Leture 2 - Strategy & Business Economics Division

Using Cultural
Differences
For Fun and Profit
Approaches to
Managing Cultural Differences
• Multi-domestic
• Assumption: diversity has no impact.
• Each national unit is regarded as independent and autonomous with random rather than planned interaction between parts
• International
• Assumption: diversity causes only problems. Homogeneity is desirable and is a source of efficiency.
• Corporate (headquarters) culture dominates
• Multi-national
• Assumption: diversity can either cause problems or lead to benefits.
• Geographical differentiation is considered indispensable. Cultural interaction is encouraged but a balance is maintained between diversity and uniformity
Applications
• Negotiations
• Human resources management
• Motivation
• Leadership
• Strategic Planning
• Design of organizations
• Marketing
• Cultural Differences (Tastes)
• Income Differences (Demographics)
General Conceptual Framework for
Planning a Negotiating Strategy
• Enumerate and characterize the parties
• Assess their interest and no-deal alternatives
• Envision potential agreements and bargaining ranges
• Craft processes for both creating value and claiming it
• Pay attention to the sustainability of agreements
• Develop a negotiating strategy (i.e. decide on a negotiating process)
Negotiation Process
• Four stages:
•
1) Non-task sounding or relationship building
2) Task-related exchange of information
3) Persuasion
4) Making concessions and reaching agreements
Context, duration and importance of each stage can differ significantly across cultures
Negotiation Behavior
Differences:
• Styles of persuasion (e.g. appeal to logic versus affective-intuitive style)
• Conflict resolution preferences (e.g. confrontation versus balance and restraint, resolution through discussion of mutual interests versus referral to higher levels )
• Initial bargaining positions (e.g. low versus high initial offers)
• Concession patterns (e.g. viewing concessions as acceptable or viewing them as displaying weakness)
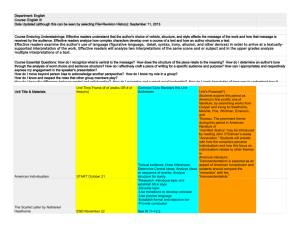
HRM: Motivation Approaches
91
US
Australia
Canada
45.5
Awards for Mastery of Work-related Skills
India
Germany
Italy
Austria
Argentina
Japan
Brazil
Employee
Relations
Hong-Kong
Taiwan Korea
0
0 56 112
HRM: Leadership Styles
94
47
Legitimate Power
Reward Power
Referent Power
Yugoslavia
Hong-Kong
Brazil
Korea
Taiwan
India
Japan
Argentina Italy
Germany
Canada
US
Australia
Expert Power
Austria
0
0 45.5
91
HRM: Strategic Planning
91
US
Canada
Australia
Italy
High-impact Planning
•
Research
•
Rules
•
Analysis
Germany
Austria
Argentina
45.5
India
Japan
Brazil
Hong-Kong
Korea
0
0
Taiwan
Flexible Planning Approaches
Trust-based Interactions
56 112
Design of Organizations
• Structures
• Authority sources
• Delegation
• Rules
• Conflict resolution processes
Culture and Advertising 1
(Hoecklin)
Culture and Advertising 2
(Hoecklin)
Culture and Advertising 3
(Hoecklin)
Marketing: Dealing with
Socio-economic
Differences
• The developing world presents a great opportunity for corporate growth
• The attitude toward developing countries must change and better understanding of their business environment much be acquired
• It is not all about culture – other socio-economic factors are at play
1980s: Imperialist
Mindset
• “New markets for old products”
• “Squeezing out profits out of sunset technologies”
• Corporate center as the locus of innovation
Late 1990s:
Flip-side of the Coin
• Competitive advantage is based on rethinking and reconfiguring business models based on direct experience in emerging markets.
• New logic: understand economic, social, and cultural constraints and transform them into opportunities
(preferences, infrastructure)
Why A Different Mindset?
Income Distribution Main Issues China India
Greater than US$20,000 Preferences 0.17% 0.78%
US$10,000 to US$20,000 Switching
US$5,000 to US$10,000 Affordability
5.03%
27.68%
7.04%
13.97%
Less than $5,000 Local loyalties 67.11% 78.21%
Key Questions
• Understand the specific needs of the local market (different demographics)
• Understand the state and the evolution of distribution networks
• Choose an appropriate mix of global/local leadership
• Decide if customized or consistent strategies are preferable
• Learning from local partners, when possible