fluidization Engineering, 2nd Edition, D. Kunii and O. Lavenspiel, ButterworthHienemann, Elsevier. MSCH3 PROCESS PLANT SIMULATION Introduction to Simulation through Modelling Introduction to modelling and simulation Mathematical Models of Chemical Engineering Systems Uses of mathematical models, Principles of formulations, Material and Energy Balance, Constituent Relationship. Modelling various unit operations of process plants like Mixers, Pumps, Compressors , Distillation Column, Reactors, Heat Exchangers, Computational Methods For Process Simulation Degree of freedom analysis, Types of simulation problems: Design, Rating, Flow sheeting etc. Usefulness and Limitation of Process Simulation. Steady State Lumped System-Partitioning Equation, Tearing Equation, Simultaneous Equation, Modular Approaches & Equation Solving Approaches, Decomposition of Networks. Methods for Solution of non linear Equations, Structural analysis and solution of systems of algebraic equations. Method for solution of Unsteady state lumped system, Stiff differential equations. Solution Methods for initial value and boundary value problem, Solution methods for Partial Differential Equations. Process Simulators Introduction to professional simulator like Aspen.Hysys and Mathematical tools like MATLAB, Introduction to SIMULINK and Poly Math etc. Application of Simulation in Different Unit Operations Diabetic CSTR, Separation Tower like Tray and Packed tower, Bio Chemical Reactor etc. Laboratory work: Experiments will be based on the syllabus covered as above. Text-Books: 1. Process Dynamics: Modeling, Analysis and Simulation, B Wayne Bequette, Prentice Hall International Inc. 2. Computational Methods for Process Simulation, 2nd ed., W F Remirez, ButterworthHeinemann. Reference Books: 1. Process Modelling, Simulation and Control for Chemical Engineers by William L. Luyben, McGraw Hill International Editions. 2. Analysis, Synthesis and Design of Chemical Processes, R Turton, R C Bailie, W B Whiting and J A Shaeiwitz, Prentice Hall International Inc.. 3. Product and Process Desing Principles-Synthesis, Analysis, and Evaluation, 2nd ed., W D Seider, J D Seader and D R Lewin, John Wiley and Sons Inc CODE SUBJECTS CREDITS MSCH5 ADVANCED PROCESS CONTROL 4 MSCH6 ADVANCED PETROLEUM REFINING PROCESSES 4 MSCH7 ADVANCED PROCESS OPTIMISATION 4 MSCH8 PROJECT 12 MSCH5 ADVANCED PROCESS CONTROL Introduction to process control Dynamic and steady state processes, development of block diagram and its reduction, PID control algorithm. routh stability criteria, bode plots, root locus Introduction to Advanced Controllers Feed forward, ratio controller, cascade, controller, adaptive controller, inferential controller. PID Controller Tuning Close loop oscillation based methods, Ziegler Nichols Algorithm, Tuning rules for First order plus dead time process, Ziegler Nichols open loop method., Direct Synthesis. Internal Model Control Static and dynamic Control law, practical open loop controller design, generalization of open loop controller design procedure, model uncertainty and disturbance, development of IMC structure and IMC design procedure. Effect of model uncertainty and disturbance, improved disturbance rejection design. IMC Base PID procedure The equivalent feedback form to IMC, IMC based feedback design for delay free processes, IMC based PID controller design for stable process. Multivariable controllers and plant wide control Principle, operation and Applications of DCS and PLC in Batch Process Control and Process Monitoring Case Studies on Heat Exchanger Control and Distillation Column control with multivariable control system. Tutorials will be based on the above using standard Software. Text Book: 1. Process Control Modeling, Design and Simulation, B Wayne Bequette, Prentice Hall of India, 2003. Reference Books: 1. Process Dynamics and Control, 2nd, D E Seborg, T F Edger and D A Mellichamp, Wiley India. 2. Chemical Process Control: An Introduction to Theory and Practice, George Stephanopoulos Stephanopoulos, George Prentice-Hall of India Pvt. Ltd,1994 MSCH6 ADVANCED PETROLEUM REFINING PROCESSES Petroleum Refining Pretreatment and Distillation, Stripping, Rerunning, Stabilization and Light End Removal, Superfractionation, Azeotropic Distillation and Extractive Distillation Thermal Cracking Introduction, Thermal Cracking, Visbreaking, Coking, Delayed Coking, Fluid Coking and Flexicoking Catalytic Cracking Introduction, Fixed Bed Processes, Moving Bed processes, Fluid Bed processes, Reaction chemistry of FCC, Mechanism and Kinetics, Process Variables: Feedstock Quality, Feedstock Preheating, Feedstock Pressure, Feedstock Conversion, Reactor Temperature, Recycle Rate, Space Velocity, Catalyst Activity, Catalyst Oil Ratio, Regenerator Temperature, Regenerator Air Rate. Catalysts for Cracking Hydrotreating Introduction, Hydrodesulfurization: Process configuration, Reaction chemistry and Kinetics, Downflow Fixed Bed Reactor, Upflow expanded Bed Reactor, Demetallization Reactor (Guard Bed Reactor), Catalysts. Distillate Hydrosulfurization, Residuum Hydrodesulfurization, Ultra low sulfur Diesel. Hydrocracking Introduction, Processes and Process Design: Reaction chemistry and Kinetics, CANMET, Gulf HDS, H-G Hydrocracking, H-Oil. IFP Hydrocracking, Isocracking, LC fining, MAK, HDC, Microcat RC, Mild Hydrocracking, MRH, RCD, Unibon (BOC), Residfining, Residue Hydroconversion, Unicrackking, Veba, CombiCracking Next Generation Processes Introduction, Thermal (Carbon Rejection) Processes: Asphalt Coking Technology Process, Comprehensive Heavy Ends reforming Refinery Processes, Deep Thermal Conversion Process, ET –II Process, Eureka Process, Fluid Thermal Cracking Process, High Conversion Soaker Cracking Process, Catalytic Cracking Processes: Asphalt Residue Treating Process, Heavy Oil Treating Process, Reduced Crude Oil Conversion Process, Residual Fluid Catalytic Cracking Process, Shell FCC Process, S&W Fluid Catalytic Cracking Process, Hydrogen Addition Processes, Asphaltenic Bottoms Cracking Process, Hydrovisbreaking (HYCAR) Pocess, Solvent Processes: Deasphalting Process, Deep Solvent Deasphalting Process, Demax Process Product Improvement Desulfurization and Heteroatom Removal: Hydrotrating, Hydrogen Sulfide Removal Reforming: Thermal Reforming, Catalytic reforming, Dehydrogenation, Catalysts, Reformulated Gasoline and other oxygenates like MTBE and others. Isomerization, Alkylation and Polymerization Process Types, Chemistry, Commercial Processes, Catalysts Hydrogen Production Introduction, Feedstocks, Process Chemistry, Commercial Processes: Heavy Residue Gasification and Combined Cycle Power Generation, Hybrid Gasification Process, Hydrocarbon Gasification, Hypro Process, Shell Gasification (Partial Oxidation) Process, Steam Methane Reforming, Steam Naphtha Reforming, Synthesis Gas Generation, Texaco Gasification (Partial Oxidation) Process. Catalysts, Hydrogen Purification Alternative sources of Petroleum based applications Hydrogen production and Fuelcells, Gas to Liquid Fuels, First & Second Generation Biofuels Tutorials will be based on the above using standard Software. Text Books: 1. Modern Petroleum Refining Processes by B.K.B. Rao, Oxford & IBH Publishing Pvt. Ltd. 2. Practical Advances in Petroleum Processing: Volume 1 & 2 by C.S. Hsu and P.R. Robinson, Springer Publications Reference Books: 1. Petroleum Refinery Engineering by W.L. Nelson, McGraw-Hill International 2. Advanced Petroleum Refining by G.N. Sarkar, Khanna Publishers 3. Petroleum Refinery Process Economics by R.E. Maples, PennWell Corporation 4. Petroleum Refining Technology by Ram Prasad, Khanna Publishers MSCH7 ADVANCED PROCESS OPTIMISATION Objective and Formulation of Optimisation Objective and Introduction, Objective Function and Decision variables, Inequality and Equality Constrains in Models Formulation of the Objective Function, Lower and Upper Bounds, Selecting Functions to Fit Empirical Data, Factorial Experimental Designs, Degrees of Freedom, Economic Objective Functions, Measures of Profitability Basic Concepts of Optimization Continuity of Function, NLP Problem Statement, Convexity and Its Applications, Interpretation of the Objective Function in Terms of its Quadratic Approximation, Necessary and Sufficient Conditions for an Extremum of an Unconstrained Function Optimization of Unconstrained Functions One-Dimensional Search Numerical Methods for Optimizing a Function of One Variable, Scanning and Bracketing Procedures, Newton and Quasi-Newton Methods of Unidimensional Search Unconstrained Multivariable Optimization Linear Programming (LP) and Applications Geometry of Linear Programs, Basic Linear Programming Definitions and Results, Simplex Algorithm, Barrier Methods, Sensitivity Analysis, Linear Mixed Integer Programs, Application of the EXCEL Solver Spreadsheet for Optimisation, Formulation. Introduction to Non linear Programming with Constraints and Mixed-Integer Programming Application of Optimisation in Chemical Engineering Examples of Optimization in Chemical Processes like optimizing recovery of waste heat, Optimal Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger Design, Optimal Design and Operation of binary Distillation Column, Optimal pipe diameter etc. Flow sheet Optimization - Case studies. Tutorials will be based on the above using standard Software. Text-Book: 1. Optimization of Chemical Processes, 2nd ed,, T F Edger, D M Himmelblau and L S Lasdon, McGraw- Hill International Edition. Reference Book: 1. Product and Process Design Principles-Synthesis, Analysis, and Evaluation, 2nd ed., W D Seider, J D Seader and D R Lewin, John Wiley and Sons Inc.